Urinary proteomics to support diagnosis of stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Urinary proteomics to support diagnosis of stroke
Jesse Dawson et al. PLoS One. 2012.
Abstract
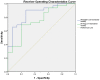
Accurate diagnosis in suspected ischaemic stroke can be difficult. We explored the urinary proteome in patients with stroke (n = 69), compared to controls (n = 33), and developed a biomarker model for the diagnosis of stroke. We performed capillary electrophoresis online coupled to micro-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Potentially disease-specific peptides were identified and a classifier based on these was generated using support vector machine-based software. Candidate biomarkers were sequenced by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. We developed two biomarker-based classifiers, employing 14 biomarkers (nominal p-value <0.004) or 35 biomarkers (nominal p-value <0.01). When tested on a blinded test set of 47 independent samples, the classification factor was significantly different between groups; for the 35 biomarker model, median value of the classifier was 0.49 (-0.30 to 1.25) in cases compared to -1.04 (IQR -1.86 to -0.09) in controls, p<0.001. The 35 biomarker classifier gave sensitivity of 56%, specificity was 93% and the AUC on ROC analysis was 0.86. This study supports the potential for urinary proteomic biomarker models to assist with the diagnosis of acute stroke in those with mild symptoms. We now plan to refine further and explore the clinical utility of such a test in large prospective clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: H. Mischak is the co-founder and co-owner of Mosaiques Diagnostics. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter the authors' adherence to all the PLoS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
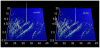
Figure 1. Urinary polypeptide signatures in cases and controls.
Normalized molecular weight (800–20 000 Da) in logarithmic scale is plotted against normalized migration time (18–45 minutes). The mean signal intensity of the polypeptide peak is given in 3-dimensional depiction. n = 26 controls and 33 cases.
Figure 2. Polypeptide signatures of the 35 biomarker model in cases and controls.
Normalized molecular weight (800–20 000 Da) in logarithmic scale is plotted against normalized migration time (18–45 minutes). The mean signal intensity of the polypeptide peak is given in 3-dimensional depiction. n = 26 controls and 33 cases.
Figure 3. Receiver operating characteristics curve for the 14 and 35 biomarker models.
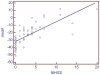
Figure 4. Scatter plot of National Institute of Health of Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score and the biomarker model classifier (modA).
Similar articles
- Urine proteome analysis in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction complicated by chronic kidney disease: feasibility, and clinical and pathogenetic correlates.
Farmakis D, Koeck T, Mullen W, Parissis J, Gogas BD, Nikolaou M, Lekakis J, Mischak H, Filippatos G. Farmakis D, et al. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016 Jul;18(7):822-9. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.544. Epub 2016 May 25. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 27220540 - Urinary proteomics for prediction of preeclampsia.
Carty DM, Siwy J, Brennand JE, Zürbig P, Mullen W, Franke J, McCulloch JW, Roberts CT, North RA, Chappell LC, Mischak H, Poston L, Dominiczak AF, Delles C. Carty DM, et al. Hypertension. 2011 Mar;57(3):561-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.164285. Epub 2011 Jan 3. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 21199994 - Urinary Proteomics Pilot Study for Biomarker Discovery and Diagnosis in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction.
Rossing K, Bosselmann HS, Gustafsson F, Zhang ZY, Gu YM, Kuznetsova T, Nkuipou-Kenfack E, Mischak H, Staessen JA, Koeck T, Schou M. Rossing K, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157167. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27308822 Free PMC article. - Capillary zone electrophoresis on-line coupled to mass spectrometry: A perspective application for clinical proteomics.
Pejchinovski M, Hrnjez D, Ramirez-Torres A, Bitsika V, Mermelekas G, Vlahou A, Zürbig P, Mischak H, Metzger J, Koeck T. Pejchinovski M, et al. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015 Jun;9(5-6):453-68. doi: 10.1002/prca.201400113. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015. PMID: 25641766 Review. - Advances in urinary proteome analysis and biomarker discovery.
Fliser D, Novak J, Thongboonkerd V, Argilés A, Jankowski V, Girolami MA, Jankowski J, Mischak H. Fliser D, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Apr;18(4):1057-71. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006090956. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17329573 Review.
Cited by
- Proteomic advance of ischemic stroke: preclinical, clinical, and intervention.
Zhao T, Zeng J, Zhang R, Pu L, Wang H, Pan L, Jiang Y, Dai X, Sha Y, Han L. Zhao T, et al. Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Dec;38(8):2521-2546. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01262-y. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37440002 Review. - Blood-based protein biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute stroke: A discovery-based SWATH-MS proteomic approach.
Misra S, Singh P, Nath M, Bhalla D, Sengupta S, Kumar A, Pandit AK, Aggarwal P, Srivastava AK, Mohania D, Prasad K, Vibha D. Misra S, et al. Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 27;13:989856. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.989856. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36237606 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular biomarkers in body fluids: progress and prospects in optical sensors.
John RV, Devasiya T, V R N, Adigal S, Lukose J, Kartha VB, Chidangil S. John RV, et al. Biophys Rev. 2022 Aug 18;14(4):1023-1050. doi: 10.1007/s12551-022-00990-2. eCollection 2022 Aug. Biophys Rev. 2022. PMID: 35996626 Free PMC article. Review. - Stroke Proteomics: From Discovery to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications.
Hochrainer K, Yang W. Hochrainer K, et al. Circ Res. 2022 Apr 15;130(8):1145-1166. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320110. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35420912 Free PMC article. Review. - Discovery of Urinary Proteomic Signature for Differential Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis.
Zhao Y, Yang L, Sun C, Li Y, He Y, Zhang L, Shi T, Wang G, Men X, Sun W, He F, Qin J. Zhao Y, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 4;2020:3896263. doi: 10.1155/2020/3896263. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32337245 Free PMC article.
References
- Libman RB, Wirkowski E, Alvir J, Rao TH. Conditions that mimic stroke in the emergency department. Implications for acute stroke trials. Arch. Neurol. 1995;52:1119–1122. - PubMed
- Dawson J, Lamb E, Quinn TJ, Horvers M, Verrijth MJ, et al. A Recognition Tool for Transient Ischaemic Attack. Quarterly Journal of Medicine. 2009;102:43–49. - PubMed
- Harbison J, Hossain O, Jenkinson D, Nor AM, Davis J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of stroke referrals from primary care, emergency room physicians, and ambulance staff using the Face Arm Speech Test. Stroke. 2003;34:71–76. - PubMed
- Nor AM, Davis J, Sen B, Shipsey D, Louw SJ, et al. The recognition of stroke in the emergency room (ROSIER) scale: development and validation of a stroke recognition instrument. 5. Lancet Neurol. 2005;4:727–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical