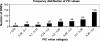Development and characterisation of an expressed sequence tags (EST)-derived single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) resource in rainbow trout - PubMed (original) (raw)
Development and characterisation of an expressed sequence tags (EST)-derived single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) resource in rainbow trout
Mekki Boussaha et al. BMC Genomics. 2012.
Abstract
Background: There is considerable interest in developing high-throughput genotyping with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for the identification of genes affecting important ecological or economical traits. SNPs are evenly distributed throughout the genome and are likely to be functionally relevant. In rainbow trout, in silico screening of EST databases represents an attractive approach for de novo SNP identification. Nevertheless, EST sequencing errors and assembly of EST paralogous sequences can lead to the identification of false positive SNPs which renders the reliability of EST-derived SNPs relatively low. Further validation of EST-derived SNPs is therefore required. The objective of this work was to assess the quality of and to validate a large number of rainbow trout EST-derived SNPs.
Results: A panel of 1,152 EST-derived SNPs was selected from the INRA Sigenae SNP database and was genotyped in standard and double haploid individuals from several populations using the Illumina GoldenGate BeadXpress assay. High-quality genotyping data were obtained for 958 SNPs representing a genotyping success rate of 83.2 %, out of which, 350 SNPs (36.5 %) were polymorphic in at least one population and were designated as true SNPs. They also proved to be a potential tool to investigate genetic diversity of the species, as the set of SNP successfully sorted individuals into three main groups using STRUCTURE software. Functional annotations revealed 28 non-synonymous SNPs, out of which four substitutions were predicted to affect protein functions. A subset of 223 true SNPs were polymorphic in the two INRA mapping reference families and were integrated into the INRA microsatellite-based linkage map.
Conclusions: Our results represent the first study of EST-derived SNPs validation in rainbow trout, a species whose genome sequences is not yet available. We designed several specific filters in order to improve the genotyping yield. Nevertheless, our selection criteria should be further improved in order to reduce the observed high rate of false positive SNPs which results from the occurrence of whole genome duplications.
Figures
Figure 1
Selection of the validation panel. Filters used to select EST-derived SNPs for validation from the INRA Sigenae SNP database release som10 were summarized.
Figure 2
Distribution of observed heterozygosity for true SNPs in three populations. SNPs were clustered into categories based on their observed heterozygosity values.
Figure 3
Frequency distribution of PIC values across the three genotyped populations. SNPs were clustered into categories based on their observed PIC values.
Figure 4
Prediction of the best value of K. Delta K analysis was performed as previously described (Evanno, 2005) in order to predict the best value of K.
Figure 5
Genetic population structure predicted by STRUCTURE software. Genetic population structure was inferred with the structure software using K = 3, a burn-in period of 50,000 200,000 iterations for the likelihood estimation. Individuals 1 to 20 correspond to the INRA-SP population, individuals 21 to 40 correspond to the INRA-SY population and individuals 41 to 84 correspond to the NCCCWA population.
Similar articles
- Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in rainbow trout by deep sequencing of a reduced representation library.
Sánchez CC, Smith TP, Wiedmann RT, Vallejo RL, Salem M, Yao J, Rexroad CE 3rd. Sánchez CC, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 25;10:559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-559. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19939274 Free PMC article. - A first generation integrated map of the rainbow trout genome.
Palti Y, Genet C, Luo MC, Charlet A, Gao G, Hu Y, Castaño-Sánchez C, Tabet-Canale K, Krieg F, Yao J, Vallejo RL, Rexroad CE 3rd. Palti Y, et al. BMC Genomics. 2011 Apr 7;12:180. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-180. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21473775 Free PMC article. - A resource of single-nucleotide polymorphisms for rainbow trout generated by restriction-site associated DNA sequencing of doubled haploids.
Palti Y, Gao G, Miller MR, Vallejo RL, Wheeler PA, Quillet E, Yao J, Thorgaard GH, Salem M, Rexroad CE 3rd. Palti Y, et al. Mol Ecol Resour. 2014 May;14(3):588-96. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12204. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Mol Ecol Resour. 2014. PMID: 24251403 - Genomics and hypertension: concepts, potentials, and opportunities.
Pratt RE, Dzau VJ. Pratt RE, et al. Hypertension. 1999 Jan;33(1 Pt 2):238-47. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.33.1.238. Hypertension. 1999. PMID: 9931111 Review. - The Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Cancer RNAi Therapies.
Gebert M, Jaśkiewicz M, Moszyńska A, Collawn JF, Bartoszewski R. Gebert M, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 25;12(11):3119. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113119. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33113880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Design and characterization of a 52K SNP chip for goats.
Tosser-Klopp G, Bardou P, Bouchez O, Cabau C, Crooijmans R, Dong Y, Donnadieu-Tonon C, Eggen A, Heuven HC, Jamli S, Jiken AJ, Klopp C, Lawley CT, McEwan J, Martin P, Moreno CR, Mulsant P, Nabihoudine I, Pailhoux E, Palhière I, Rupp R, Sarry J, Sayre BL, Tircazes A, Jun Wang, Wang W, Zhang W; International Goat Genome Consortium. Tosser-Klopp G, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e86227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086227. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465974 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the rainbow trout spleen transcriptome and identification of immune-related genes.
Ali A, Rexroad CE, Thorgaard GH, Yao J, Salem M. Ali A, et al. Front Genet. 2014 Oct 14;5:348. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00348. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25352861 Free PMC article. - Identification of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Differentially Expressed Genes Favoring Soybean Meal Tolerance in Higher-Growth Zebrafish (Danio rerio).
Ulloa PE, Jilberto F, Lam N, Rincón G, Valenzuela L, Cordova-Alarcón V, Hernández AJ, Dantagnan P, Ravanal MC, Elgueta S, Araneda C. Ulloa PE, et al. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024 Aug;26(4):754-765. doi: 10.1007/s10126-024-10343-7. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2024. PMID: 38958822 - Population genetic analysis of aquaculture salmonid populations in China using a 57K rainbow trout SNP array.
Zhang HY, Zhao ZX, Xu J, Xu P, Bai QL, Yang SY, Jiang LK, Chen BH. Zhang HY, et al. PLoS One. 2018 Aug 17;13(8):e0202582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202582. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30118517 Free PMC article. - Resistance to a rhabdovirus (VHSV) in rainbow trout: identification of a major QTL related to innate mechanisms.
Verrier ER, Dorson M, Mauger S, Torhy C, Ciobotaru C, Hervet C, Dechamp N, Genet C, Boudinot P, Quillet E. Verrier ER, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055302. Epub 2013 Feb 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23390526 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials