Linking crystallographic model and data quality - PubMed (original) (raw)
Linking crystallographic model and data quality
P Andrew Karplus et al. Science. 2012.
Abstract
In macromolecular x-ray crystallography, refinement R values measure the agreement between observed and calculated data. Analogously, R(merge) values reporting on the agreement between multiple measurements of a given reflection are used to assess data quality. Here, we show that despite their widespread use, R(merge) values are poorly suited for determining the high-resolution limit and that current standard protocols discard much useful data. We introduce a statistic that estimates the correlation of an observed data set with the underlying (not measurable) true signal; this quantity, CC*, provides a single statistically valid guide for deciding which data are useful. CC* also can be used to assess model and data quality on the same scale, and this reveals when data quality is limiting model improvement.
Figures
Figure 1
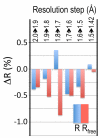
Higher resolution data, even if weak, improves refinement behaviour. For each incremental step of resolution from X->Y (top legend), the pair of bars gives the changes in overall Rwork (blue) and Rfree (red) for the model refined at resolution Y with respect to those for the model refined at resolution X, with both R values calculated at resolution X. The first pair of bars shows that Rwork and Rfree dropped 0.38 and 0.34% upon isotropic refinement, respectively, when the refinement resolution limit was extended from 2.0 to 1.9 Å; the other pairs of bars show the improvement upon anisotropic refinement.
Figure 2
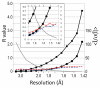
Data quality R values behave differently than those from crystallographic refinement, and useful data extend well beyond what standard cutoff criteria would suggest. Rmeas (squares) and Rpim (circles) are compared with Rwork (blue) and Rfree (red) from 1.42 Å resolution refinements against the EXP dataset. <I‒∕σ(I‒)> (grey X) is also plotted. Inset is a close-up of the plot beyond 2 Å resolution.
Figure 3
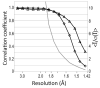
Signal as a function of resolution as measured by correlation coefficients. Plotted as a function of resolution for the EXP data is CC1/2 (diamonds) and the CC for a comparison with the 3ELN reference dataset (triangles). <I‒∕σ(I‒)> (grey) is also shown. All determined CC1/2 values shown have expected standard errors of <0.025 (21, 22).
Figure 4
The CC1/2 / CC* relationship and the utility of comparing CC* with CCwork and CCfree from a refined model. (A) Plotted is the analytical relationship (eqn. 3) between CC1/2 and CC* (black curve). Also roughly following the CC* curve are the CC values for the EXP data compared with 3ELN (triangles) as a function of CC1/2. (B) Plotted as a function of resolution are CC* (black solid) for the EXP dataset as well as CCwork (blue dashed) and CCfree (red dashed) calculated on intensities from the 1.42 Å refined model. Also shown are CCwork (blue dotted) and CCfree (red dotted) between the 1.42 Å refined model and the 3ELN dataset.
Comment in
- Biochemistry. Resolving some old problems in protein crystallography.
Evans P. Evans P. Science. 2012 May 25;336(6084):986-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1222162. Science. 2012. PMID: 22628641 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Better models by discarding data?
Diederichs K, Karplus PA. Diederichs K, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Jul;69(Pt 7):1215-22. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913001121. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23793147 Free PMC article. - Biochemistry. Resolving some old problems in protein crystallography.
Evans P. Evans P. Science. 2012 May 25;336(6084):986-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1222162. Science. 2012. PMID: 22628641 No abstract available. - Using a conformation-dependent stereochemical library improves crystallographic refinement of proteins.
Tronrud DE, Berkholz DS, Karplus PA. Tronrud DE, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010 Jul;66(Pt 7):834-42. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910019207. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010. PMID: 20606264 Free PMC article. - You are lost without a map: Navigating the sea of protein structures.
Lamb AL, Kappock TJ, Silvaggi NR. Lamb AL, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1854(4):258-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.12.021. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25554228 Free PMC article. Review. - Collection of X-Ray Diffraction Data from Macromolecular Crystals.
Dauter Z. Dauter Z. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:165-184. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7000-1_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28573573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Covid-19.bioreproducibility.org: A web resource for SARS-CoV-2-related structural models.
Brzezinski D, Kowiel M, Cooper DR, Cymborowski M, Grabowski M, Wlodawer A, Dauter Z, Shabalin IG, Gilski M, Rupp B, Jaskolski M, Minor W. Brzezinski D, et al. Protein Sci. 2021 Jan;30(1):115-124. doi: 10.1002/pro.3959. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 32981130 Free PMC article. - Structure of the N-terminal domain of the protein Expansion: an 'Expansion' to the Smad MH2 fold.
Beich-Frandsen M, Aragón E, Llimargas M, Benach J, Riera A, Pous J, Macias MJ. Beich-Frandsen M, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 Apr;71(Pt 4):844-53. doi: 10.1107/S1399004715001443. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015. PMID: 25849395 Free PMC article. - Structure-guided design and optimization of dipeptidyl inhibitors of norovirus 3CL protease. Structure-activity relationships and biochemical, X-ray crystallographic, cell-based, and in vivo studies.
Galasiti Kankanamalage AC, Kim Y, Weerawarna PM, Uy RA, Damalanka VC, Mandadapu SR, Alliston KR, Mehzabeen N, Battaile KP, Lovell S, Chang KO, Groutas WC. Galasiti Kankanamalage AC, et al. J Med Chem. 2015 Apr 9;58(7):3144-55. doi: 10.1021/jm5019934. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25761614 Free PMC article. - Characterisation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe α-actinin.
Addario B, Sandblad L, Persson K, Backman L. Addario B, et al. PeerJ. 2016 Mar 28;4:e1858. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1858. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27069798 Free PMC article. - Structural characterization of a soil viral auxiliary metabolic gene product - a functional chitosanase.
Wu R, Smith CA, Buchko GW, Blaby IK, Paez-Espino D, Kyrpides NC, Yoshikuni Y, McDermott JE, Hofmockel KS, Cort JR, Jansson JK. Wu R, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 19;13(1):5485. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32993-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36123347 Free PMC article.
References
- Wilson AJC. Largest likely values for the reliability index. Acta Cryst. 1950;3:397–398.
- Brünger ATB. Free R value: a novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature. 1992;355:472. - PubMed
- Arndt UW, Crowther RA, Mallett JFW. A computer-linked cathode-ray tube microdensitometer for X-ray crystallography. J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 1968;1:510. - PubMed
- Diederichs K, Karplus PA. Improved R-factors for diffraction data analysis in macromolecular crystallography. Nature Structural Biology. 1997;4:269. - PubMed
- Weiss MS. Global indicators of X-ray data quality. J. Appl. Cryst. 2001;34:130.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources