Third generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their development in advanced renal cell carcinoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Third generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their development in advanced renal cell carcinoma
Ronald M Bukowski. Front Oncol. 2012.
Abstract
Angiogenesis in general and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling axis in particular is a validated target in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Clear-cell carcinoma of the kidney is now recognized as a malignancy that is sensitive to inhibitors of the VEGF pathway. Treatment options for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma have evolved in dramatic fashion over the past 6 years, and a new paradigm has developed. The cytokines interferon-α and interleukin-2 were previously utilized for therapy, but since December 2005, six new agents have been approved in the United States for the treatment of advanced RCC. Two are tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI's) including sunitinib and recently pazopanib, and the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib. The current review examines the evolving data with the next generation of TKI's, axitinib and tivozanib being developed for the treatment of advanced RCC. These agents were synthesized to provide increased target specificity and enhanced target inhibition. The preclinical and clinical data are examined, an overview of the development of these TKI's is provided, and discussion plus speculation concerning their potential roles as RCC therapy is provided.
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Figures
Figure 1
Molecular structures and chemical data for two third generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors, axitinib (Hu-Lowe et al., 2008), and tivozanib (Gupta and Fishman, 2011).
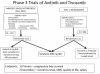
Figure 2
Phase 3 pivotal trial (AXIS and TIVO-1) designs for studies of axitinib or tivozanib vs sorafenib.
Similar articles
- Tivozanib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma.
Hepgur M, Sadeghi S, Dorff TB, Quinn DI. Hepgur M, et al. Biologics. 2013;7:139-48. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S32958. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Biologics. 2013. PMID: 23788831 Free PMC article. - Pazopanib: a multikinase inhibitor with activity in advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Bukowski RM. Bukowski RM. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010 May;10(5):635-45. doi: 10.1586/era.10.38. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20469994 Review. - Axitinib for the treatment of patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) after failure of prior systemic treatment.
Grünwald V, Merseburger AS. Grünwald V, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2012;5:111-7. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S23273. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Onco Targets Ther. 2012. PMID: 22787405 Free PMC article. - Optimal management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: current status.
Escudier B, Albiges L, Sonpavde G. Escudier B, et al. Drugs. 2013 Apr;73(5):427-38. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0043-1. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23572408 Review. - The prospects of pazopanib in advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Gupta S, Spiess PE. Gupta S, et al. Ther Adv Urol. 2013 Oct;5(5):223-32. doi: 10.1177/1756287213495099. Ther Adv Urol. 2013. PMID: 24082917 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Renal Carcinoma: an Update.
da Silva RD, Gustafson D, Nogueira L, Werahera PN, Molina WR, Kim FJ. da Silva RD, et al. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2014 Oct 21;1(6):63-73. doi: 10.15586/jkcvhl.2014.14. eCollection 2014. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2014. PMID: 28326251 Free PMC article. - Clear-cell renal cell carcinoma - A comprehensive review of agents used in the contemporary management of advanced/metastatic disease.
Gkolfinopoulos S, Psyrri A, Bamias A. Gkolfinopoulos S, et al. Oncol Rev. 2021 Feb 26;15(1):530. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2021.530. eCollection 2021 Feb 26. Oncol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33747368 Free PMC article. - Research progress on advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Song XD, Tian YN, Li H, Liu B, Zhang AL, Hong Y. Song XD, et al. J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520924265. doi: 10.1177/0300060520924265. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32529862 Free PMC article. Review. - A randomised, phase II study of nintedanib or sunitinib in previously untreated patients with advanced renal cell cancer: 3-year results.
Eisen T, Loembé AB, Shparyk Y, MacLeod N, Jones RJ, Mazurkiewicz M, Temple G, Dressler H, Bondarenko I. Eisen T, et al. Br J Cancer. 2015 Oct 20;113(8):1140-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.313. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26448178 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Imatinib‑ and ponatinib‑mediated cardiotoxicity in zebrafish embryos and H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.
Zakaria ZZ, Suleiman M, Benslimane FM, Al-Badr M, Sivaraman S, Korashy HM, Ahmad F, Uddin S, Mraiche F, Yalcin HC. Zakaria ZZ, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):187. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13311. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39219269 Free PMC article.
References
- Bhargava P., Esteves B., Al-Adhami M., Nosov D. A., Lipatov O. N., Lyulko A. A., Anischenko A. A., Chacko R. T., Doval D. C., Slichenmyer W. (2010). Activity of tivozanib (AV-951) in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC): subgroup analysis from a phase II randomized discontinuation trial (RDT). J. Clin. Oncol. 28(Suppl.), 15s.10.1200/JCO.2009.24.9326 - DOI - PubMed
- Cella D., Escudier B., Rini B. I., Chen C., Bhattacharyya H., Tarazi J. C., Rosbrook B., Kim S., Motzer R. J. (2011). Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in a phase III AXIS trial of axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 29(Suppl.), abstr. 4504
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous