RAxML-Light: a tool for computing terabyte phylogenies - PubMed (original) (raw)
RAxML-Light: a tool for computing terabyte phylogenies
A Stamatakis et al. Bioinformatics. 2012.
Abstract
Motivation: Due to advances in molecular sequencing and the increasingly rapid collection of molecular data, the field of phyloinformatics is transforming into a computational science. Therefore, new tools are required that can be deployed in supercomputing environments and that scale to hundreds or thousands of cores.
Results: We describe RAxML-Light, a tool for large-scale phylogenetic inference on supercomputers under maximum likelihood. It implements a light-weight checkpointing mechanism, deploys 128-bit (SSE3) and 256-bit (AVX) vector intrinsics, offers two orthogonal memory saving techniques and provides a fine-grain production-level message passing interface parallelization of the likelihood function. To demonstrate scalability and robustness of the code, we inferred a phylogeny on a simulated DNA alignment (1481 taxa, 20 000 000 bp) using 672 cores. This dataset requires one terabyte of RAM to compute the likelihood score on a single tree. CODE AVAILABILITY: https://github.com/stamatak/RAxML-Light-1.0.5 DATA AVAILABILITY: http://www.exelixis-lab.org/onLineMaterial.tar.bz2
Contact: alexandros.stamatakis@h-its.org
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
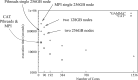
Fig. 1.
Parallel execution times of the MPI and PThreads versions under CAT and Γ on a DNA dataset with 150 taxa and 20 000 000 sites
Similar articles
- Exploring parallel MPI fault tolerance mechanisms for phylogenetic inference with RAxML-NG.
Hübner L, Kozlov AM, Hespe D, Sanders P, Stamatakis A. Hübner L, et al. Bioinformatics. 2021 Nov 18;37(22):4056-4063. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab399. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34037680 Free PMC article. - RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference.
Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, Morel B, Stamatakis A. Kozlov AM, et al. Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 1;35(21):4453-4455. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31070718 Free PMC article. - RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies.
Stamatakis A. Stamatakis A. Bioinformatics. 2014 May 1;30(9):1312-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24451623 Free PMC article. - RAxML-III: a fast program for maximum likelihood-based inference of large phylogenetic trees.
Stamatakis A, Ludwig T, Meier H. Stamatakis A, et al. Bioinformatics. 2005 Feb 15;21(4):456-63. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti191. Epub 2004 Dec 17. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15608047 - A RESTful API for Access to Phylogenetic Tools via the CIPRES Science Gateway.
Miller MA, Schwartz T, Pickett BE, He S, Klem EB, Scheuermann RH, Passarotti M, Kaufman S, O'Leary MA. Miller MA, et al. Evol Bioinform Online. 2015 Mar 16;11:43-8. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S21501. eCollection 2015. Evol Bioinform Online. 2015. PMID: 25861210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- ExaML version 3: a tool for phylogenomic analyses on supercomputers.
Kozlov AM, Aberer AJ, Stamatakis A. Kozlov AM, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Aug 1;31(15):2577-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv184. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25819675 Free PMC article. - COMT gene locus: new functional variants.
Meloto CB, Segall SK, Smith S, Parisien M, Shabalina SA, Rizzatti-Barbosa CM, Gauthier J, Tsao D, Convertino M, Piltonen MH, Slade GD, Fillingim RB, Greenspan JD, Ohrbach R, Knott C, Maixner W, Zaykin D, Dokholyan NV, Reenilä I, Männistö PT, Diatchenko L. Meloto CB, et al. Pain. 2015 Oct;156(10):2072-2083. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000273. Pain. 2015. PMID: 26207649 Free PMC article. - Whole-genome sequencing-based genetic diversity, transmission dynamics, and drug-resistant mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from extrapulmonary tuberculosis patients in western Ethiopia.
Chekesa B, Singh H, Gonzalez-Juarbe N, Vashee S, Wiscovitch-Russo R, Dupont CL, Girma M, Kerro O, Gumi B, Ameni G. Chekesa B, et al. Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 9;12:1399731. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1399731. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39185123 Free PMC article. - Best practice for wildlife gut microbiome research: A comprehensive review of methodology for 16S rRNA gene investigations.
Combrink L, Humphreys IR, Washburn Q, Arnold HK, Stagaman K, Kasschau KD, Jolles AE, Beechler BR, Sharpton TJ. Combrink L, et al. Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1092216. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1092216. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36910202 Free PMC article. Review. - The Birth and Death of Olfactory Receptor Gene Families in Mammalian Niche Adaptation.
Hughes GM, Boston ESM, Finarelli JA, Murphy WJ, Higgins DG, Teeling EC. Hughes GM, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2018 Jun 1;35(6):1390-1406. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy028. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29562344 Free PMC article.
References
- Izquierdo-Carrasco F., et al. Trading memory for running time in phylogenetic likelihood computations. Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies; 2011b. Technical report.
- Ott M., et al. Large-scale maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analysis on the IBM BlueGene/L. Proceedings of IEEE/ACM Supercomputing Conference 2007 (SC2007). 2007
- Rambaut A., Grass N. Seq-gen: an application for the monte carlo simulation of dna sequence evolution along phylogenetic trees. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1997;13:235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous