Wnt signaling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Wnt signaling
Roel Nusse. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012.
Abstract
Wnt proteins bind to Frizzled family members on the surface of the cell to regulate developmental processes (e.g., cell fate and morphogenesis).
Figures
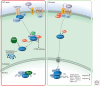
Figure 1.
Canonical Wnt signaling.
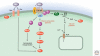
Figure 2.
Non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways.
Similar articles
- Wnt signaling orients the proximal-distal axis of chick kidney nephrons.
Schneider J, Arraf AA, Grinstein M, Yelin R, Schultheiss TM. Schneider J, et al. Development. 2015 Aug 1;142(15):2686-95. doi: 10.1242/dev.123968. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Development. 2015. PMID: 26116665 - Coupling planar cell polarity signaling to morphogenesis.
Axelrod JD, McNeill H. Axelrod JD, et al. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002 Feb 15;2:434-54. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2002.105. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002. PMID: 12806028 Free PMC article. Review. - Ptk7 promotes non-canonical Wnt/PCP-mediated morphogenesis and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin-dependent cell fate decisions during vertebrate development.
Hayes M, Naito M, Daulat A, Angers S, Ciruna B. Hayes M, et al. Development. 2013 Apr;140(8):1807-18. doi: 10.1242/dev.090183. Development. 2013. PMID: 23533179 - PCP and Wnt pathway components act in parallel during zebrafish mechanosensory hair cell orientation.
Navajas Acedo J, Voas MG, Alexander R, Woolley T, Unruh JR, Li H, Moens C, Piotrowski T. Navajas Acedo J, et al. Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 5;10(1):3993. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12005-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31488837 Free PMC article. - Ror-family receptor tyrosine kinases in noncanonical Wnt signaling: their implications in developmental morphogenesis and human diseases.
Minami Y, Oishi I, Endo M, Nishita M. Minami Y, et al. Dev Dyn. 2010 Jan;239(1):1-15. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21991. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 19530173 Review.
Cited by
- Curcumin and Wnt/β‑catenin signaling in exudative age‑related macular degeneration (Review).
Vallée A. Vallée A. Int J Mol Med. 2022 Jun;49(6):79. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5135. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35445729 Free PMC article. Review. - miR-363-3p induces EMT via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in glioma cells by targeting CELF2.
Fan B, Su B, Song G, Liu X, Yan Z, Wang S, Hu F, Yang J. Fan B, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10418-10429. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16970. Epub 2021 Oct 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34636136 Free PMC article. - Wnt5a promotes hippocampal postsynaptic development and GluN2B-induced expression via the eIF2α HRI kinase.
Ramos-Fernández E, Arrázola MS, Oliva CA, Arredondo SB, Varela-Nallar L, Inestrosa NC. Ramos-Fernández E, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):7395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86708-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33795747 Free PMC article. - Sfrp5 modulates both Wnt and BMP signaling and regulates gastrointestinal organogenesis [corrected] in the zebrafish, Danio rerio.
Stuckenholz C, Lu L, Thakur PC, Choi TY, Shin D, Bahary N. Stuckenholz C, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 29;8(4):e62470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062470. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23638093 Free PMC article. - Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation.
Duronio RJ, Xiong Y. Duronio RJ, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Mar 1;5(3):a008904. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008904. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23457258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Neel B, Muthuswarmy S 2012. Signaling in development 2—cell differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 10.1101/cshperspect.005884 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources