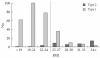Challenges in diagnosing type 1 diabetes in different populations - PubMed (original) (raw)
Challenges in diagnosing type 1 diabetes in different populations
Marian Rewers. Diabetes Metab J. 2012 Apr.
Abstract
Diabetes affects today an estimated 366 million people world-wide, including 20 million to 40 million of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). While T1D accounts for 5% to 20% of those with diabetes, it is associated with higher morbidity, mortality and health care cost than the more prevalent type 2 diabetes. Patients with T1D require exogenous insulin for survival and should be identified as soon as possible after diagnosis to avoid high morbidity due to a delay in insulin treatment. It is also important to present to the patient correct prognosis that differs by the type of diabetes. From the research point of view, correct classification should help to identify the etiologies and to develop specific prevention for T1D. This review summarizes evidence that may be helpful in diagnosing T1D in various ethnic groups. Challenges in interpretation of results commonly used to determine the type of diabetes are highlighted.
Keywords: African diabetes; C-peptide; Diabetes mellitus, type 1; Diagnostic criteria; Ethnic differences; Fulminant diabetes; Genetics; Insulin sensitivity; Islet autoantibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Fig. 1
Current classification of diabetes. APS1, autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes 1; IPEX, immunodeficiency, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome; MODY, maturity-onset diabetes of the young.
Fig. 2
Distribution of body mass index (BMI) at diagnosis by type of diabetes, age 10 to 19 years. Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, Denver, USA.
Fig. 3
Practical diabetes classification algorithm in U.S. patients <20 years at diagnosis. IAA, autoantibodies to insulin; GADA, glutamic acid decarboxylase; IA-2A, the tyrosine phosphatase insulinoma antigen; ZnT8A, zinc transporter 8; T1aD, type 1a (autoimmune) diabetes; T2D, type 2 diabetes. *Needs to be refined for non-white populations groups.
Similar articles
- Clinical heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes (T1D) found in Asia.
Park Y, Wintergerst KA, Zhou Z. Park Y, et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017 Oct;33(7). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2907. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28544229 Review. - Emergence of anti-islet autoantibodies in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes.
Horie I, Kawasaki E, Shimomura A, Satoh T, Ueki I, Kuwahara H, Ando T, Abiru N, Usa T, Eguchi K. Horie I, et al. Endocr J. 2010;57(7):623-8. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k10e-068. Epub 2010 May 25. Endocr J. 2010. PMID: 20505260 - Antibodies to post-translationally modified insulin as a novel biomarker for prediction of type 1 diabetes in children.
Strollo R, Vinci C, Napoli N, Pozzilli P, Ludvigsson J, Nissim A. Strollo R, et al. Diabetologia. 2017 Aug;60(8):1467-1474. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4296-1. Epub 2017 May 20. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28526919 Free PMC article. - Type 1 diabetes and autoimmunity.
Kawasaki E. Kawasaki E. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014 Oct;23(4):99-105. doi: 10.1297/cpe.23.99. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25374439 Free PMC article. Review. - Type 1 diabetes: A predictable disease.
Simmons KM, Michels AW. Simmons KM, et al. World J Diabetes. 2015 Apr 15;6(3):380-90. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.380. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25897349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Diagnostic criteria for acute-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (2012): Report of the Committee of Japan Diabetes Society on the Research of Fulminant and Acute-onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Kawasaki E, Maruyama T, Imagawa A, Awata T, Ikegami H, Uchigata Y, Osawa H, Kawabata Y, Kobayashi T, Shimada A, Shimizu I, Takahashi K, Nagata M, Makino H, Hanafusa T. Kawasaki E, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2014 Feb 12;5(1):115-8. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12119. Epub 2013 Aug 13. J Diabetes Investig. 2014. PMID: 24843746 Free PMC article. - Supporting islet function in a PVDF membrane based macroencapsulation delivery device by solvent non-solvent casting using PVP.
de Bont DFA, Mohammed SG, de Vries RHW, Paulino da Silva Filho O, Vaithilingam V, Jetten MJ, Engelse MA, de Koning EJP, van Apeldoorn AA. de Bont DFA, et al. PLoS One. 2025 Mar 12;20(3):e0298114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298114. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40073008 Free PMC article. - Variation of C peptide decay rate in diabetic patients with positive glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody: better discrimination with initial fasting C peptide.
Li X, Huang G, Lin J, Yang L, Zhou Z. Li X, et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2013 Mar 1;13:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-13-10. BMC Endocr Disord. 2013. PMID: 23452723 Free PMC article. - Analysis of immune cell components and immune-related gene expression profiles in peripheral blood of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Lin J, Lu Y, Wang B, Jiao P, Ma J. Lin J, et al. J Transl Med. 2021 Jul 26;19(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02991-3. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34311758 Free PMC article. - A Genome-Wide Analysis of Long Noncoding RNAs in Circulating Leukocytes and Their Differential Expression in Type 1 Diabetes Patients.
Liu Y, Du X, Cui J, Li C, Guo M, Lv J, Liu X, Dou J, Du X, Fang H, Chen Z. Liu Y, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2020 Nov 25;2020:9010314. doi: 10.1155/2020/9010314. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 33299893 Free PMC article.
References
- Writing Group for the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. Dabelea D, Bell RA, D'Agostino RB, Jr, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, Liu LL, Loots B, Marcovina S, Mayer-Davis EJ, Pettitt DJ, Waitzfelder B. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA. 2007;297:2716–2724. - PubMed
- Diabetes Epidemiology Research International Group. Secular trends in incidence of childhood IDDM in 10 countries. Diabetes. 1990;39:858–864. - PubMed
- DIAMOND Project Group. Incidence and trends of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990-1999. Diabet Med. 2006;23:857–866. - PubMed
- Harjutsalo V, Sjoberg L, Tuomilehto J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371:1777–1782. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources