Thiamin biosynthesis: still yielding fascinating biological chemistry - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Thiamin biosynthesis: still yielding fascinating biological chemistry
Tadhg P Begley et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012.
Abstract
The present paper describes the biosynthesis of the thiamin thiazole in Bacillus subtilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The two pathways are quite different: in B. subtilis, the thiazole is formed by an oxidative condensation of glycine, deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate and a protein thiocarboxylate, whereas, in S. cerevisiae, the thiazole is assembled from glycine, NAD and Cys205 of the thiazole synthase.
Figures
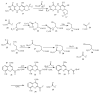
Figure 1
The bacterial thiamin biosynthetic pathway.
Figure 2
Four additional examples of protein-thiocarboxylate-dependent biosynthetic pathways. A) Molybdopterin biosynthesis in bacteria, B) Cysteine biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, C) Homocysteine biosynthesis in Wolinella succinogenes, D) Thioquinolobactin biosynthesis in Pseudomonas fluorescens.
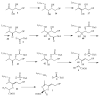
Figure 3
Mechanistic proposal for the formation of the thiazole tautomer 7.
Figure 4
Thiamin pyrophosphate biosynthesis in S. cerevisiae.
Figure 5
Mechanistic proposal for the THI4 mediated formation of ADP-thiazole 64.
Similar articles
- The biosynthesis of the thiazole phosphate moiety of thiamin: the sulfur transfer mediated by the sulfur carrier protein ThiS.
Dorrestein PC, Zhai H, McLafferty FW, Begley TP. Dorrestein PC, et al. Chem Biol. 2004 Oct;11(10):1373-81. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.08.009. Chem Biol. 2004. PMID: 15489164 - Biosynthesis of the thiazole moiety of thiamin pyrophosphate (vitamin B1).
Park JH, Dorrestein PC, Zhai H, Kinsland C, McLafferty FW, Begley TP. Park JH, et al. Biochemistry. 2003 Oct 28;42(42):12430-8. doi: 10.1021/bi034902z. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14567704 - The Biosynthesis of the Thiazole Moiety of Thiamin in the Archaeon Halobacterium salinarum.
Hayashi M, Kijima Y, Tazuya-Murayama K, Yamada K. Hayashi M, et al. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2015;61(3):270-4. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.61.270. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 26226965 - Thiamin biosynthesis in prokaryotes.
Begley TP, Downs DM, Ealick SE, McLafferty FW, Van Loon AP, Taylor S, Campobasso N, Chiu HJ, Kinsland C, Reddick JJ, Xi J. Begley TP, et al. Arch Microbiol. 1999 Apr;171(5):293-300. doi: 10.1007/s002030050713. Arch Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10382260 Review. - Structural biology of enzymes of the thiamin biosynthesis pathway.
Settembre E, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Settembre E, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003 Dec;13(6):739-47. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2003.10.006. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 14675553 Review.
Cited by
- Biosynthetic versatility and coordinated action of 5'-deoxyadenosyl radicals in deazaflavin biosynthesis.
Philmus B, Decamps L, Berteau O, Begley TP. Philmus B, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Apr 29;137(16):5406-13. doi: 10.1021/ja513287k. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25781338 Free PMC article. - Urm1: A Non-Canonical UBL.
Termathe M, Leidel SA. Termathe M, et al. Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 22;11(2):139. doi: 10.3390/biom11020139. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33499055 Free PMC article. Review. - YcaO-Dependent Posttranslational Amide Activation: Biosynthesis, Structure, and Function.
Burkhart BJ, Schwalen CJ, Mann G, Naismith JH, Mitchell DA. Burkhart BJ, et al. Chem Rev. 2017 Apr 26;117(8):5389-5456. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00623. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28256131 Free PMC article. Review. - Conserved active site cysteine residue of archaeal THI4 homolog is essential for thiamine biosynthesis in Haloferax volcanii.
Hwang S, Cordova B, Chavarria N, Elbanna D, McHugh S, Rojas J, Pfeiffer F, Maupin-Furlow JA. Hwang S, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;14:260. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0260-0. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25348237 Free PMC article. - The biosynthesis of nitrogen-, sulfur-, and high-carbon chain-containing sugars.
Lin CI, McCarty RM, Liu HW. Lin CI, et al. Chem Soc Rev. 2013 May 21;42(10):4377-407. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35438a. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Chem Soc Rev. 2013. PMID: 23348524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK044083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK67081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM016609/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK044083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK44083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM16609/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM016609/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases