Microglia and drug-induced plasticity in reward-related neuronal circuits - PubMed (original) (raw)
Microglia and drug-induced plasticity in reward-related neuronal circuits
Krisztina J Kovács. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
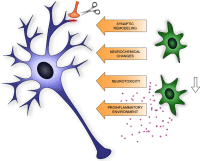
Schematic summary of microglia (shown in green) – neuron (shown in blue) interaction relevant to neuroplasticity in addiction.
Similar articles
- Depletion of microglia in developing cortical circuits reveals its critical role in glutamatergic synapse development, functional connectivity, and critical period plasticity.
Ma X, Chen K, Cui Y, Huang G, Nehme A, Zhang L, Li H, Wei J, Liong K, Liu Q, Shi L, Wu J, Qiu S. Ma X, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2020 Oct;98(10):1968-1986. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24641. Epub 2020 Jun 28. J Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 32594561 - Glial neuroimmune signaling in opioid reward.
Zhang H, Largent-Milnes TM, Vanderah TW. Zhang H, et al. Brain Res Bull. 2020 Feb;155:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 31790721 Free PMC article. Review. - Microglia: actively surveying and shaping neuronal circuit structure and function.
Wake H, Moorhouse AJ, Miyamoto A, Nabekura J. Wake H, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2013 Apr;36(4):209-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23260014 Review. - Chronic fluoxetine treatment impairs motivation and reward learning by affecting neuronal plasticity in the central amygdala.
Puścian A, Winiarski M, Łęski S, Charzewski Ł, Nikolaev T, Borowska J, Dzik JM, Bijata M, Lipp HP, Dziembowska M, Knapska E. Puścian A, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;178(3):672-688. doi: 10.1111/bph.15319. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33171527 - Synaptic plasticity in drug reward circuitry.
Winder DG, Egli RE, Schramm NL, Matthews RT. Winder DG, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2002 Nov;2(7):667-76. doi: 10.2174/1566524023361961. Curr Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12420805 Review.
Cited by
- Is biological aging accelerated in drug addiction?
Bachi K, Sierra S, Volkow ND, Goldstein RZ, Alia-Klein N. Bachi K, et al. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017 Feb;13:34-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.09.007. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017. PMID: 27774503 Free PMC article. - Administration of the Glial Condition Medium in the Nucleus Accumbens Prolong Maintenance and Intensify Reinstatement of Morphine-Seeking Behavior.
Arezoomandan R, Khodagholi F, Haghparast A. Arezoomandan R, et al. Neurochem Res. 2016 Apr;41(4):855-68. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1762-3. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26547198 - The pharmacology of neurokinin receptors in addiction: prospects for therapy.
Sandweiss AJ, Vanderah TW. Sandweiss AJ, et al. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2015 Sep 7;6:93-102. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S70350. eCollection 2015. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 26379454 Free PMC article. Review. - Mitigation of cocaine-mediated mitochondrial damage, defective mitophagy and microglial activation by superoxide dismutase mimetics.
Thangaraj A, Periyasamy P, Guo ML, Chivero ET, Callen S, Buch S. Thangaraj A, et al. Autophagy. 2020 Feb;16(2):289-312. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1607686. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 30990365 Free PMC article. - Cocaine-mediated activation of microglia and microglial MeCP2 and BDNF production.
Cotto B, Li H, Tuma RF, Ward SJ, Langford D. Cotto B, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Sep;117:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 30. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29859319 Free PMC article.
References
- Bruce-Keller A. J., Turchan-Cholewo J., Smart E. J., Geurin T., Chauhan A., Reid R., Xu R., Nath A., Knapp P. E., Hauser K. F. (2008). Morphine causes rapid increases in glial activation and neuronal injury in the striatum of inducible HIV-1 Tat transgenic mice. Glia 56, 1414–142710.1002/glia.20708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources