Anti-hepatitis C virus activity and toxicity of type III phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase beta inhibitors - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2012 Oct;56(10):5149-56.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.00946-12. Epub 2012 Jul 23.
J Borawski, A Bose, C Capacci-Daniel, R Colvin, M Dennehy, J Ding, M Dobler, J Drumm, L A Gaither, J Gao, X Jiang, K Lin, U McKeever, X Puyang, P Raman, S Thohan, R Tommasi, K Wagner, X Xiong, T Zabawa, S Zhu, B Wiedmann
Affiliations
- PMID: 22825118
- PMCID: PMC3457382
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00946-12
Anti-hepatitis C virus activity and toxicity of type III phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase beta inhibitors
M J Lamarche et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Oct.
Abstract
Type III phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase beta (PI4KIIIβ) was previously implicated in hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication by small interfering RNA (siRNA) depletion and was therefore proposed as a novel cellular target for the treatment of hepatitis C. Medicinal chemistry efforts identified highly selective PI4KIIIβ inhibitors that potently inhibited the replication of genotype 1a and 1b HCV replicons and genotype 2a virus in vitro. Replicon cells required more than 5 weeks to reach low levels of 3- to 5-fold resistance, suggesting a high resistance barrier to these cellular targets. Extensive in vitro profiling of the compounds revealed a role of PI4KIIIβ in lymphocyte proliferation. Previously proposed functions of PI4KIIIβ in insulin secretion and the regulation of several ion channels were not perturbed with these inhibitors. Moreover, PI4KIIIβ inhibitors were not generally cytotoxic as demonstrated across hundreds of cell lines and primary cells. However, an unexpected antiproliferative effect in lymphocytes precluded their further development for the treatment of hepatitis C.
Figures
Fig 1
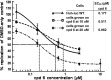
Incremental development of resistance to compound (cpd) 6 causes low EC50 shifts. Susceptibility curves were plotted and EC50s (means) calculated using XlFit from triplicate samples for the wild type (WT) and five replicas for the resistant cell lines.
Fig 2
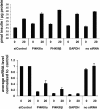
siRNA-mediated depletion of PI4KIIIβ has no effect on basal or glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in Min6 cells. The insulin levels were not significantly changed when the PI4KIIIβ mRNA concentration was reduced to 10 to 20%. The x axis values indicate the glucose concentration in mM and the siRNA targets. Shown are mean values of triplicates ± SEMs from a representative experiment.
Fig 3
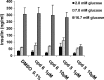
Inhibition of PI4KIIIβ does not change glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in INS-E1 cells. Compound 6, a potent PI4KIIIβ inhibitor, and compound 5, a structural analog lacking PI4KIIIβ activity, were used to treat INS-E1 cells stimulated to different degrees with glucose. Mean secreted insulin concentrations and SEMs were calculated from triplicate samples.
Fig 4
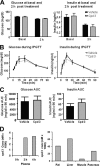
PI4KIIIβ inhibition does not affect insulin secretion or glucose metabolism in an in vivo glucose tolerance test in rats. Fasted rats (n = 8 per group) were given an oral dose of compound or vehicle at 2.5 h before an intraperitoneal injection of glucose. Blood was drawn from the tails to analyze glucose, insulin, and compound levels. (A and B) Glucose and insulin levels in compound- and vehicle-treated rats were measured at 0 h (basal) and 2 h (A) and at short time intervals (B). (C and D) The area under the curve (AUC) for glucose and insulin during the glucose tolerance test was calculated using integrated area of excursion above the baseline (C), and the compound concentration was estimated at 0, 2, and 4 h in plasma and at 4 h in tissues (D). Graphs and columns show mean values for 8 animals ± SEMs.
Fig 5
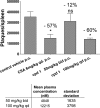
PI4KIIIβ inhibition over 4 days reduces the T-cell-mediated B-cell activation and antibody formation in response to an injection of sheep red blood cells into rats. Treatment of rats with 100 mg/kg over 4 days resulted in a 12 μM compound concentration in plasma 2 h after last dose and reduced the plaque-forming antibody titer per spleen to the same extent as the control compound cyclosporine (CSA). Plaques per spleen and compound concentrations in blood are mean values from 4 animals ± SEMs analyzed using Graph Pad Prism software. The decrease of antibody production is shown as the percentage of the value for the vehicle control above each treatment. The asterisk indicates a significant change and ns a nonsignificant change as determined by ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple-comparison test.
Similar articles
- PI4KIII inhibitor enviroxime impedes the replication of the hepatitis C virus by inhibiting PI3 kinases.
Delang L, Harak C, Benkheil M, Khan H, Leyssen P, Andrews M, Lohmann V, Neyts J. Delang L, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Dec 1;73(12):3375-3384. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky327. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30219827 - Class III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha and beta are novel host factor regulators of hepatitis C virus replication.
Borawski J, Troke P, Puyang X, Gibaja V, Zhao S, Mickanin C, Leighton-Davies J, Wilson CJ, Myer V, Cornellataracido I, Baryza J, Tallarico J, Joberty G, Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Bouwmeester T, Mathy JE, Lin K, Compton T, Labow M, Wiedmann B, Gaither LA. Borawski J, et al. J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):10058-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02418-08. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19605471 Free PMC article. - Metabolism of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα-dependent PI4P Is subverted by HCV and is targeted by a 4-anilino quinazoline with antiviral activity.
Bianco A, Reghellin V, Donnici L, Fenu S, Alvarez R, Baruffa C, Peri F, Pagani M, Abrignani S, Neddermann P, De Francesco R. Bianco A, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(3):e1002576. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002576. Epub 2012 Mar 8. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22412376 Free PMC article. - Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta is essential for replication of human rhinovirus and its inhibition causes a lethal phenotype in vivo.
Spickler C, Lippens J, Laberge MK, Desmeules S, Bellavance É, Garneau M, Guo T, Hucke O, Leyssen P, Neyts J, Vaillancourt FH, Décor A, O'Meara J, Franti M, Gauthier A. Spickler C, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jul;57(7):3358-68. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00303-13. Epub 2013 May 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23650168 Free PMC article. - 2-Alkyloxazoles as potent and selective PI4KIIIβ inhibitors demonstrating inhibition of HCV replication.
Keaney EP, Connolly M, Dobler M, Karki R, Honda A, Sokup S, Karur S, Britt S, Patnaik A, Raman P, Hamann LG, Wiedmann B, LaMarche MJ. Keaney EP, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Aug 15;24(16):3714-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.07.015. Epub 2014 Jul 12. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 25065492
Cited by
- Enterovirus A71 antivirals: Past, present, and future.
Wang J, Hu Y, Zheng M. Wang J, et al. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Apr;12(4):1542-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.017. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35847514 Free PMC article. - Phosphoinositides in the hepatitis C virus life cycle.
Bishé B, Syed G, Siddiqui A. Bishé B, et al. Viruses. 2012 Oct 19;4(10):2340-58. doi: 10.3390/v4102340. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23202467 Free PMC article. Review. - In silico molecular screening of bioactive natural compounds of rosemary essential oil and extracts for pharmacological potentials against rhinoviruses.
Singh D, Mittal N, Mittal P, Tiwari N, Khan SU, Ali MAM, Chaudhary AA, Siddiqui MH. Singh D, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 29;14(1):17426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68450-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39075176 Free PMC article. - Identification of a series of compounds with potent antiviral activity for the treatment of enterovirus infections.
MacLeod AM, Mitchell DR, Palmer NJ, Van de Poël H, Conrath K, Andrews M, Leyssen P, Neyts J. MacLeod AM, et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 8;4(7):585-9. doi: 10.1021/ml400095m. eCollection 2013 Jul 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24900715 Free PMC article. - Enterovirus Replication Organelles and Inhibitors of Their Formation.
Li X, Wang M, Cheng A, Wen X, Ou X, Mao S, Gao Q, Sun D, Jia R, Yang Q, Wu Y, Zhu D, Zhao X, Chen S, Liu M, Zhang S, Liu Y, Yu Y, Zhang L, Tian B, Pan L, Chen X. Li X, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1817. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01817. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ahn J, et al. 2004. Systematic identification of hepatocellular proteins in interacting with NS5A of the hepatitis C virus. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 37:741–748 - PubMed
- Balla A, Balla T. 2006. Phosphatidylinositol4-kinases: old enzymes with emerging functions. Trends Cell Biol. 16:351–361 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources