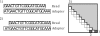AdapterRemoval: easy cleaning of next-generation sequencing reads - PubMed (original) (raw)
AdapterRemoval: easy cleaning of next-generation sequencing reads
Stinus Lindgreen. BMC Res Notes. 2012.
Abstract
Background: With the advent of next-generation sequencing there is an increased demand for tools to pre-process and handle the vast amounts of data generated. One recurring problem is adapter contamination in the reads, i.e. the partial or complete sequencing of adapter sequences. These adapter sequences have to be removed as they can hinder correct mapping of the reads and influence SNP calling and other downstream analyses.
Findings: We present a tool called AdapterRemoval which is able to pre-process both single and paired-end data. The program locates and removes adapter residues from the reads, it is able to combine paired reads if they overlap, and it can optionally trim low-quality nucleotides. Furthermore, it can look for adapter sequence in both the 5' and 3' ends of the reads. This is a flexible tool that can be tuned to accommodate different experimental settings and sequencing platforms producing FASTQ files. AdapterRemoval is shown to be good at trimming adapters from both single-end and paired-end data.
Conclusions: AdapterRemoval is a comprehensive tool for analyzing next-generation sequencing data. It exhibits good performance both in terms of sensitivity and specificity. AdapterRemoval has already been used in various large projects and it is possible to extend it further to accommodate application-specific biases in the data.
Figures
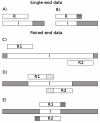
Figure 1
Illustration of different constructs and the reads produced. Single-end data on top, paired-end below. Inserts are denoted I, single-end reads R and paired-end reads _R_1 and _R_2. Read length denoted L R, insert length denoted L I. A) L I ≥ L R: No adapter contamination. B) L I < L R: adapter contamination occurs in 3’ end. C) L I ≥ 2· L R: No adapter contamination and no overlap between reads. D) L R < L I < 2 · L R: No adapter contamination but the two reads overlap. E) L I < L R: adapter contamination in 3’ ends of both reads, overlap between 5’ ends of reads. This information can be used to perform the pairwise alignment needed (after reverse complementing mate 2 from the pair) to locate adapter contamination and/or overlap between reads
Figure 2
The need for shifting the alignment due to missing nucleotides. If the read is missing a few nucleotides in the 5’ end, the proper alignment will not be recoverable if the procedure stops at the first position. As shown in 1), this leads to multiple mismatches and possibly missed adapter contamination. If the alignment is shifted by S nucleotides as shown in 2), the correct alignment can be found. The dynamic programming matrix in 3) shows which entries in the matrix leads to the two solutions shown here. The light grey part is the upper half of the matrix that is calculated by default; the two dark grey entries illustrate the two alignments shown in 1) and 2)
Similar articles
- AdapterRemoval v2: rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging.
Schubert M, Lindgreen S, Orlando L. Schubert M, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2016 Feb 12;9:88. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-1900-2. BMC Res Notes. 2016. PMID: 26868221 Free PMC article. - Sequence-matching adapter trimmers generate consistent quality and assembly metrics for Illumina sequencing of RNA viruses.
Nabakooza G, Wagner DD, Momin N, Marine RL, Weldon WC, Oberste MS. Nabakooza G, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2024 Oct 14;17(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s13104-024-06951-0. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 39402647 Free PMC article. - Skewer: a fast and accurate adapter trimmer for next-generation sequencing paired-end reads.
Jiang H, Lei R, Ding SW, Zhu S. Jiang H, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Jun 12;15:182. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-182. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24925680 Free PMC article. - Btrim: a fast, lightweight adapter and quality trimming program for next-generation sequencing technologies.
Kong Y. Kong Y. Genomics. 2011 Aug;98(2):152-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.05.009. Epub 2011 May 30. Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21651976 - MiSeq: A Next Generation Sequencing Platform for Genomic Analysis.
Ravi RK, Walton K, Khosroheidari M. Ravi RK, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1706:223-232. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423801 Review.
Cited by
- Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella oxytoca transmission linked to preoperative shaving in emergency neurosurgery, tracked by rapid detection via chromogenic medium and whole genome sequencing.
Jiang YL, Lyu YY, Liu LL, Li ZP, Liu D, Tai JH, Hu XQ, Zhang WH, Chu WW, Zhao X, Huang W, Wu YL. Jiang YL, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 17;14:1464411. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1464411. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39483120 Free PMC article. - Massively parallel binding assay (MPBA) reveals limited transcription factor binding cooperativity, challenging models of specificity.
Jana Lang T, Brodsky S, Manadre W, Vidavski M, Valinsky G, Mindel V, Ilan G, Carmi M, Jonas F, Barkai N. Jana Lang T, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Nov 11;52(20):12227-12243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae846. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39413205 Free PMC article. - In vivo treatment with a non-aromatizable androgen rapidly alters the ovarian transcriptome of previtellogenic secondary growth coho salmon (Onchorhynchus kisutch).
Monson C, Goetz G, Forsgren K, Swanson P, Young G. Monson C, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Oct 9;19(10):e0311628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311628. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39383164 Free PMC article. - Female sex bias in Iberian megalithic societies through bioarchaeology, aDNA and proteomics.
Díaz-Zorita Bonilla M, Jiménez Aranda G, Sánchez Romero M, Fregel R, Rebay-Salisbury K, Kanz F, Vílchez Suárez M, Robles Carrasco S, Becerra Fuello P, Ordónez AC, Wolf M, González Serrano J, Milesi García L. Díaz-Zorita Bonilla M, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 23;14(1):21818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72148-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39313501 Free PMC article. - Long genetic and social isolation in Neanderthals before their extinction.
Slimak L, Vimala T, Seguin-Orlando A, Metz L, Zanolli C, Joannes-Boyau R, Frouin M, Arnold LJ, Demuro M, Devièse T, Comeskey D, Buckley M, Camus H, Muth X, Lewis JE, Bocherens H, Yvorra P, Tenailleau C, Duployer B, Coqueugniot H, Dutour O, Higham T, Sikora M. Slimak L, et al. Cell Genom. 2024 Sep 11;4(9):100593. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100593. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 39265525 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources