Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates adult hippocampal cell proliferation through MEK/ERK- and PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling - PubMed (original) (raw)
Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates adult hippocampal cell proliferation through MEK/ERK- and PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling
Neil M Fournier et al. Neuropharmacology. 2012 Sep.
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a hypoxia-induced angiogenic protein that exhibits a broad range of neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects in the central nervous system. Given that neurogenesis occurs in close proximity to blood vessels, increasing evidence has suggested that VEGF may constitute an important link between neurogenesis and angiogenesis. Although it is known that VEGF can directly stimulate the proliferation of neuronal progenitors, the underlying signaling pathways responsible in this process are not fully understood. Thus, in the present study, we set out to examine the requirement of two downstream targets of the VEGF/Flk-1 signaling network, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathways, in producing the mitogenic effects of VEGF. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that a single treatment of VEGF activated Erk1/2 and Akt signaling pathways in the adult rat hippocampus and in cultured hippocampal neuronal progenitor cells. This effect was blocked with the VEGF/Flk-1 inhibitor SU5416. Importantly, microinfusion of VEGF into the rat brain also induced pCREB expression in the dentate gyrus and increased the number of BrdU-labeled cells in the dentate subgranular zone. Double immunofluorescence labeling revealed that a large proportion of BrdU-labeled cells expressed activated forms of Flk-1, Erk1/2, and Akt. Interestingly, treatment with the SSRI fluoxetine, which is well known to stimulate neurogenesis and VEGF-signaling, also produced a similar expression pattern of Erk1/2 and Akt in proliferating cells. Finally, pharmacological experiments showed that administration of inhibitors of either MAPK/ERK (U0126) or PI3K (LY294002) blocked VEGF-stimulation of hippocampal cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that the proliferative actions of VEGF require activation of both ERK and Akt signaling cascades and that these intracellular pathways are stimulated almost exclusively in actively proliferating neuronal progenitor cells of the adult hippocampus.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
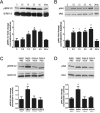
Figure 1. Effect of VEGF on phospho-activated forms of ERK1/2 and Akt in hippocampus
(A and B) Time-course western blot analysis of activated ERK1/2 and Akt in hippocampal homogenates at 0, 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hr, 4 hr, and 24 hr after microinfusion of VEGF (50 ng/μl; n=3 per time point). Levels of phospho-ERK1/2 are increased 1 hr after VEGF microinfusion and persist for 4 hrs. In contrast, levels of phospho-Akt are increased 0.5 hr after VEGF microinfusion and persist for 4 hrs. One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni: * P<.05 vs. 0 hr. (C and D) Representative bands of phospho-ERK1/2 and phospho-Akt in the hippocampus taken 1 hr after VEGF in rats pretreated with either DMSO or the Flk-1 inhibitor SU5416. DMSO or SU5416 was i.c.v. administered 30 minutes before VEGF or PBS microinfusion and blocked the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (C) and Akt (D). Student _t_-test: * P<.05 vs. DMSO/PBS controls. Error bars denote mean ± SEM
Figure 2. Effect of VEGF on phospho-CREB expression in the hippocampus
(A) Time course western blot analysis of phospho-CREB expression in hippocampal homogenates at 0, 0.5 hr, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr after VEGF microinfusion. Levels of phospho-CREB in the hippocampus are increased 0.5 hr after VEGF microinfusion and persist for 4 hrs. One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni: * P<.05 vs. 0 hr. (B) Representative photomicrographs showing phospho-CREB expression in DMSO/PBS, DMSO/VEGF, SU5416/PBS, and SU5416/VEGF treated rats sacrificed 3 hrs later. DMSO or SU5416 was administered 30 minutes before treatment with PBS or VEGF. (C) Quantitative analysis of the inner dentate granule cell layer/SGZ, middle dentate granule cell layer, and outer regions of the dentate granule cell layer shows that VEGF increased phospho-CREB expression in the inner/SGZ and middle dentate granule cell layers. Pretreatment with the Flk-1 inhibitor SU5416 prevents VEGF-stimulation of CREB in these regions. Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni: * P<.05 vs. DMSO/PBS controls. Error bars denote mean ± SEM
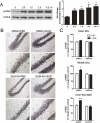
Figure 3. VEGF stimulation of hippocampal cell proliferation requires MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling
(A) Representative photomicrographs showing BrdU-labeled cells in the adult dentate SGZ of rats treated with DMSO, U0126 (MEK/ERK inhibitor), or LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor) 30 minutes before PBS or VEGF microinfusion. (B) Quantitative cell counting of the number of BrdU-labeled cells indicates that VEGF increased the number of BrdU-labeled cells in the dentate SGZ. However, pretreatment with either U0126 or LY294002 significantly blocked VEGF stimulation of hippocampal cell proliferation. One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni: * P <.002 vs. DMSO/PBS controls. Error bars denote mean ± SEM
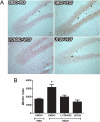
Figure 4. Phospho-activated forms of Flk-1, ERK, and Akt among proliferating cells
(A) Representative photomicrographs showing phosphorylated forms of Flk-1, ERK, and Akt of BrdU-cells located in the dentate SGZ. pFlk-1, pERK, pAkT (green) and BrdU (red). Scale bar: 50 μm (pFlk-1, pERK) and 10 μm (pAkt). (B) Quantitative analysis showing the percentage of BrdU-labeled cells co-expressing pFlk-1, pERK, and pAkt after VEGF or PBS microinfusion. Student _t_-test: * P < .05 vs. PBS controls. (C) Quantitative analysis showing the percentage of BrdU-labeled co-expressing pFlk-1, pERK, and pAkt after chronic fluoxetine or vehicle treatment (representative images are from fluoxetine treated rat brains). Student _t_-test: * P <.02 vs. Vehicle. Error bars denote mean ± SEM
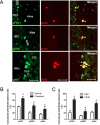
Figure 5. VEGF stimulation of adult hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation requires MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling
(A) Adult hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells cultures (5 days after one passage) treated with Flk-1 (SU5416), MEK/ERK (U0126), or PI3K (LY294002) inhibitors 30 minutes before stimulation with VEGF (50 ng/mL). Cells were fixed 2 hrs later and immunostained with SOX2 (red) and BrdU (green). BrdU (10 μM) was added 30 minutes after VEGF stimulation. (B) Quantitative analysis showed that VEGF treatment significantly increased the number of BrdU-labeled cells. (C) Analysis of the percentage of BrdU-labeled cells that express Sox2 revealed that pretreatment with inhibitors of Flk-1, MEK/ERK, or Akt all blocked VEGF-stimulation of cell proliferation. One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni: * P <.05 vs. DMSO/PBS-treated cells. Error bars denote mean ± SEM
Similar articles
- Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates primate choroid-retinal endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation through PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK dependent signaling.
Jin J, Yuan F, Shen MQ, Feng YF, He QL. Jin J, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Sep;381(1-2):267-72. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1710-y. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23749166 - Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator 1α Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor That Protects Against Neuronal Cell Death Following Status Epilepticus through PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK Signaling.
Huang JB, Hsu SP, Pan HY, Chen SD, Chen SF, Lin TK, Liu XP, Li JH, Chen NC, Liou CW, Hsu CY, Chuang HY, Chuang YC. Huang JB, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 30;21(19):7247. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197247. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33008083 Free PMC article. - Multiple signaling pathways mediate ghrelin-induced proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells.
Chung H, Li E, Kim Y, Kim S, Park S. Chung H, et al. J Endocrinol. 2013 Jun 1;218(1):49-59. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0045. Print 2013 Jul. J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23608221 - The interplay of neurovasculature and adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
Kim TA, Chen L, Ge S. Kim TA, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2021 Aug 24;760:136071. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136071. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 34147540 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways for synergic effects on improving features of peripheral diabetic neuropathy.
Pham VM. Pham VM. J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Nov;15(11):1537-1544. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14289. Epub 2024 Aug 20. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 39162579 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Unbiased classification of the elderly human brain proteome resolves distinct clinical and pathophysiological subtypes of cognitive impairment.
Higginbotham L, Carter EK, Dammer EB, Haque RU, Johnson ECB, Duong DM, Yin L, De Jager PL, Bennett DA, Felsky D, Tio ES, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Seyfried NT. Higginbotham L, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Oct 1;186:106286. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106286. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37689213 Free PMC article. - Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits activation of key members of the RTK family in gastric cancer cells.
Jiang L, Chen Y, Sang J, Li Y, Lan T, Wang Y, Tao Y, Qian H. Jiang L, et al. Biomed Rep. 2013 May;1(3):399-404. doi: 10.3892/br.2013.85. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Biomed Rep. 2013. PMID: 24648957 Free PMC article. - Angiotensin receptor type 2 activation induces neuroprotection and neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury.
Umschweif G, Liraz-Zaltsman S, Shabashov D, Alexandrovich A, Trembovler V, Horowitz M, Shohami E. Umschweif G, et al. Neurotherapeutics. 2014 Jul;11(3):665-78. doi: 10.1007/s13311-014-0286-x. Neurotherapeutics. 2014. PMID: 24957202 Free PMC article. - Focal Cerebral Ischemia Induces Global Subacute Changes in the Number of Neuroblasts and Neurons and the Angiogenic Factor Density in Mice.
Pilipenko V, Dzirkale Z, Rozkalne R, Upite J, Hellal F, Plesnila N, Jansone B. Pilipenko V, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 14;59(12):2168. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122168. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138271 Free PMC article. - Traditional Chinese Medicine Shenmayizhi Decoction Ameliorates Memory and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Multiple Cerebral Infarctions.
Sun C, Liu J, Li N, Liu M, Luo Z, Li H. Sun C, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 30;2021:6648455. doi: 10.1155/2021/6648455. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33859709 Free PMC article.
References
- Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Palmer TD, Alborn AM, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Rosengren LE, Olsson T, Gage FH, Eriksson PS. IGF-I has a direct proliferative effect in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:23–40. - PubMed
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J.Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
- Brandt MD, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G, Reuter K, Bick-Sander A, von der BW, Kempermann G. Transient calretinin expression defines early postmitotic step of neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. Mol.Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:603–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 MH025642/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 2 P01 MH25642/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH45481/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH045481/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH045481/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous