The crystal structure of human Argonaute2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
The crystal structure of human Argonaute2
Nicole T Schirle et al. Science. 2012.
Abstract
Argonaute proteins form the functional core of the RNA-induced silencing complexes that mediate RNA silencing in eukaryotes. The 2.3 angstrom resolution crystal structure of human Argonaute2 (Ago2) reveals a bilobed molecule with a central cleft for binding guide and target RNAs. Nucleotides 2 to 6 of a heterogeneous mixture of guide RNAs are positioned in an A-form conformation for base pairing with target messenger RNAs. Between nucleotides 6 and 7, there is a kink that may function in microRNA target recognition or release of sliced RNA products. Tandem tryptophan-binding pockets in the PIWI domain define a likely interaction surface for recruitment of glycine-tryptophan-182 (GW182) or other tryptophan-rich cofactors. These results will enable structure-based approaches for harnessing the untapped therapeutic potential of RNA silencing in humans.
Figures
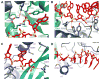
Figure 1. Structure of human Ago2
A. Schematic of the Ago2 primary sequence. B. Front and top views of Ago2 with the N (purple), PAZ (navy), MID (green), PIWI (grey) domains and linkers L1 (teal) and L2 (blue). A generic guide RNA (red) can be traced for nucleotides 1–8 and 21. Tryptophan molecules (orange) bind to tandem hydrophobic pockets in the PIWI domain.
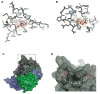
Figure 2. Comparison of bacterial and human Argonaute structures
A. Superposition of N-PAZ and MID-PIWI lobes of Ago2 (colored as in Fig. 1) onto corresponding lobes from T. thermophiles (yellow). B. Individual domains of Ago2 superimposed on the corresponding domains from T. thermophilus with root-mean-square deviation (rmsd) values for equivalent alpha-carbons indicated. Functional points of interest in Ago2 are labeled.
Figure 3. Conformation of bound guide RNAs
A. The 5′ nucleotides of guide RNAs are recognized by extensive interactions with the MID and PIWI domains. An ordered water molecule is shown as a pink sphere. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed orange lines B, C. Ago2 organizes the seed region in an A-form helix by extensive interactions with the phosphate backbone. D. Helix-7 (α7) introduces a kink in the guide RNA between bases 6 and 7 that disrupts helical stacking.
Figure 4. Tandem tryptophan-binding pockets in the PIWI domain
A, B. Residues forming the binding pockets of tryptophan 1 and 2 shown, with hydrogen bonds indicated (dashed, yellow lines). Tryptophan molecules are shown with surrounding unbiased Fo-Fc maps contoured at two sigma (orange). C. Surface representation showing the tryptophan binding pockets. D. Close up view of boxed area in panel C. White dots indicate the shortest direct path connecting the two sites along the surface of Ago2.
Comment in
- Biochemistry. Guided tour to the heart of RISC.
Kaya E, Doudna JA. Kaya E, et al. Science. 2012 May 25;336(6084):985-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1223549. Science. 2012. PMID: 22628640 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Beyond the seed: structural basis for supplementary microRNA targeting by human Argonaute2.
Sheu-Gruttadauria J, Xiao Y, Gebert LF, MacRae IJ. Sheu-Gruttadauria J, et al. EMBO J. 2019 Jul 1;38(13):e101153. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018101153. Epub 2019 Apr 26. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31268608 Free PMC article. - Helix-7 in Argonaute2 shapes the microRNA seed region for rapid target recognition.
Klum SM, Chandradoss SD, Schirle NT, Joo C, MacRae IJ. Klum SM, et al. EMBO J. 2018 Jan 4;37(1):75-88. doi: 10.15252/embj.201796474. Epub 2017 Sep 22. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 28939659 Free PMC article. - Structural basis for microRNA targeting.
Schirle NT, Sheu-Gruttadauria J, MacRae IJ. Schirle NT, et al. Science. 2014 Oct 31;346(6209):608-13. doi: 10.1126/science.1258040. Science. 2014. PMID: 25359968 Free PMC article. - Function of GW182 and GW bodies in siRNA and miRNA pathways.
Yao B, Li S, Chan EK. Yao B, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:71-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224966 Review. - Why Argonaute is needed to make microRNA target search fast and reliable.
Klein M, Chandradoss SD, Depken M, Joo C. Klein M, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 May;65:20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.05.017. Epub 2016 May 26. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27235676 Review.
Cited by
- Transition of a microRNA from repressing to activating translation depending on the extent of base pairing with the target.
Saraiya AA, Li W, Wang CC. Saraiya AA, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055672. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405193 Free PMC article. - Defining fundamental steps in the assembly of the Drosophila RNAi enzyme complex.
Iwasaki S, Sasaki HM, Sakaguchi Y, Suzuki T, Tadakuma H, Tomari Y. Iwasaki S, et al. Nature. 2015 May 28;521(7553):533-6. doi: 10.1038/nature14254. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25822791 - RNA-guided RNA silencing by an Asgard archaeal Argonaute.
Bastiaanssen C, Bobadilla Ugarte P, Kim K, Finocchio G, Feng Y, Anzelon TA, Köstlbacher S, Tamarit D, Ettema TJG, Jinek M, MacRae IJ, Joo C, Swarts DC, Wu F. Bastiaanssen C, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 29;15(1):5499. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49452-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38951509 Free PMC article. - Elucidation of the conformational dynamics and assembly of Argonaute-RNA complexes by distinct yet coordinated actions of the supplementary microRNA.
Zhuang H, Fan X, Ji D, Wang Y, Fan J, Li M, Ni D, Lu S, Li X, Chai Z. Zhuang H, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Mar 7;20:1352-1365. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.03.001. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35356544 Free PMC article. - The N-terminal extension of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE 1 is essential for microRNA activities.
Xu Y, Zhang Y, Li Z, Soloria AK, Potter S, Chen X. Xu Y, et al. PLoS Genet. 2023 Mar 8;19(3):e1010450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010450. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36888599 Free PMC article.
References
- Liu J, et al. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science. 2004 Sep 3;305:1437. - PubMed
- Meister G, et al. Human Argonaute2 mediates RNA cleavage targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol Cell. 2004 Jul 23;15:185. - PubMed
- Braun JE, Huntzinger E, Fauser M, Izaurralde E. GW182 proteins directly recruit cytoplasmic deadenylase complexes to miRNA targets. Mol Cell. 2011 Oct 7;44:120. - PubMed
- Fabian MR, et al. miRNA-mediated deadenylation is orchestrated by GW182 through two conserved motifs that interact with CCR4-NOT. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;18:1211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases