Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances
Wei-Ye Liu et al. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Aug.
Abstract
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a dynamic interference that regulates the nutrition and toxic substance in and out of the central nervous system (CNS), and plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable circumstance of the CNS. Tight junctions among adjacent cells form the basic structure of BBB to limiting paracellular permeability. In the present review, the constituents of tight junction proteins are depicted in detail, together with the regulation of tight junction under stimulation and in pathological conditions. Tight junction modulators are also discussed.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
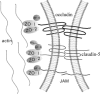
Figure 1
Molecular component of endothelial tight junctions in the BBB.
Similar articles
- Tight junction proteins: from barrier to tumorigenesis.
Runkle EA, Mu D. Runkle EA, et al. Cancer Lett. 2013 Aug 28;337(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.038. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23743355 Free PMC article. Review. - Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood-brain barrier: structural and functional aspects.
Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg H, Blasig IE. Haseloff RF, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Feb;38:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.004. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25433243 Review. - Claudin-12 is not required for blood-brain barrier tight junction function.
Castro Dias M, Coisne C, Baden P, Enzmann G, Garrett L, Becker L, Hölter SM; German Mouse Clinic Consortium; Hrabě de Angelis M, Deutsch U, Engelhardt B. Castro Dias M, et al. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019 Sep 12;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12987-019-0150-9. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019. PMID: 31511021 Free PMC article. - The Basic Requirement of Tight Junction Proteins in Blood-Brain Barrier Function and Their Role in Pathologies.
Dithmer S, Blasig IE, Fraser PA, Qin Z, Haseloff RF. Dithmer S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 21;25(11):5601. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115601. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891789 Free PMC article. Review. - Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells increase the permeability of blood-brain barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins.
Feng S, Cen J, Huang Y, Shen H, Yao L, Wang Y, Chen Z. Feng S, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e20599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020599. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857898 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Resveratrol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced dysfunction of blood-brain barrier in endothelial cells via AMPK activation.
Hu M, Liu B. Hu M, et al. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;20(4):325-32. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.325. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27382348 Free PMC article. Retracted. - cPLA2 in Epilepsy: Shutting Down the Leaker at Its Source.
Gross C. Gross C. Epilepsy Curr. 2018 Sep-Oct;18(5):334-335. doi: 10.5698/1535-7597.18.5.334. Epilepsy Curr. 2018. PMID: 30464739 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Powassan Viruses Spread Cell to Cell during Direct Isolation from Ixodes Ticks and Persistently Infect Human Brain Endothelial Cells and Pericytes.
Conde JN, Sanchez-Vicente S, Saladino N, Gorbunova EE, Schutt WR, Mladinich MC, Himmler GE, Benach J, Kim HK, Mackow ER. Conde JN, et al. J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0168221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01682-21. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34643436 Free PMC article. - The molecular constituents of the blood-brain barrier.
Chow BW, Gu C. Chow BW, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2015 Oct;38(10):598-608. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2015.08.003. Trends Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26442694 Free PMC article. Review. - Morphogens and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease.
Wevers NR, de Vries HE. Wevers NR, et al. Tissue Barriers. 2015 Sep 11;4(1):e1090524. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2015.1090524. eCollection 2016 Jan-Mar. Tissue Barriers. 2015. PMID: 27141417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Cardoso FL, Brites D, Brito MA. Looking at the blood‐brain barrier: Molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev 2010;64:328–363. - PubMed
- Tam SJ, Watts RJ. Connecting vascular and nervous system development: Angiogenesis and the blood‐brain barrier. Annu Rev Neurosci 2010;33:379–408. - PubMed
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood‐brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 2005;57:173–185. - PubMed
- Pardridge WM. Blood‐brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov Today 2007;12:54–61. - PubMed
- Neuwelt EA. Mechanisms of disease: The blood‐brain barrier. Neurosurgery 2004;54:131–140; discussion 141–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources