An unbiased analysis method to quantify mRNA localization reveals its correlation with cell motility - PubMed (original) (raw)
An unbiased analysis method to quantify mRNA localization reveals its correlation with cell motility
Hye Yoon Park et al. Cell Rep. 2012.
Abstract
Localization of mRNA is a critical mechanism used by a large fraction of transcripts to restrict its translation to specific cellular regions. Although current high-resolution imaging techniques provide ample information, the analysis methods for localization have either been qualitative or employed quantification in nonrandomly selected regions of interest. Here, we describe an analytical method for objective quantification of mRNA localization using a combination of two characteristics of its molecular distribution, polarization and dispersion. The validity of the method is demonstrated using single-molecule FISH images of budding yeast and fibroblasts. Live-cell analysis of endogenous β-actin mRNA in mouse fibroblasts reveals that mRNA polarization has a half-life of ~16 min and is cross-correlated with directed cell migration. This novel approach provides insights into the dynamic regulation of mRNA localization and its physiological roles.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
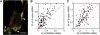
Figure 1. Quantification of ASH1 mRNA Distributions in Wild-Type and ΔSHE2 Budding Yeasts
(A) A schematic showing the polarization vector of mRNA distribution pointing from the centroid of the cell to the centroid of the single mRNA positions. (B) Overlay image of ASH1 mRNA molecules (magenta), and nuclei (blue) in a wild-type cell. ASH1 mRNAs localize to the daughter bud tip. Scale bar represents 1 μm. (C) Scatter plot of polarization index in x axis and dispersion index in y axis for wild-type cells. (D) Overlay image of ASH1 mRNA molecules, and nuclei in a ΔSHE2 cell. Deletion of She2p causes a complete delocalization of ASH1 transcripts. Scale bar represents 1 μm. (E) Scatter plot of polarization index versus dispersion index for ΔSHE2 cells. The red arrow heads indicate the data points for the cells shown in (B) and (D). See also Figure S1.
Figure 2. Comparison of GAPDH and β-Actin mRNA Distributions in Chicken Embryonic Fibroblasts
(A) FISH image of GAPDH mRNA (red), and β-actin mRNA (green). Scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) Scatter plot of polarization index for GAPDH mRNA in x axis and β-actin mRNA in y axis. (C) Scatter plot of dispersion index for GAPDH mRNA in x axis and β-actin mRNA in y axis. Red dashed lines indicate cells that have the same index for GAPDH and β-actin mRNA. See also Figure S2.
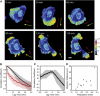
Figure 3. Localization of β-Actin mRNA in a Migrating Cell
(A) Time-lapse images of a mouse embryonic fibroblast. The color map shows the fluorescence intensity of MCP-GFP labeling endogenous β-actin transcripts divided by the intensity of red fluorescent cytoplasmic dye. Yellow arrows show the polarization vector of mRNA distribution, and red arrows show the protrusion vector of the cell. (B) Mean auto-correlation curves of the polarization vector (black) and the protrusion vector (red) (n = 11 cells). The shaded areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. (C) Mean cross-correlation curve of the polarization vector and the protrusion vector (black curve) and 95% confidence interval (gray area) for n = 11 cells. (D) Migration distance as a function of the time-average of the polarization index over 2 hr. The correlation coefficient between the polarization index and the migration distance is 0.75. See also Figure S3 and Movie S1.
Similar articles
- Single-molecule tracking of mRNA in living cells.
Yamagishi M, Shirasaki Y, Funatsu T. Yamagishi M, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;950:153-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-137-0_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23086875 - The physiological significance of beta -actin mRNA localization in determining cell polarity and directional motility.
Shestakova EA, Singer RH, Condeelis J. Shestakova EA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jun 19;98(13):7045-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121146098. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11416185 Free PMC article. - Quantification and real-time tracking of RNA in live cells using Sticky-flares.
Briley WE, Bondy MH, Randeria PS, Dupper TJ, Mirkin CA. Briley WE, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 4;112(31):9591-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1510581112. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26195734 Free PMC article. - Using fluorescent proteins to study mRNA trafficking in living cells.
Querido E, Chartrand P. Querido E, et al. Methods Cell Biol. 2008;85:273-92. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)85012-1. Methods Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18155467 Review. - Principles of mRNA transport in yeast.
Heym RG, Niessing D. Heym RG, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jun;69(11):1843-53. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0902-4. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22159587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression?
Bell JL, Wächter K, Mühleck B, Pazaitis N, Köhn M, Lederer M, Hüttelmaier S. Bell JL, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Aug;70(15):2657-75. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1186-z. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23069990 Free PMC article. Review. - Glutamate-induced RNA localization and translation in neurons.
Yoon YJ, Wu B, Buxbaum AR, Das S, Tsai A, English BP, Grimm JB, Lavis LD, Singer RH. Yoon YJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 1;113(44):E6877-E6886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614267113. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27791158 Free PMC article. - Targeted RNA editing: novel tools to study post-transcriptional regulation.
Xu W, Biswas J, Singer RH, Rosbash M. Xu W, et al. Mol Cell. 2022 Jan 20;82(2):389-403. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.10.010. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 34739873 Free PMC article. Review. - In the right place at the right time: visualizing and understanding mRNA localization.
Buxbaum AR, Haimovich G, Singer RH. Buxbaum AR, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;16(2):95-109. doi: 10.1038/nrm3918. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25549890 Free PMC article. Review. - Characterization of a Long Non-Coding RNA, the Antisense RNA of Na/K-ATPase α1 in Human Kidney Cells.
Fan X, Ashraf UM, Drummond CA, Shi H, Zhang X, Kumarasamy S, Tian J. Fan X, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 21;19(7):2123. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072123. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30037072 Free PMC article.
References
- Bertrand E, Chartrand P, Schaefer M, Shenoy SM, Singer RH, Long RM. Localization of ASH1 mRNA particles in living yeast. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:437–445. - PubMed
- Femino AM, Fay FS, Fogarty K, Singer RH. Visualization of single RNA transcripts in situ. Science. 1998;280:585–590. - PubMed
- Jeffery WR, Tomlinson CR, Brodeur RD. Localization of actin messenger RNA during early ascidian development. Dev. Biol. 1983;99:408–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 GM087122/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM057071/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32-GM087122/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM86217/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM57071/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM84364/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086217/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084364/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases