RNAiAtlas: a database for RNAi (siRNA) libraries and their specificity - PubMed (original) (raw)
RNAiAtlas: a database for RNAi (siRNA) libraries and their specificity
Slawek Mazur et al. Database (Oxford). 2012.
Abstract
Large-scale RNA interference (RNAi) experiments, especially the ones based on short-interfering RNA (siRNA) technology became increasingly popular over the past years. For such knock-down/screening purposes, different companies offer sets of oligos/reagents targeting the whole genome or a subset of it for various organisms. Obviously, the sequence (and structure) of the corresponding oligos is a key factor in obtaining reliable results in these large-scale studies and the companies use a variety of (often not fully public) algorithms to design them. Nevertheless, as the genome annotations are still continuously changing, oligos may become obsolete, so siRNA reagents should be periodically re-annotated according to the latest version of the sequence database (which of course has serious consequences also on the interpretation of the screening results). In our article, we would like to introduce a new software/database tool, the RNAiAtlas. It has been created for exploration, analysis and distribution of large scale RNAi libraries (currently limited to the human genome) with their latest annotation (including former history) but in addition it contains also specific on-target analysis results (design quality, side effects, off-targets). Database URL: http://www.rnaiatlas.ethz.ch.
Figures
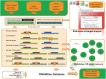
Figure 1
Overview of RNAiAtlas database content. The re-annotation of commercially available human genome-wide siRNA (three human, genome-wide) libraries with different NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq) were collected in a database. On-target analysis calculations were performed using a dedicated design/evaluation pipeline to quantitatively assess the specificity of the constructs. Interactive network visualization allows the inspection of the off-target network between an siRNA and its target genes.
Figure 2
Example of selected siRNAs and their on-target analysis results are shown from Qiagen, Ambion and Dharmacon libraries, analyzed with RefSeq 2012. The columns can be classified into five functional groups that contain information about: original target, transcripts information, off-targets, wrong predicted and on-target. The table illustrates all possible on-target analysis results that are incorporated into RNAiAtlas. The table data is generated off-line and fed into RNAiAtlas.
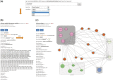
Figure 3
Example of a database search for gene LOC285697. (a) The search page allows for gene, siRNA sequence or siRNA ID. The search page provides a combo-box with selection possibility for the year of RefSeq database used for on-target analysis. Here LOC285697 as gene symbol was queried with the selected year of 2011 for RefSeq annotation. (b) Results card showing siRNAs, annotation for the queried gene and specificity parameters. (c) An example of the off-target network view in RNAiAtlas, centered on the query siRNA AGGCAGCAACAAGGATGGGAT (SI00495747) of gene ‘LOC285697’ from Qiagen human genome wide library (Network URL:
http://rnaiatlas.ethz.ch/index/network/gene/LOC285697/library/3
). Nodes in square (eg. gray squares) are individual siRNAs of same gene. Each node may have connection to off-target gene (represented again by three or four siRNAs). If off-targets genes are not existing in RNAiAtlas (e.g. pseudogenes, discontinued genes) siRNAs are having one edge to off-target gene (orange nodes).
Similar articles
- Annotation and specificity of existing genome-wide small interfering RNA libraries.
Kozak K. Kozak K. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Feb;23(1):71-80. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0387. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 23276255 - E-RNAi: a web application for the multi-species design of RNAi reagents--2010 update.
Horn T, Boutros M. Horn T, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(Web Server issue):W332-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq317. Epub 2010 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20444868 Free PMC article. - RFRCDB-siRNA: improved design of siRNAs by random forest regression model coupled with database searching.
Jiang P, Wu H, Da Y, Sang F, Wei J, Sun X, Lu Z. Jiang P, et al. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2007 Sep;87(3):230-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2007. PMID: 17644215 - Bioinformatics tools for achieving better gene silencing in plants.
Ahmed F, Dai X, Zhao PX. Ahmed F, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1287:43-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2453-0_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25740355 Review. - RNAi screening: new approaches, understandings, and organisms.
Mohr SE, Perrimon N. Mohr SE, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Mar-Apr;3(2):145-58. doi: 10.1002/wrna.110. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 21953743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- ASPsiRNA: A Resource of ASP-siRNAs Having Therapeutic Potential for Human Genetic Disorders and Algorithm for Prediction of Their Inhibitory Efficacy.
Monga I, Qureshi A, Thakur N, Gupta AK, Kumar M. Monga I, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Sep 7;7(9):2931-2943. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.044024. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28696921 Free PMC article. - The genomic and transcriptomic landscape of a HeLa cell line.
Landry JJ, Pyl PT, Rausch T, Zichner T, Tekkedil MM, Stütz AM, Jauch A, Aiyar RS, Pau G, Delhomme N, Gagneur J, Korbel JO, Huber W, Steinmetz LM. Landry JJ, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Aug 7;3(8):1213-24. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.005777. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23550136 Free PMC article.
References
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
- Hannon GJ. RNA: A Guide to Gene Silencing. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2003.
- Zuck P, Murray EM, Stec E, et al. A cell-based β-lactamase reporter gene assay for the identification of inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication. Anal. Biochem. 2004;334:344–355. - PubMed
- MacKeigan JP, Murphy LO, Blenis J. Sensitized RNAi screen of human kinases and phosphatases identifies new regulators of apoptosis and chemoresistance. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005;7:591–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous