Poly(ADP-ribose) regulates post-transcriptional gene regulation in the cytoplasm - PubMed (original) (raw)
Poly(ADP-ribose) regulates post-transcriptional gene regulation in the cytoplasm
Anthony Leung et al. RNA Biol. 2012 May.
Abstract
Since its discovery in 1963, poly(ADP-ribose) (pADPr) has been shown to play important functions in the nucleus of multicellular eukaryotes. Each of these functions centers upon DNA metabolism, including DNA-damage repair, chromatin remodeling, transcription and telomere functions. We recently described two novel functions for pADPr in the cytoplasm, both of which involve RNA metabolism - 1) the assembly of cytoplasmic stress granules, cellular macrostructures that aggregate translationally stalled mRNA/protein complexes, and 2) modulation of microRNA activities. Multiple stress granule-localized, post-transcriptional gene regulators, including microRNA-binding argonaute family members, are substrates for pADPr modification and are increasingly modified by pADPr upon stress. Interestingly, the cytoplasmic RNA regulatory functions for PARPs are likely mediated through activities of catalytically inactive PARP-13/ARTD13/ZC3HAV1/ZAP and mono/poly(ADP-ribose)-synthesizing enzymes, including PARP-5a/ARTD5/TNKS1, PARP-12/ARTD12/ZC3HDC1 and PARP-15/ARTD7/BAL3. These data are consistent with other recent work, which suggests that mono(ADP-ribosyl)ated residues can be poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated by different enzymes.
Figures
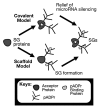
Figure 1. Two novel functions for pADPr in the cytoplasm. The covalent model indicates the alteration of protein properties inherently (highlighted with a star in the figure) whereas the caffold model indicates that the change of protein function relies on new non-covalent protein associations through pADPr.
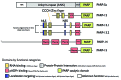
Figure 2. Domain structure of PARPs localized in SGs.
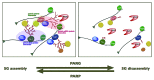
Figure 3. Proposed model of SG assembly.
Figure 4. Proposed model of SG disassembly.
Similar articles
- Poly(ADP-ribose) regulates stress responses and microRNA activity in the cytoplasm.
Leung AK, Vyas S, Rood JE, Bhutkar A, Sharp PA, Chang P. Leung AK, et al. Mol Cell. 2011 May 20;42(4):489-99. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.015. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21596313 Free PMC article. - Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase in the control of poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism.
Davidovic L, Vodenicharov M, Affar EB, Poirier GG. Davidovic L, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2001 Aug 1;268(1):7-13. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5263. Exp Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11461113 Review. - Methods for purification of proteins associated with cellular poly(ADP-ribose) and PARP-specific poly(ADP-ribose).
Rood JE, Leung AK, Chang P. Rood JE, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;780:153-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-270-0_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21870260 Free PMC article. - The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs): new roles in intracellular transport.
Abd Elmageed ZY, Naura AS, Errami Y, Zerfaoui M. Abd Elmageed ZY, et al. Cell Signal. 2012 Jan;24(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.07.019. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 21840394 Review. - Reprogramming cellular events by poly(ADP-ribose)-binding proteins.
Krietsch J, Rouleau M, Pic É, Ethier C, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Masson JY, Poirier GG, Gagné JP. Krietsch J, et al. Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1066-87. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.005. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23268355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Novel insights into PARPs in gene expression: regulation of RNA metabolism.
Ke Y, Zhang J, Lv X, Zeng X, Ba X. Ke Y, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Sep;76(17):3283-3299. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03120-6. Epub 2019 May 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31055645 Free PMC article. Review. - ADPriboDB: The database of ADP-ribosylated proteins.
Vivelo CA, Wat R, Agrawal C, Tee HY, Leung AK. Vivelo CA, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D204-D209. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw706. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27507885 Free PMC article. - Arabidopsis PARG1 is the key factor promoting cell survival among the enzymes regulating post-translational poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation.
Zhang H, Gu Z, Wu Q, Yang L, Liu C, Ma H, Xia Y, Ge X. Zhang H, et al. Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 30;5:15892. doi: 10.1038/srep15892. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26516022 Free PMC article. - A novel predicted ADP-ribosyltransferase-like family conserved in eukaryotic evolution.
Wyżewski Z, Gradowski M, Krysińska M, Dudkiewicz M, Pawłowski K. Wyżewski Z, et al. PeerJ. 2021 Mar 10;9:e11051. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11051. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33854844 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources