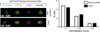Optimized protocol for the isolation of spleen-resident murine neutrophils - PubMed (original) (raw)
Optimized protocol for the isolation of spleen-resident murine neutrophils
Christine M Coquery et al. Cytometry A. 2012 Sep.
Abstract
Neutrophils are an important cellular component of the innate immune system that provides immediate protection to the host from infection. Neutrophil infiltration into inflamed peripheral tissues during infection is beneficial for immunity through phagocytosis of microbes, the release of antimicrobial factors, and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Recent reports further suggest that spleen-infiltrating neutrophils play a role in the adaptive immune response by providing survival signals to B cells. However, neutrophils may have detrimental effects on immunity in inflammatory diseases where their recruitment to lymphoid tissues and activation occur abnormally. To determine the contribution of neutrophils that reside in secondary lymphoid tissues to adaptive immunity, direct evaluation of the functional properties of tissue-resident neutrophils is required. We have developed a modified magnetic bead isolation approach for purifying neutrophils from inflamed spleens of autoimmune-prone mice by negative selection. Using this approach, we yielded neutrophils with greater than 90% purity without compromising cell viability. Equally important, the isolation procedure had little effect on the activation of neutrophils and did not impair phagocytic function. Thus, isolation of spleen-resident neutrophils by this optimized approach could be useful for interrogating the functional role of murine neutrophils in normal and abnormal immune responses.
Copyright © 2012 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures
Figure 1
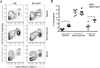
B6.Fas_lpr_/J mice have increased percentages of circulating and spleen-resident neutrophils. Single cell suspensions from spleens, blood, and bone marrow of age-matched B6 and B6.Fas_lpr_/J mice were analyzed for the percentage of CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils by flow cytometry. (A) Representative contour plots demonstrating that the frequency of neutrophils is higher in spleen and blood samples from B6.Fas_lpr_/J mice are shown. (B) Data from 5 to 7 individual mice are shown. Student’s t -test was performed on the indicated groups. *P < 0.05 compared to B6.
Figure 2
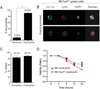
Isolation of splenic neutrophils using the OAC protocol generates a pure neutrophil population with limited cell death. Spleens were isolated from 5-month-old B6.Fas_lpr_/J and B6 mice. Single cell suspensions were analyzed before (pre-enrich) and after (post-enrich) isolation of neutrophils using the OAC method. (A) Data from four separate animals of the percentages of splenic neutrophils are shown. **P < 0.0005 compared to the pre-enriched group. (B) Enriched CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils were analyzed for multilobulated nuclei on the ImageStreamX cytometer. Samples were stained with CD11b-FITC, Ly6G-PECy7, and DAPI to stain nuclei. Original magnification 60×. Data shown are from 500 images and are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Neutrophils from samples shown in panel (A) were analyzed for cell viability by flow cytometry. Data from four separate experiments of the percentages of viable splenic neutrophils are shown. (D) Enriched neutrophils were analyzed for cell viability over a period of 18 h using the Live/Dead Aqua discriminator by flow cytometry. Data are presented as a viability ratio that was calculated by dividing the percentage of viable neutrophils at the outset of the experiment (0 h) by the percentage of viable neutrophils at each of the indicated time points. Data from four independent experiments are shown. *P < 0.05 compared to B6 neutrophils at 18 h.
Figure 3
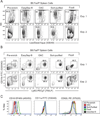
Comparison of the OAC method to previously established neutrophil isolation procedures. Neutrophils were isolated from 5-month-old B6.Fas_lpr_/J mice using the indicated method. Cell viability (A) and cell purity (B) were measured before and after each isolation protocol. Data presented from two independent experiments. (C) Expression of the activation markers CD18, CD11a, and CD62L on isolated neutrophils 4 h after purification. One representative experiment from two independent experiments is shown.
Figure 4
Isolation of cells by the OAC and sort-purification methods result in similar phagocytic function. Neutrophils were isolated from 5-month-old B6.Fas_lpr_/J mice using the OAC protocol or by sort-purification. Isolated neutrophils were incubated in the presence of fluorescently labeled S. aureus particles with prior opsonization for 2 h. Engulfment of opsonized S. aureus by neutrophils was confirmed by high-resolution microscopy and flow cytometry using ImageStreamX technology. One representative image from more than 250 images taken from two separate animals for each purification method is shown. Uptake of S. aureus for each neutrophil was calculated as an internalization score (I.S.). The I.S. from 50 randomly selected neutrophils for each isolation method is shown in the right panel, demonstrating that the uptake of particles by neutrophils is equivalent between the two isolation methods.
Similar articles
- A Comparative Study of Different Protocols for Isolation of Murine Neutrophils from Bone Marrow and Spleen.
Sounbuli K, Alekseeva LA, Markov OV, Mironova NL. Sounbuli K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17273. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417273. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139101 Free PMC article. - CD36 Is Essential for Regulation of the Host Innate Response to Staphylococcus aureus α-Toxin-Mediated Dermonecrosis.
Castleman MJ, Febbraio M, Hall PR. Castleman MJ, et al. J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):2294-302. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500500. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26223653 Free PMC article. - Marginal Zone B Cells Assist With Neutrophil Accumulation to Fight Against Systemic Staphylococcus aureus Infection.
Lo LW, Chang CW, Chiang MF, Lin IY, Lin KI. Lo LW, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 May 10;12:636818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636818. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34040603 Free PMC article. - Epic Immune Battles of History: Neutrophils vs. Staphylococcus aureus.
Guerra FE, Borgogna TR, Patel DM, Sward EW, Voyich JM. Guerra FE, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00286. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713774 Free PMC article. Review. - The Regulatory Effects of Interleukin-4 Receptor Signaling on Neutrophils in Type 2 Immune Responses.
Egholm C, Heeb LEM, Impellizzieri D, Boyman O. Egholm C, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 24;10:2507. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02507. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31708926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A protocol for rapid monocyte isolation and generation of singular human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.
Chometon TQ, Siqueira MDS, Sant Anna JC, Almeida MR, Gandini M, Martins de Almeida Nogueira AC, Antas PRZ. Chometon TQ, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0231132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231132. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271804 Free PMC article. - Changes in the Gut Microbiome Contribute to the Development of Behcet's Disease via Adjuvant Effects.
Wang Q, Yi S, Su G, Du Z, Pan S, Huang X, Cao Q, Yuan G, Kijlstra A, Yang P. Wang Q, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 8;9:716760. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.716760. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568329 Free PMC article. - A Comparative Study of Different Protocols for Isolation of Murine Neutrophils from Bone Marrow and Spleen.
Sounbuli K, Alekseeva LA, Markov OV, Mironova NL. Sounbuli K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17273. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417273. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139101 Free PMC article. - Dissociation of skeletal muscle for flow cytometric characterization of immune cells in macaques.
Liang F, Ploquin A, Hernández JD, Fausther-Bovendo H, Lindgren G, Stanley D, Martinez AS, Brenchley JM, Koup RA, Loré K, Sullivan NJ. Liang F, et al. J Immunol Methods. 2015 Oct;425:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jun 20. J Immunol Methods. 2015. PMID: 26099800 Free PMC article. - scTree: An R package to generate antibody-compatible classifiers from single-cell sequencing data.
Paez JS, Wendt MK, Lanman NA. Paez JS, et al. J Open Source Softw. 2020;5(48):2061. doi: 10.21105/joss.02061. Epub 2020 Apr 26. J Open Source Softw. 2020. PMID: 32954206 Free PMC article.
References
- Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: Challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:173–182. - PubMed
- Pelletier M, Maggi L, Micheletti A, Lazzeri E, Tamassia N, Costantini C, Cosmi L, Lunardi C, Annunziato F, Romagnani S, et al. Evidence for a cross-talk between human neutrophils and Th17 cells. Blood. 2010;115:335–343. - PubMed
- Scapini P, Bazzoni F, Cassatella MA. Regulation of B-cell-activating factor (BAFF)/B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) expression in human neutrophils. Immunol Lett. 2008;116:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous