Lipid and lipid mediator profiling of human synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis patients by means of LC-MS/MS - PubMed (original) (raw)
Lipid and lipid mediator profiling of human synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis patients by means of LC-MS/MS
Martin Giera et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov.
Abstract
Human synovial fluid (SF) provides nutrition and lubrication to the articular cartilage. Particularly in arthritic diseases, SF is extensively accumulating in the synovial junction. During the last decade lipids have attracted considerable attention as their role in the development and resolution of diseases became increasingly recognized. Here, we describe a capillary LC-MS/MS screening platform that was used for the untargeted screening of lipids present in human SF of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Using this platform we give a detailed overview of the lipids and lipid-derived mediators present in the SF of RA patients. Almost 70 different lipid components from distinct lipid classes were identified and quantification was achieved for the lysophosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylcholine species. In addition, we describe a targeted LC-MS/MS lipid mediator metabolomics strategy for the detection, identification and quantification of maresin 1, lipoxin A(4) and resolvin D5 in SF from RA patients. Additionally, we present the identification of 5S,12S-diHETE as a major marker of lipoxygenase pathway interactions in the investigated SF samples. These results are the first to provide a comprehensive approach to the identification and profiling of lipids and lipid mediators present in SF and to describe the presence of key anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving lipid mediators identified in SF from RA patients.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
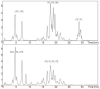
Figure 1
Base Peak Intensity chromatograms (BPI) of the ESI+ mode (above) and the ESI-mode (below), the abbreviations mark the elution windows of the different lipid classes, assignments are given in the ESI+, ESI- or both modes according to table 1
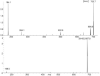
Figure 2
comparison of different MS2 extracted ion chromatograms (EIC), lower right corner mass spectrometric identification of PI(18:0/20:4) [46]
Figure 3
MS/MS spectra of SM(34:1) in the positive and negative ESI mode
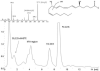
Figure 4
Extracted ion chromatogram (ESI-) of the ion traces m/z 327.2, 343.3, 301.2, 317.2, 319.2 and 335.3 referring to FA 22:6, FA 20:5, their respective hydroxylated species and 5S,12S-diHETE in the RA pool sample. The upper left corner shows the obtained MS/MS spectrum for the precursor _m/_z 335 at 1.6 min. The upper right corner shows 5S,12S-diHETE and its preferred fragmentation yielding m/z 195.
Figure 5
Identification of MaR1 in human synovial fluid, upper left corner selected reaction monitoring chromatograms of the transition m/z 359→221, black – unspiked sample, red - co-injection of a synthetic MaR1 standard (100 pg on column spike level), upper right corner – MS/MS spectrum of MaR1, lower right corner - MS3 spectrum of the characteristic MaR1 fragment m/z 221 corresponding to the sample, lower left corner MS3 spectrum of synthetic MaR1 (m/z 221) – standard sample (10 pg on column).
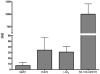
Figure 6
Lipid mediator amounts identified and quantified in five different human SF samples. Absolute amounts in pg on column are given. Error bars show one standard deviation (n=5). For the individual values see supplementary material S5.
Similar articles
- Application of global metabolomic profiling of synovial fluid for osteoarthritis biomarkers.
Carlson AK, Rawle RA, Adams E, Greenwood MC, Bothner B, June RK. Carlson AK, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 5;499(2):182-188. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.117. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29551687 Free PMC article. - A lipidomic study of phospholipid classes and species in human synovial fluid.
Kosinska MK, Liebisch G, Lochnit G, Wilhelm J, Klein H, Kaesser U, Lasczkowski G, Rickert M, Schmitz G, Steinmeyer J. Kosinska MK, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Sep;65(9):2323-33. doi: 10.1002/art.38053. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23784884 - Lipid Mediator Metabolomics Via LC-MS/MS Profiling and Analysis.
Dalli J, Colas RA, Walker ME, Serhan CN. Dalli J, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1730:59-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7592-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29363065 - Metabololipidomic profiling of functional immunoresolvent clusters and eicosanoids in mammalian tissues.
Norris PC, Serhan CN. Norris PC, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 7;504(3):553-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.037. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29524409 Free PMC article. Review. - Synovial fluid lipids and apolipoproteins: a contemporary perspective.
Prete PE, Gurakar-Osborne A, Kashyap ML. Prete PE, et al. Biorheology. 1995 Jan-Feb;32(1):1-16. doi: 10.3233/bir-1995-32101. Biorheology. 1995. PMID: 7548857 Review.
Cited by
- Fatty acid desaturation and lipoxygenase pathways support trained immunity.
Ferreira AV, Alarcon-Barrera JC, Domínguez-Andrés J, Bulut Ö, Kilic G, Debisarun PA, Röring RJ, Özhan HN, Terschlüsen E, Ziogas A, Kostidis S, Mohammed Y, Matzaraki V, Renieris G, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Netea MG, Giera M. Ferreira AV, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 15;14(1):7385. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43315-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37968313 Free PMC article. - Bioactive products formed in humans from fish oils.
Skarke C, Alamuddin N, Lawson JA, Li X, Ferguson JF, Reilly MP, FitzGerald GA. Skarke C, et al. J Lipid Res. 2015 Sep;56(9):1808-20. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M060392. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26180051 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Metabolomic profiles of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Kim J, Kang SC, Yoon NE, Kim Y, Choi J, Park N, Jung H, Jung BH, Ju JH. Kim J, et al. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Nov 15;10(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1408-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31730022 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of neogenin fosters resolution of inflammation and tissue regeneration.
Schlegel M, Körner A, Kaussen T, Knausberg U, Gerber C, Hansmann G, Jónasdóttir HS, Giera M, Mirakaj V. Schlegel M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2018 Oct 1;128(10):4711-4726. doi: 10.1172/JCI96259. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30222138 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Maresin 1 Promotes Wound Healing and Socket Bone Regeneration for Alveolar Ridge Preservation.
Wang CW, Yu SH, Fretwurst T, Larsson L, Sugai JV, Oh J, Lehner K, Jin Q, Giannobile WV. Wang CW, et al. J Dent Res. 2020 Jul;99(8):930-937. doi: 10.1177/0022034520917903. Epub 2020 May 8. J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 32384864 Free PMC article.
References
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;7:429–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical