Sustained low efficiency dialysis using a single-pass batch system in acute kidney injury - a randomized interventional trial: the REnal Replacement Therapy Study in Intensive Care Unit PatiEnts - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2012 Jul 27;16(4):R140.
doi: 10.1186/cc11445.
Markus A Weigand, Oskar Hoffmann, Ralf Dikow, Lars P Kihm, Jörg Seckinger, Nexhat Miftari, Matthias Schaier, Stefan Hofer, Caroline Haar, Peter P Nawroth, Martin Zeier, Eike Martin, Christian Morath
- PMID: 22839577
- PMCID: PMC3580725
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11445
Clinical Trial
Sustained low efficiency dialysis using a single-pass batch system in acute kidney injury - a randomized interventional trial: the REnal Replacement Therapy Study in Intensive Care Unit PatiEnts
Vedat Schwenger et al. Crit Care. 2012.
Erratum in
- Crit Care. 2012;16(5):451
Abstract
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with a high mortality of up to 60%. The mode of renal replacement therapy (intermittent versus continuous) has no impact on patient survival. Sustained low efficiency dialysis using a single-pass batch dialysis system (SLED-BD) has recently been introduced for the treatment of dialysis-dependent AKI. To date, however, only limited evidence is available in the comparison of SLED-BD versus continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH) in intensive care unit (ICU) patients with AKI.
Methods: Prospective, randomized, interventional, clinical study at a surgical intensive care unit of a university hospital. Between 1 April 2006 and 31 January 2009, 232 AKI patients who underwent renal replacement therapy (RRT) were randomized in the study. Follow-up was assessed until 30 August 2009. Patients were either assigned to 12-h SLED-BD or to 24-h predilutional CVVH. Both therapies were performed at a blood flow of 100 to 120 ml/min.
Results: 115 patients were treated with SLED-BD (total number of treatments n = 817) and 117 patients with CVVH (total number of treatments n = 877).The primary outcome measure, 90-day mortality, was similar between groups (SLED: 49.6% vs. CVVH: 55.6%, P = 0.43). Hemodynamic stability did not differ between SLED-BD and CVVH, whereas patients in the SLED-BD group had significantly fewer days of mechanical ventilation (17.7 ± 19.4 vs. 20.9 ± 19.8, P = 0.047) and fewer days in the ICU (19.6 ± 20.1 vs. 23.7 ± 21.9, P = 0.04). Patients treated with SLED needed fewer blood transfusions (1,375 ± 2,573 ml vs. 1,976 ± 3,316 ml, P = 0.02) and had a substantial reduction in nursing time spent for renal replacement therapy (P < 0.001) resulting in lower costs.
Conclusions: SLED-BD was associated with reduced nursing time and lower costs compared to CVVH at similar outcomes. In the light of limited health care resources, SLED-BD offers an attractive alternative for the treatment of AKI in ICU patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00322530.
Figures
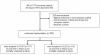
Figure 1
Enrolment, randomization and inclusion of study patients. Numbers of ICU patients enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to different treatment groups.
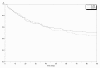
Figure 2
Probabilities of survival in sustained low efficiency dialysis (SLED) and continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH) treatment groups (Kaplan-Meier estimates) during the first 90 days. Mortality at 90 days was similar in ICU patients with acute kidney disease (AKI) treated with SLED-BD or with CVVH.
Comment in
- Concerns regarding use of one-tailed tests in the SLED-BD vs. CVVH trial.
Doig GS. Doig GS. Crit Care. 2012 Sep 14;16(5):448. doi: 10.1186/cc11490. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22979957 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Good-bye CRRT, here comes SLED? ... not so fast!
Joannidis M. Joannidis M. Crit Care. 2012 Nov 5;16(6):167. doi: 10.1186/cc11651. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 23148709 Free PMC article. - Sustained low-efficiency dialysis in surgical acute kidney injury - really useful?
Heringlake M, Schön J, Paarmann H. Heringlake M, et al. Crit Care. 2013 Jan 22;17(1):407. doi: 10.1186/cc11908. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23336336 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Authors' response.
Schwenger V, Weigand M, Morath C. Schwenger V, et al. Crit Care. 2013;17(1):407. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 25215363 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- The effect of continuous versus intermittent renal replacement therapy on the outcome of critically ill patients with acute renal failure (CONVINT): a prospective randomized controlled trial.
Schefold JC, von Haehling S, Pschowski R, Bender T, Berkmann C, Briegel S, Hasper D, Jörres A. Schefold JC, et al. Crit Care. 2014 Jan 10;18(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/cc13188. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24405734 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The hemodynamic effects during sustained low-efficiency dialysis versus continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for uremic patients with brain hemorrhage: a crossover study.
Wu VC, Huang TM, Shiao CC, Lai CF, Tsai PR, Wang WJ, Huang HY, Wang KC, Ko WJ, Wu KD; NSARF Group. Wu VC, et al. J Neurosurg. 2013 Nov;119(5):1288-95. doi: 10.3171/2013.4.JNS122102. Epub 2013 May 24. J Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23706048 Clinical Trial. - Sustained low-efficiency extended dialysis (SLED) with single-pass batch system in critically-ill patients with acute kidney injury (AKI).
Caires RA, Abdulkader RCRM, Costa E Silva VT, Ferreira GS, Burdmann EA, Yu L, Macedo E. Caires RA, et al. J Nephrol. 2016 Jun;29(3):401-409. doi: 10.1007/s40620-015-0224-y. Epub 2015 Aug 23. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26298845 - Acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit.
Kes P, Basić Jukić N. Kes P, et al. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010 Apr;10 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S8-12. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2010.2639. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20433438 Free PMC article. Review. - A single-pass batch dialysis system: an ideal dialysis method for the patient in intensive care with acute renal failure.
Fliser D, Kielstein JT. Fliser D, et al. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2004 Dec;10(6):483-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ccx.0000145101.58940.dc. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2004. PMID: 15616390 Review.
Cited by
- The effect of continuous versus intermittent renal replacement therapy on the outcome of critically ill patients with acute renal failure (CONVINT): a prospective randomized controlled trial.
Schefold JC, von Haehling S, Pschowski R, Bender T, Berkmann C, Briegel S, Hasper D, Jörres A. Schefold JC, et al. Crit Care. 2014 Jan 10;18(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/cc13188. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24405734 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Acute kidney injury in the ICU: from injury to recovery: reports from the 5th Paris International Conference.
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Mehta RL, Asfar P, Boisramé-Helms J, Darmon M, Diehl JL, Duranteau J, Hoste EAJ, Olivier JB, Legrand M, Lerolle N, Malbrain MLNG, Mårtensson J, Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Parienti JJ, Payen D, Perinel S, Peters E, Pickkers P, Rondeau E, Schetz M, Vinsonneau C, Wendon J, Zhang L, Laterre PF. Bellomo R, et al. Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Dec;7(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0260-y. Epub 2017 May 4. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28474317 Free PMC article. Review. - Debate: Intermittent Hemodialysis versus Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy in the Critically Ill Patient: The Argument for CKRT.
Bagshaw SM, Neyra JA, Tolwani AJ, Wald R. Bagshaw SM, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 May 1;18(5):647-660. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000056. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 39074305 Free PMC article. - Plasmadiafiltration ameliorating gut mucosal barrier dysfunction and improving survival in porcine sepsis models.
Li MX, Liu JF, Lu JD, Zhu Y, Kuang DW, Xiang JB, Sun P, Wang W, Xue J, Gu Y, Hao CM. Li MX, et al. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016 Dec;4(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40635-016-0105-2. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016. PMID: 27682607 Free PMC article. - Acute kidney injury in neurocritical care.
Husain-Syed F, Takeuchi T, Neyra JA, Ramírez-Guerrero G, Rosner MH, Ronco C, Tolwani AJ. Husain-Syed F, et al. Crit Care. 2023 Sep 3;27(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04632-1. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37661277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous