Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers
Wahajuddin et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012.
Abstract
A targeted drug delivery system is the need of the hour. Guiding magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with the help of an external magnetic field to its target is the principle behind the development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as novel drug delivery vehicles. SPIONs are small synthetic γ-Fe₂O₃ (maghemite) or Fe₃O₄ (magnetite) particles with a core ranging between 10 nm and 100 nm in diameter. These magnetic particles are coated with certain biocompatible polymers, such as dextran or polyethylene glycol, which provide chemical handles for the conjugation of therapeutic agents and also improve their blood distribution profile. The current research on SPIONs is opening up wide horizons for their use as diagnostic agents in magnetic resonance imaging as well as for drug delivery vehicles. Delivery of anticancer drugs by coupling with functionalized SPIONs to their targeted site is one of the most pursued areas of research in the development of cancer treatment strategies. SPIONs have also demonstrated their efficiency as nonviral gene vectors that facilitate the introduction of plasmids into the nucleus at rates multifold those of routinely available standard technologies. SPION-induced hyperthermia has also been utilized for localized killing of cancerous cells. Despite their potential biomedical application, alteration in gene expression profiles, disturbance in iron homeostasis, oxidative stress, and altered cellular responses are some SPION-related toxicological aspects which require due consideration. This review provides a comprehensive understanding of SPIONs with regard to their method of preparation, their utility as drug delivery vehicles, and some concerns which need to be resolved before they can be moved from bench top to bedside.
Keywords: SPIONs; coating; functionalization; superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; targeted delivery; targeting ligands; toxicity.
Figures
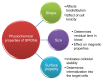
Figure 1
Physicochemical considerations of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery.
Figure 2
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle targeting approaches.
Similar articles
- Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic agents: opportunities and challenges.
Laurent S, Saei AA, Behzadi S, Panahifar A, Mahmoudi M. Laurent S, et al. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Sep;11(9):1449-70. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.924501. Epub 2014 May 29. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24870351 Review. - Biocompatible superparamagnetic core-shell nanoparticles for potential use in hyperthermia-enabled drug release and as an enhanced contrast agent.
Patil-Sen Y, Torino E, De Sarno F, Ponsiglione AM, Chhabria V, Ahmed W, Mercer T. Patil-Sen Y, et al. Nanotechnology. 2020 Sep 11;31(37):375102. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab91f6. Epub 2020 May 11. Nanotechnology. 2020. PMID: 32392545 - Targeting experimental orthotopic glioblastoma with chitosan-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (CS-DX-SPIONs).
Shevtsov M, Nikolaev B, Marchenko Y, Yakovleva L, Skvortsov N, Mazur A, Tolstoy P, Ryzhov V, Multhoff G. Shevtsov M, et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 12;13:1471-1482. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S152461. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29559776 Free PMC article. - In vitro and in vivo experiments with iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with DEXTRAN or polyethylene glycol for medical applications: magnetic targeting.
Mojica Pisciotti ML, Lima E Jr, Vasquez Mansilla M, Tognoli VE, Troiani HE, Pasa AA, Creczynski-Pasa TB, Silva AH, Gurman P, Colombo L, Goya GF, Lamagna A, Zysler RD. Mojica Pisciotti ML, et al. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014 May;102(4):860-8. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33068. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014. PMID: 24458920 - Magnetic nanoparticle-based drug delivery for cancer therapy.
Tietze R, Zaloga J, Unterweger H, Lyer S, Friedrich RP, Janko C, Pöttler M, Dürr S, Alexiou C. Tietze R, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Dec 18;468(3):463-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.022. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26271592 Review.
Cited by
- An ultra pH-sensitive and aptamer-equipped nanoscale drug-delivery system for selective killing of tumor cells.
Zhao N, You J, Zeng Z, Li C, Zu Y. Zhao N, et al. Small. 2013 Oct 25;9(20):3477-84. doi: 10.1002/smll.201202694. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Small. 2013. PMID: 23609964 Free PMC article. - Investigation of Aggregation and Disaggregation of Self-Assembling Nano-Sized Clusters Consisting of Individual Iron Oxide Nanoparticles upon Interaction with HEWL Protein Molecules.
Sarimov RM, Nagaev EI, Matveyeva TA, Binhi VN, Burmistrov DE, Serov DA, Astashev ME, Simakin AV, Uvarov OV, Khabatova VV, Akopdzhanov AG, Schimanowskii NL, Gudkov SV. Sarimov RM, et al. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;12(22):3960. doi: 10.3390/nano12223960. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432246 Free PMC article. - Magnetofection: a reproducible method for gene delivery to melanoma cells.
Prosen L, Prijic S, Music B, Lavrencak J, Cemazar M, Sersa G. Prosen L, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:209452. doi: 10.1155/2013/209452. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23862136 Free PMC article. - Gadolinium embedded iron oxide nanoclusters as T1-T2 dual-modal MRI-visible vectors for safe and efficient siRNA delivery.
Wang X, Zhou Z, Wang Z, Xue Y, Zeng Y, Gao J, Zhu L, Zhang X, Liu G, Chen X. Wang X, et al. Nanoscale. 2013 Sep 7;5(17):8098-104. doi: 10.1039/c3nr02797j. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 23884164 Free PMC article. - Magnetic nanoparticles for "smart liposomes".
Nakayama Y, Mustapić M, Ebrahimian H, Wagner P, Kim JH, Hossain MS, Horvat J, Martinac B. Nakayama Y, et al. Eur Biophys J. 2015 Dec;44(8):647-54. doi: 10.1007/s00249-015-1059-0. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Eur Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26184724
References
- Freeman MW, Arrott A, Watson JHL. Magnetism in medicine. J Appl Phys. 1960;31:S404.
- Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(1–2):24–46. - PubMed
- Dave SR, Gao X. Monodispersed magnetic nanoparticles for biodetection, imaging, and drug delivery: a versatile and evolving technology. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009;1(6):583–609. - PubMed
- Kodama RH. Magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater. 1999;200(1–3):359–372.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources