Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
Daniel W Foster. J Clin Invest. 2012 Jun.
Abstract
In the catabolic state with no food intake, the liver generates ketones by breaking down fatty acids. During the nocturnal fast or longer starvation periods, this protects the brain, which cannot oxidize fatty acids. In 1977, we published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that malonyl-CoA, the substrate of fatty acid synthesis, was also an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation. Subsequent experiments have borne out this finding and furthered our understanding of molecular metabolism.
Figures
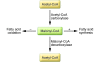
Figure 1. Regulation of malonyl-CoA determines the switch between fatty acid synthesis and oxidation.
Adapted with permission from the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (8).
References
- McGarry JD, Meier JM, Foster DW. The effects of starvation and refeeding on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in vivo and in the perfused rat liver. The relationship between fatty acid oxidation and esterification in the regulation of ketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1973;248(1):270–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources