Evaluation of methods to concentrate and purify ocean virus communities through comparative, replicated metagenomics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Evaluation of methods to concentrate and purify ocean virus communities through comparative, replicated metagenomics
Bonnie L Hurwitz et al. Environ Microbiol. 2013 May.
Free PMC article
Abstract
Viruses have global impact through mortality, nutrient cycling and horizontal gene transfer, yet their study is limited by complex methodologies with little validation. Here, we use triplicate metagenomes to compare common aquatic viral concentration and purification methods across four combinations as follows: (i) tangential flow filtration (TFF) and DNase + CsCl, (ii) FeCl3 precipitation and DNase, (iii) FeCl3 precipitation and DNase + CsCl and (iv) FeCl3 precipitation and DNase + sucrose. Taxonomic data (30% of reads) suggested that purification methods were statistically indistinguishable at any taxonomic level while concentration methods were significantly different at family and genus levels. Specifically, TFF-concentrated viral metagenomes had significantly fewer abundant viral types (Podoviridae and Phycodnaviridae) and more variability among Myoviridae than FeCl3 -precipitated viral metagenomes. More comprehensive analyses using protein clusters (66% of reads) and k-mers (100% of reads) showed 50-53% of these data were common to all four methods, and revealed trace bacterial DNA contamination in TFF-concentrated metagenomes and one of three replicates concentrated using FeCl3 and purified by DNase alone. Shared k-mer analyses also revealed that polymerases used in amplification impact the resulting metagenomes, with TaKaRa enriching for 'rare' reads relative to PfuTurbo. Together these results provide empirical data for making experimental design decisions in culture-independent viral ecology studies.
© 2012 Society for Applied Microbiology and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Fig. 1
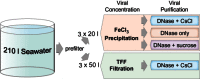
Workflow showing the process of creating each viral metagenomic replicate using different concentration (TFF or FeCl3) and purification methods (DNase only, DNase + CsCl or DNase + sucrose) from a 210 l sample of seawater taken from Scripps Pier, San Diego, CA. The ‘3 ×’ refers to that each subsample was processed independently from the 210 l pooled initial sample.
Fig. 2
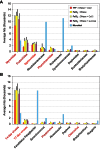
Rank abundance curve of (A) family-level (B) and genus-level taxonomy for the top 10 taxa observed in the data. Only four family-level and four genus-level taxa are viral (highlighted with red text); the remaining are microbial taxa.
Fig. 3
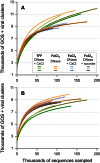
Rarefaction analysis of hits to protein clusters from each viral metagenome using (A) all sequences and (B) abundant (k-mer > 1) sequences. To be conservative, only protein clusters with > 20 members were used in these analyses.
Fig. 4
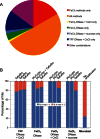
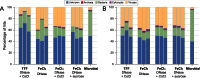
K-mer-based analysis of shared reads between methods and replicates. (A) Percentage of total reads that are shared between methods based on a k-mer-based analysis and (B) percentage of ‘rare’ (k-mer = 1) versus abundant sequences (k-mer > 1) in each of the four viral metagenomic methods and a non-replicated microbial metagenome. The enzymes used for linker amplification (TaKaRa or PfuTurbo) are listed above each sample. The microbial sample includes more ‘rare’ sequences because the diversity in the sample is undersampled based upon rarefaction analysis (data not shown).
Fig. 5
Superkingdom taxonomic profile of reads for each triplicate sample from the four viral metagenome methods and a non-replicated microbial metagenome for (A) rare (k-mer = 1) and (B) abundant (k-mer > 1) reads.
Similar articles
- The Pacific Ocean virome (POV): a marine viral metagenomic dataset and associated protein clusters for quantitative viral ecology.
Hurwitz BL, Sullivan MB. Hurwitz BL, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057355. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468974 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of methods to purify virus-like particles for metagenomic sequencing of intestinal viromes.
Kleiner M, Hooper LV, Duerkop BA. Kleiner M, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 Jan 22;16(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12864-014-1207-4. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25608871 Free PMC article. - Modeling ecological drivers in marine viral communities using comparative metagenomics and network analyses.
Hurwitz BL, Westveld AH, Brum JR, Sullivan MB. Hurwitz BL, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 22;111(29):10714-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319778111. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25002514 Free PMC article. - Aquatic viral metagenomics: Lights and shadows.
Rastrojo A, Alcamí A. Rastrojo A, et al. Virus Res. 2017 Jul 15;239:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.021. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27889617 Review. - Critical issues in application of molecular methods to environmental virology.
Hamza IA, Bibby K. Hamza IA, et al. J Virol Methods. 2019 Apr;266:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30659861 Review.
Cited by
- Emerging methods to study bacteriophage infection at the single-cell level.
Dang VT, Sullivan MB. Dang VT, et al. Front Microbiol. 2014 Dec 23;5:724. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00724. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25566233 Free PMC article. Review. - Metagenomic analysis of viral communities in (hado)pelagic sediments.
Yoshida M, Takaki Y, Eitoku M, Nunoura T, Takai K. Yoshida M, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057271. Epub 2013 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468952 Free PMC article. - Diversity of Microbial Signatures in Asthmatic Airways.
Alamri A. Alamri A. Int J Gen Med. 2021 Apr 16;14:1367-1378. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S304339. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 33889017 Free PMC article. Review. - Distributions, interactions, and dynamics of prokaryotes and phages in a hybrid biological wastewater treatment system.
Wang D, Liu L, Xu X, Wang C, Wang Y, Deng Y, Zhang T. Wang D, et al. Microbiome. 2024 Jul 22;12(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01853-6. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39039555 Free PMC article. - Freshwater viral metagenome reveals novel and functional phage-borne antibiotic resistance genes.
Moon K, Jeon JH, Kang I, Park KS, Lee K, Cha CJ, Lee SH, Cho JC. Moon K, et al. Microbiome. 2020 Jun 1;8(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00863-4. Microbiome. 2020. PMID: 32482165 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous