Brief report: a phase II "window-of-opportunity" frontline study of the MTOR inhibitor, temsirolimus given as a single agent in patients with advanced NSCLC, an NCCTG study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31824de0d6.
Julian R Molina, Sumithra J Mandrekar, Katie Allen-Ziegler, Kendrith M Rowland, Nicholas F Reuter, Ronnie F Luyun, Grace K Dy, Randolph S Marks, Steven E Schild, James R Jett, Alex A Adjei
Affiliations
- PMID: 22722792
- PMCID: PMC5740874
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31824de0d6
Clinical Trial
Brief report: a phase II "window-of-opportunity" frontline study of the MTOR inhibitor, temsirolimus given as a single agent in patients with advanced NSCLC, an NCCTG study
Thanyanan Reungwetwattana et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2012 May.
Abstract
Background: In an effort to evaluate the single agent activity of temsirolimus in previously untreated non-small-cell lung cancer, the North Central Cancer Treatment Group undertook a frontline "window-of-opportunity" study.
Methods: Patients received 25 mg of temsirolimus administered intravenously as a weekly 30 minute infusion, on a 4-week cycle. Based on a two-stage Fleming design, the treatment would be promising if at least four of the first 25 evaluable patients in stage I or at least six of the 50 evaluable patients at the end of stage II have a confirmed response. Fresh tumor biopsies were obtained to evaluate predictive markers of temsirolimus activity.
Results: A total of 55 patients were enrolled with 52 patients being evaluable. The median age was 64 years. Adverse events (grade 3/4) occurring in 33 patients included dyspnea (12%), fatigue (10%), hyperglycemia (8%), hypoxia (8%), nausea (8%), and rash/desquamation (6%). The clinical benefit rate was 35% with four patients achieving a confirmed partial response and 14 patients with stable disease for 8 weeks or more. The 24-week progression-free survival rate was 25%. Median progression-free survival and overall survival were 2.3 and 6.6 months, respectively. Expression of p70s6 kinase, phospho-p70s6 kinase, Akt, phospho-Akt, and phosphatase and tensin homolog mutation did not correlate with clinical outcome.
Conclusions: Temsirolimus given as a single agent in frontline therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer was tolerable and demonstrated clinical benefit but did not meet the primary objective in this study. Patient selection will be needed to enhance the efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
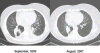
FIGURE 1
Computed tomography chest showed partial response during the treatment of one of the participating patients.
FIGURE 2
Kaplan-Meier survival curve. CI, confidence interval.
FIGURE 3
Immunohistochemistry staining of p70s6kinase phosphorylation in pretreatment tumor samples.
Similar articles
- Potential histologic and molecular predictors of response to temsirolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Cho D, Signoretti S, Dabora S, Regan M, Seeley A, Mariotti M, Youmans A, Polivy A, Mandato L, McDermott D, Stanbridge E, Atkins M. Cho D, et al. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2007 Sep;5(6):379-85. doi: 10.3816/CGC.2007.n.020. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17956710 - Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in advanced pancreatic cancer: results of two phase II studies.
Javle MM, Shroff RT, Xiong H, Varadhachary GA, Fogelman D, Reddy SA, Davis D, Zhang Y, Wolff RA, Abbruzzese JL. Javle MM, et al. BMC Cancer. 2010 Jul 14;10:368. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-368. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20630061 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase II study of temsirolimus (CCI-779) in women with recurrent, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic carcinoma of the cervix. A trial of the NCIC Clinical Trials Group (NCIC CTG IND 199).
Tinker AV, Ellard S, Welch S, Moens F, Allo G, Tsao MS, Squire J, Tu D, Eisenhauer EA, MacKay H. Tinker AV, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2013 Aug;130(2):269-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 11. Gynecol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23672928 Clinical Trial. - Phase II trial of temsirolimus (CCI-779) in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study.
Galanis E, Buckner JC, Maurer MJ, Kreisberg JI, Ballman K, Boni J, Peralba JM, Jenkins RB, Dakhil SR, Morton RF, Jaeckle KA, Scheithauer BW, Dancey J, Hidalgo M, Walsh DJ; North Central Cancer Treatment Group. Galanis E, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Aug 10;23(23):5294-304. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.23.622. Epub 2005 Jul 5. J Clin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15998902 Clinical Trial. - Temsirolimus, an mTOR inhibitor for treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Malizzia LJ, Hsu A. Malizzia LJ, et al. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2008 Aug;12(4):639-46. doi: 10.1188/08.CJON.639-646. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18676330 Review.
Cited by
- The prognostic role of mTOR and p-mTOR for survival in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Li L, Liu D, Qiu ZX, Zhao S, Zhang L, Li WM. Li L, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0116771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116771. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25680114 Free PMC article. Review. - Antitumor activity and safety of sirolimus for solid tumors with PIK3CA mutations: A multicenter, open-label, prospective single-arm study (KM 02-01, KCSG UN17-16).
Byeon S, Kang MJ, Choi YJ, Kim YJ, Kim M, Yun J, Yi SY, Kim JY, Kim ST, Lee J. Byeon S, et al. Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3222-3230. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.04.07. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117688 Free PMC article. - Metformin reverses multidrug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel‑7402/5‑fluorouracil cells.
Ling S, Tian Y, Zhang H, Jia K, Feng T, Sun D, Gao Z, Xu F, Hou Z, Li Y, Wang L. Ling S, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2014 Dec;10(6):2891-7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2614. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25310259 Free PMC article. - PTEN in Lung Cancer: Dealing with the Problem, Building on New Knowledge and Turning the Game Around.
Gkountakos A, Sartori G, Falcone I, Piro G, Ciuffreda L, Carbone C, Tortora G, Scarpa A, Bria E, Milella M, Rosell R, Corbo V, Pilotto S. Gkountakos A, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 9;11(8):1141. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081141. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31404976 Free PMC article. Review. - Dual Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway and Role of Autophagy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.
Jeong EH, Choi HS, Lee TG, Kim HR, Kim CH. Jeong EH, et al. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2012 Apr;72(4):343-51. doi: 10.4046/trd.2012.72.4.343. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2012. PMID: 23227075 Free PMC article.
References
- Scagliotti GV, De Marinis F, Rinaldi M, et al. Italian Lung Cancer Project Phase III randomized trial comparing three platinum-based doublets in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4285–4291. - PubMed
- Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, et al. SATURN investigators Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:521–529. - PubMed
- Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C, et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2009;374:1432–1440. - PubMed
- Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Link W, Leal JF. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;8:187–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous