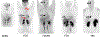Molecular imaging of adrenal neoplasms - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2012 Oct 1;106(5):532-42.
doi: 10.1002/jso.23162. Epub 2012 May 24.
Affiliations
- PMID: 22628250
- PMCID: PMC9207744
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.23162
Review
Molecular imaging of adrenal neoplasms
Clara C Chen et al. J Surg Oncol. 2012.
Abstract
The adrenal glands are complex structures from which a variety of benign and malignant tumors may arise and are a common site of metastatic disease. Several radiopharmaceuticals are used for imaging the adrenals, including I-123/I-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG), norcholesterol derivatives, In-111 pentetreotide and Ga-68 somatostatin analogs, [F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose, [F-18]fluorodopa, [F-18]fluorodopamine, C-11 meta hydroxyephedrine, and C-11/F-18/I-123 Metomidate (MTO) or its analogs. In this review we focus on the role of these reagents in metastatic lesions, cortical neoplasms, pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma, and neuroblastoma (NB).
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Patient with an 8.2 × 5.3 cm adrenal cortical carcinoma showing hypermetabolic activity on FDG in primary tumor with SUVmax of 11.9 (long arrows) and tumor thrombus SUVmax 10.2 (short arrows) confirmed at surgery. Coronal FDG (left panel), CT (middle panel), and fused PET/CT (right panel) images.
Fig. 2.
Patient with SDHD and metastatic PHEO/PGL. Imaging with a variety of radiopharmaceutical shows heterogeneity in uptake. MIBG panel (MIP—top, and coronal slice—bottom) shows uptake in bilateral adrenal PHEOs (black arrows). Two foci in lower midline chest are thought to be due to swallowed activity in esophagus, glomus tumor is not visualized. FDG MIP panel shows intense bilateral uptake in the adrenal PHEOs and a right atrial PGL (white arrow). Mild uptake in a right glomus jugulare PGL was also seen (not shown this projection). Foci in mediastinum and upper abdomen (red arrows) represent uptake in brown fat. FDOPA MIP panel shows intense uptake in right glomus jugulare PGL (chevron) and right atrial lesion. Mild uptake was seen in the left adrenal PHEO but not right (not seen in this view). FDA MIP shows intense uptake in bilateral adrenal PHEOs with faint uptake in atrial lesion. Physiologic gallbladder activity is also seen. No intracranial uptake was seen. SRS panel shows In-111 pentetreotide MIP images with intense uptake in the right glomus jugulare tumor and cardiac lesion but no uptake in the bilateral adrenal tumors. Images courtesy of Dr. Karel Pacak, NICHD, NIH.
Similar articles
- Radionuclide therapy of adrenal tumors.
Carrasquillo JA, Pandit-Taskar N, Chen CC. Carrasquillo JA, et al. J Surg Oncol. 2012 Oct 1;106(5):632-42. doi: 10.1002/jso.23196. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22718415 Review. - Imaging of neuroendocrine tumors.
Rufini V, Calcagni ML, Baum RP. Rufini V, et al. Semin Nucl Med. 2006 Jul;36(3):228-47. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2006.03.007. Semin Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16762613 Review. - Staging and functional characterization of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography.
Timmers HJ, Chen CC, Carrasquillo JA, Whatley M, Ling A, Eisenhofer G, King KS, Rao JU, Wesley RA, Adams KT, Pacak K. Timmers HJ, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 May 2;104(9):700-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs188. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22517990 Free PMC article. - Adrenal Molecular Imaging.
Sundin A. Sundin A. Front Horm Res. 2016;45:70-9. doi: 10.1159/000442317. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Front Horm Res. 2016. PMID: 27003680 Review. - Contemporary approach to diagnosis and treatment of neuroblastoma.
Charron M. Charron M. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013 Mar;57(1):40-52. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23474634 Review.
Cited by
- Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: diagnosis, genetics, management, and treatment.
Martucci VL, Pacak K. Martucci VL, et al. Curr Probl Cancer. 2014 Jan-Feb;38(1):7-41. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Curr Probl Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24636754 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Metabolic and anatomic characteristics of benign and malignant adrenal masses on positron emission tomography/computed tomography: a review of literature.
Kandathil A, Wong KK, Wale DJ, Zatelli MC, Maffione AM, Gross MD, Rubello D. Kandathil A, et al. Endocrine. 2015 May;49(1):6-26. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0440-6. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 25273320 Review. - MIBG (metaiodobenzylguanidine) theranostics in pediatric and adult malignancies.
Agrawal A, Rangarajan V, Shah S, Puranik A, Purandare N. Agrawal A, et al. Br J Radiol. 2018 Nov;91(1091):20180103. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180103. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30048149 Free PMC article. Review. - Progress in the diagnosis and treatment of paraganglioma.
Wang B, Qiu J. Wang B, et al. Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Nov;8(7):2624-2635. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.10.11. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35117020 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the differential diagnosis of primary benign and malignant unilateral adrenal tumors.
Ma G, Zhang X, Wang M, Xu X, Xu B, Guan Z. Ma G, et al. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021 May;11(5):2013-2018. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-875. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021. PMID: 33936982 Free PMC article.
References
- Wieland DM, Swanson DP, Brown LE, et al.: Imaging the adrenal-medulla with an 1–131-labeled antiadrenergic agent. J Nucl Med 1979;20:155–158. - PubMed
- Furuta N, Kiyota H, Yoshigoe F, et al.: Diagnosis of pheochromocytoma using [I-123]-compared with [I-131]-metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy. Int J Urol 1999;6:119–124. - PubMed
- Hoyer D, Bell GI, Berelowitz M, et al.: Classification and nomenclature of somatostatin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1995;16:86–88. - PubMed
- Khan MU, Khan S, Ei-Refaie S, et al.: Clinical indications forGallium-68 positron emission tomography imaging. Eur J Surg Oncol 2009;35:561–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical