imDEV: a graphical user interface to R multivariate analysis tools in Microsoft Excel - PubMed (original) (raw)
imDEV: a graphical user interface to R multivariate analysis tools in Microsoft Excel
Dmitry Grapov et al. Bioinformatics. 2012.
Abstract
Interactive modules for Data Exploration and Visualization (imDEV) is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet embedded application providing an integrated environment for the analysis of omics data through a user-friendly interface. Individual modules enables interactive and dynamic analyses of large data by interfacing R's multivariate statistics and highly customizable visualizations with the spreadsheet environment, aiding robust inferences and generating information-rich data visualizations. This tool provides access to multiple comparisons with false discovery correction, hierarchical clustering, principal and independent component analyses, partial least squares regression and discriminant analysis, through an intuitive interface for creating high-quality two- and a three-dimensional visualizations including scatter plot matrices, distribution plots, dendrograms, heat maps, biplots, trellis biplots and correlation networks.
Availability and implementation: Freely available for download at http://sourceforge.net/projects/imdev/. Implemented in R and VBA and supported by Microsoft Excel (2003, 2007 and 2010).
Figures
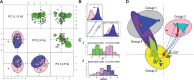
Fig. 1
Analysis of the relationship between circulating metabolite levels and systolic blood pressure (sBP). Exploratory PCA was used to identify gender-specific differences in metabolite concentrations and sBP. A PLS model was developed for the prediction of sBP given gender-adjusted metabolite concentrations. Network analysis of the PLS model parameters was used to highlight a previously known relationship between sBP and GGT, and identified a novel group of related metabolites (Group 2) that are negatively correlated with both sBP and GGT. (A) PCA scores and loadings trellis-plots. Scores (bottom left) where size indicates sBP, while color and shape indicate gender (pink squares, female; blue diamonds, male), with an outlier highlighted in red. Loading (top right) sizes indicate _P_-values from Mann–Whitney U-test for gender-specific differences in metabolite concentrations. (B) Variable distribution and scatter plot matrix displaying the effect of covariate adjustment for gender on a representative variable. (C) Comparison of gender-adjusted sBP PLS model Q2 (C1) and RMSEP (C2) statistic distributions to their respective permuted null distributions. (D) A multi-dimensionally scaled PLS model correlation network visualizing correlations (Spearman's rho, P < 0.05) displayed by colored edges (orange, positive; blue, negative) between sBP (red diamond) and model parameters (triangles). Triangle (i.e. network vertex) characteristics encode PLS coefficient magnitude (size) and sign (upward, positive; inverted, negative). Major groups of correlated variables, defined by a hierarchal cluster analysis, are displayed by ellipses, and biologically related classes of metabolites are shown using similar vertex colors and polygons
Similar articles
- A Microsoft-Excel-based tool for running and critically appraising network meta-analyses--an overview and application of NetMetaXL.
Brown S, Hutton B, Clifford T, Coyle D, Grima D, Wells G, Cameron C. Brown S, et al. Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 29;3:110. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-3-110. Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25267416 Free PMC article. - mcaGUI: microbial community analysis R-Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Copeland WK, Krishnan V, Beck D, Settles M, Foster JA, Cho KC, Day M, Hickey R, Schütte UM, Zhou X, Williams CJ, Forney LJ, Abdo Z. Copeland WK, et al. Bioinformatics. 2012 Aug 15;28(16):2198-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts338. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22692220 Free PMC article. - ClustVis: a web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap.
Metsalu T, Vilo J. Metsalu T, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W566-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv468. Epub 2015 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25969447 Free PMC article. - Insufficient evidence for interactive or animated graphics for communicating probability.
Ancker JS, Benda NC, Zikmund-Fisher BJ. Ancker JS, et al. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024 Nov 1;31(11):2760-2765. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae123. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38904366 Free PMC article. Review. - From a glimpse into the key aspects of calibration and correlation to their practical considerations in chemical analysis.
Stalikas C, Sakkas V. Stalikas C, et al. Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Jan 9;191(2):81. doi: 10.1007/s00604-023-06157-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38191690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Impact of post-collection freezing delay on the reliability of serum metabolomics in samples reflecting the California mid-term pregnancy biobank.
La Frano MR, Carmichael SL, Ma C, Hardley M, Shen T, Wong R, Rosales L, Borkowski K, Pedersen TL, Shaw GM, Stevenson DK, Fiehn O, Newman JW. La Frano MR, et al. Metabolomics. 2018 Nov 15;14(11):151. doi: 10.1007/s11306-018-1450-9. Metabolomics. 2018. PMID: 30830400 - Oleocanthal-rich extra virgin olive oil demonstrates acute anti-platelet effects in healthy men in a randomized trial.
Agrawal K, Melliou E, Li X, Pedersen TL, Wang SC, Magiatis P, Newman JW, Holt RR. Agrawal K, et al. J Funct Foods. 2017 Sep;36:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.06.046. Epub 2017 Jul 3. J Funct Foods. 2017. PMID: 29904393 Free PMC article. - Review of Statistical Learning Methods in Integrated Omics Studies (An Integrated Information Science).
Zeng ISL, Lumley T. Zeng ISL, et al. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2018 Feb 20;12:1177932218759292. doi: 10.1177/1177932218759292. eCollection 2018. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2018. PMID: 29497285 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of stimulation technique, anatomical region, and time on human sweat lipid mediator profiles.
Agrawal K, Waller JD, Pedersen TL, Newman JW. Agrawal K, et al. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018 Jan;134:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018. PMID: 28942325 Free PMC article. - ExcelAutomat: a tool for systematic processing of files as applied to quantum chemical calculations.
Laloo JZA, Laloo N, Rhyman L, Ramasami P. Laloo JZA, et al. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2017 Jul;31(7):667-673. doi: 10.1007/s10822-017-0031-8. Epub 2017 Jun 17. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2017. PMID: 28624971
References
- Baier T, Neuwirth E. Excel :: COM :: R. Comput. Stat. 2007;22:91–108.
- Box GEP, Cox DR. An analysis of transformations. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. 1964;26:211–252.
- Castelo R, Roverato A. A robust procedure for Gaussian graphical model search from microarray data with p larger than n. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006;7:2621–2650.
- D'Agostino,R.B. and Stephens,M.A. (eds.) (1986) Goodness-of-Fit Techniques. Marcel Dekker, New York.
- De Jong S. SIMPLS: an alternative approach to partial least squares regression. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1993;18:251–263.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DK078328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008799/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK078328-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM008799/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States