Viral disruption of the blood-brain barrier - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Viral disruption of the blood-brain barrier
Katherine R Spindler et al. Trends Microbiol. 2012 Jun.
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) provides significant protection against microbial invasion of the brain. However, the BBB is not impenetrable, and mechanisms by which viruses breach it are becoming clearer. In vivo and in vitro model systems are enabling identification of host and viral factors contributing to breakdown of the unique BBB tight junctions. Key mechanisms of tight junction damage from inside and outside cells are disruption of the actin cytoskeleton and matrix metalloproteinase activity, respectively. Viral proteins acting in BBB disruption are described for HIV-1, currently the most studied encephalitic virus; other viruses are also discussed.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
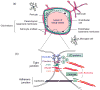
Figure 1
The neurovascular unit and junctions between endothelial cells. (a) cross-section of a brain microvessel, showing cells of the neurovascular unit. Neurons and their contacts with astrocytes are not shown. Cells in the lumen (bloodstream) include red blood cells, lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils (not shown). Note the two basement membranes; the space between them is known as the perivascular space. (b) Enlargement of an endothelial cell-cell junction. Major molecules of the tight junction and adherens junction are shown; no order of the tight junction proteins within the tight junction is implied by the figure. Abbreviations: JAMs, junctional adhesion molecules; ESAM, endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule; CAR, Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor; ZO, zona occludens. The figure is based on figures in [7,95].
Similar articles
- Disruption of the blood brain barrier is vital property of neurotropic viral infection of the central nervous system.
Al-Obaidi MMJ, Bahadoran A, Wang SM, Manikam R, Raju CS, Sekaran SD. Al-Obaidi MMJ, et al. Acta Virol. 2018;62(1):16-27. doi: 10.4149/av_2018_102. Acta Virol. 2018. PMID: 29521099 Review. - Viral Infection of the Central Nervous System and Neuroinflammation Precede Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption during Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection.
Li F, Wang Y, Yu L, Cao S, Wang K, Yuan J, Wang C, Wang K, Cui M, Fu ZF. Li F, et al. J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5602-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00143-15. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25762733 Free PMC article. - Brain Invasion by Mouse Hepatitis Virus Depends on Impairment of Tight Junctions and Beta Interferon Production in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.
Bleau C, Filliol A, Samson M, Lamontagne L. Bleau C, et al. J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(19):9896-908. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01501-15. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26202229 Free PMC article. - West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases.
Roe K, Kumar M, Lum S, Orillo B, Nerurkar VR, Verma S. Roe K, et al. J Gen Virol. 2012 Jun;93(Pt 6):1193-1203. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.040899-0. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22398316 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of the blood-brain barrier disruption in HIV-1 infection.
Toborek M, Lee YW, Flora G, Pu H, András IE, Wylegala E, Hennig B, Nath A. Toborek M, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2005 Feb;25(1):181-99. doi: 10.1007/s10571-004-1383-x. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 15962513 Review.
Cited by
- Neurological Complications Associated with the Blood-Brain Barrier Damage Induced by the Inflammatory Response During SARS-CoV-2 Infection.
Alquisiras-Burgos I, Peralta-Arrieta I, Alonso-Palomares LA, Zacapala-Gómez AE, Salmerón-Bárcenas EG, Aguilera P. Alquisiras-Burgos I, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Feb;58(2):520-535. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02134-7. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32978729 Free PMC article. Review. - Hydrogen improves neurological function through attenuation of blood-brain barrier disruption in spontaneously hypertensive stroke-prone rats.
Takeuchi S, Nagatani K, Otani N, Nawashiro H, Sugawara T, Wada K, Mori K. Takeuchi S, et al. BMC Neurosci. 2015 Apr 20;16:22. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0165-3. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25925889 Free PMC article. - Nipah Virus Infection of Immature Dendritic Cells Increases Its Transendothelial Migration Across Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.
Tiong V, Shu MH, Wong WF, AbuBakar S, Chang LY. Tiong V, et al. Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2747. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02747. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30483242 Free PMC article. - Cell-Mediated Immune Responses and Immunopathogenesis of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus-Infection.
Blom K, Cuapio A, Sandberg JT, Varnaite R, Michaëlsson J, Björkström NK, Sandberg JK, Klingström J, Lindquist L, Gredmark Russ S, Ljunggren HG. Blom K, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 26;9:2174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02174. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319632 Free PMC article. Review. - Hepatitis E Virus Quasispecies in Cerebrospinal Fluid with Neurological Manifestations.
Abravanel F, Nicot F, Lhomme S, Cazabat M, Drumel T, Velay A, Latour J, Belliere J, Cintas P, Kamar N, Izopet J. Abravanel F, et al. Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Oct 19;9(10):1205. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9101205. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34696313 Free PMC article.
References
- Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
- Salinas S, et al. A hitchhiker’s guide to the nervous system: the complex journey of viruses and toxins. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:645–655. - PubMed
- Abbott NJ, et al. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37:13–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI068645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI023762/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI023762/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI068645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091721/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI023762/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI091721/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources