Circulating visfatin level and visfatin/insulin ratio in obese women with metabolic syndrome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Circulating visfatin level and visfatin/insulin ratio in obese women with metabolic syndrome
Magdalena Olszanecka-Glinianowicz et al. Arch Med Sci. 2012.
Abstract
Introduction: Visfatin is an adipokine secreted by visceral adipose tissue with insulin-mimetic properties. Higher circulating visfatin levels were reported in type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to analyse circulating visfatin and insulin levels and the visfatin/insulin ratio in obese women with and without metabolic syndrome (MetS).
Material and methods: The study involved 92 obese women. Subjects were diagnosed with MetS according to IDF 2005 criteria. The MetS group consisted of 71 subjects (age: 52.8 ±9.4 years, body mass index [BMI]: 39.1 ±5.6 kg/m(2), waist circumference: 109.6 ±11.4 cm and fat mass: 52.0 ±12.8 kg) while the non-MetS group consisted of 21 subjects (age: 51.7 ±9.5 years, BMI: 36.3 ±5.2 kg/m(2), waist circumference: 104.7 ±11.0 cm and fat mass: 45.2 ±10.7 kg). In addition to anthropometric measurements and assessment of serum glucose and lipids, plasma concentrations of visfatin were estimated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and of insulin by radioimmunoassay (RIA). Homeostatic model assessment insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and visfatin/insulin ratio were calculated.
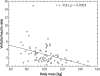
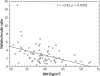
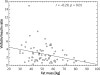
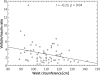
Results: In the MetS group significantly higher (p < 0.01) plasma concentrations of insulin and HOMA-IR values but similar visfatin levels were observed than in the non-MetS group. As a consequence of the significantly higher plasma insulin concentration the visfatin/insulin ratio was significantly lower in the MetS group (p < 0.05). The visfatin/insulin ratio correlated inversely with anthropometric parameters such as body mass, BMI, body fat and waist circumference (r = -0.41, p = 0.0003; r = -0.42, p = 0.0002; r = -0.29, p = 0.01; r = -0.23, p = 0.04, respectively).
Conclusions: We conclude that the visfatin/insulin ratio declining with increasing visceral obesity may predispose to the development of insulin resistance.
Keywords: insulin; metabolic syndrome; obesity; visfatin.
Figures
Figure 1
Correlation between body mass and visfatin to insulin ratio
Figure 2
Correlation between BMI and visfatin to insulin ratio
Figure 3
Correlation between fat mass and visfatin to insulin ratio
Figure 4
Correlation between waist circumference and visfatin to insulin ratio
Similar articles
- Visfatin in obese children and adolescents and its association with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
Nourbakhsh M, Nourbakhsh M, Gholinejad Z, Razzaghy-Azar M. Nourbakhsh M, et al. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015 Apr;75(2):183-8. doi: 10.3109/00365513.2014.1003594. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 25723377 - Increased plasma levels of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in obese and overweight patients with metabolic syndrome.
Filippatos TD, Derdemezis CS, Kiortsis DN, Tselepis AD, Elisaf MS. Filippatos TD, et al. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007 Apr;30(4):323-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03346300. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007. PMID: 17556870 - Plasma visfatin concentrations and fat depot-specific mRNA expression in humans.
Berndt J, Klöting N, Kralisch S, Kovacs P, Fasshauer M, Schön MR, Stumvoll M, Blüher M. Berndt J, et al. Diabetes. 2005 Oct;54(10):2911-6. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.10.2911. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 16186392 - Cut-off values of waist circumference to predict metabolic syndrome in obese adolescents.
Masquio DC, Ganen Ade P, Campos RM, Sanches Pde L, Corgosinho FC, Caranti D, Tock L, de Mello MT, Tufik S, Dâmaso AR. Masquio DC, et al. Nutr Hosp. 2015 Apr 1;31(4):1540-50. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.31.4.8442. Nutr Hosp. 2015. PMID: 25795939 - Role of visfatin in obesity-induced insulin resistance.
Abdalla MMI. Abdalla MMI. World J Clin Cases. 2022 Oct 26;10(30):10840-10851. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i30.10840. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36338223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Insulin Resistance in Children.
Rotondo E, Chiarelli F. Rotondo E, et al. Biomedicines. 2020 May 28;8(6):137. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8060137. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32481506 Free PMC article. Review. - Study of Visfatin Level in Type 1 Diabetic Children and Adolescents.
El Samahi MH, Ismail NA, Matter RM, Selim A, Ibrahim AA, Nabih W. El Samahi MH, et al. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jun 11;5(3):299-304. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.065. eCollection 2017 Jun 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28698746 Free PMC article. - Serum visfatin levels in non-obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and matched controls.
Kim JJ, Choi YM, Hong MA, Kim MJ, Chae SJ, Kim SM, Hwang KR, Yoon SH, Ku SY, Suh CS, Kim SH. Kim JJ, et al. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018 Mar;61(2):253-260. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2018.61.2.253. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29564317 Free PMC article. - Adipokines NUCB2/nesfatin-1 and visfatin as novel inflammatory factors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Leivo-Korpela S, Lehtimäki L, Hämälainen M, Vuolteenaho K, Kööbi L, Järvenpää R, Kankaanranta H, Saarelainen S, Moilanen E. Leivo-Korpela S, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:232167. doi: 10.1155/2014/232167. Epub 2014 May 6. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24891763 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome and health behaviours of postmenopausal women working in agriculture.
Pinkas J, Bojar I, Owoc A, Wierzbińska-Stępniak A, Raczkiewicz D. Pinkas J, et al. Arch Med Sci. 2017 Aug;13(5):1040-1048. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2017.68952. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Arch Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28883844 Free PMC article.
References
- Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, et al. Visfatin: aprotein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effect of insulin. Science. 2005;307:426–30. - PubMed
- Bernt J, Klöting N, Kralisch S, et al. Plasma visfatin concentrations and fat depot – specific mRNA expression in humans. Diabetes. 2005;54:2911–6. - PubMed
- Pagano C, Pilon C, Olivieri M, et al. Reduced plasma visfatin/pre-B cell colony – enhancing factor in obesity is not related to insulin resistance in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3165–70. - PubMed
- Chen CC, Li TC, Li CI, et al. The relationship between visfatin levels and anthropometric and metabolic parameters: association with cholesterol levels in women. Metabolism. 2007;56:1216–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials