A re-evaluation of 9-HODE activity at TRPV1 channels in comparison with anandamide: enantioselectivity and effects at other TRP channels and in sensory neurons - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
A re-evaluation of 9-HODE activity at TRPV1 channels in comparison with anandamide: enantioselectivity and effects at other TRP channels and in sensory neurons
Luciano De Petrocellis et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Two oxidation products of linoleic acid, 9- and 13-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acids (HODEs), have recently been suggested to act as endovanilloids, that is, endogenous agonists of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) channels, thereby contributing to inflammatory hyperalgesia in rats. However, HODE activity at rat TRPV1 in comparison with the best established endovanilloid, anandamide, and its enantioselectivity and selectivity towards other TRP channels that are also abundant in sensory neurons have never been investigated.
Experimental approach: We studied the effect of 9(R)-HODE, 9(S)-HODE, (+/-)13-HODE, 15(S)-hydroxyanandamide and anandamide on [Ca(2+) ](i) in HEK-293 cells stably expressing the rat or human recombinant TRPV1, or rat recombinant TRPV2, TRPA1 or TRPM8, and also the effect of 9(S)-HODE in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons by calcium imaging.
Key results: Anandamide and 15(S)-hydroxyanandamide were the most potent endovanilloids at human TRPV1, whereas 9(S)-HODE was approximately threefold less efficacious and 75- and 3-fold less potent, respectively, and did not perform much better at rat TRPV1. The 9(R)-HODE and (+/-)13-HODE were almost inactive at TRPV1. Unlike anandamide and 15(S)-hydroxyanandamide, all HODEs were very weak at desensitizing TRPV1 to the action of capsaicin, but activated rat TRPV2 [only (+/-)13-HODE] and rat TRPA1, and antagonized rat TRPM8, at concentrations higher than those required to activate TRPV1. Finally, 9(S)-HODE elevated [Ca(2+) ](i) in DRG neurons almost exclusively in capsaicin-sensitive cells but only at concentrations between 25 and 100 μM.
Conclusions and implications: The present data suggest that HODEs are less important endovanilloids than anandamide.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Cannabinoids. To view the other articles in this section visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.2012.167.issue-8.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Figure 1
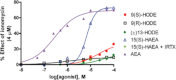
Effect of 9(S)-HODE, 9(R)-HODE, (+/–)13-HODE and 15(S)-hydroxy-anandamide [15(S)-HAEA] on intracellular Ca2+ elevation in HEK-293 cells overexpressing the human recombinant TRPV1 channel. The effect of a 5 min pre-incubation with the TRPV1 antagonist iodo-resiniferatoxin (IRTX) on the response to 10 μM 15(S)-HAEA is also shown. Also the effect of AEA is shown. Data are means of n = 3 separate determinations. SEM bars are not shown for the sake of clarity and were never higher than 10% of the means.
Figure 2
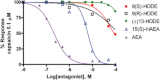
Desensitization by 5 min pre-incubation with 15(S)-hydroxy-anandamide [15(S)-HAEA] or 9(S)-HODE, 9(R)-HODE, (+/–)13-HODE and AEA, of capsaicin (0.1 μM)-induced Ca2+ elevation in HEK-293 cells over-expressing the human recombinant TRPV1 channel. Data are means of n = 3 separate determinations. SEM bars are not shown for the safe of clarity and were never higher than 10% of the means. The curves were fitted by considering 100% inhibition at 1 mM.
Figure 3
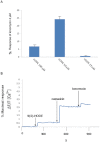
9(S)-HODE 50 μM induces an increase in [Ca2+]i in rat DRG neurons. (A) Normalized increase in Fluo-4 fluorescence (mean ± SD) induced by 9(S)-HODE, 25, 50 and 100 μM. The application of 9(S)-HODE in the bath triggered a calcium response in a concentration-dependent manner. The 25 and 100 μM concentrations of 9(S)-HODE were less efficacious than the 50 μM concentration. Data are means ± SD of measures made in n = 30 cells for each concentration tested. (B) Shows the representative time course of the Fluo-4 signals recorded from 20 to 40 cells as response to 9(S)-HODE (50 μM), capsaicin (1 μM) and ionomycin (4 μM). Arrows indicate when compounds were added. Images were collected continuously for 30 min. Note that 9(S)-HODE exhibited a low efficacy (on average 24.7 ± 3.5% of the effect of 4 μM ionomycin and 27.4 ± 5.2% of the effect of 1 μM capsaicin; means ± SD of n = 30).
Similar articles
- Effects of anandamide and noxious heat on intracellular calcium concentration in nociceptive drg neurons of rats.
Fischbach T, Greffrath W, Nawrath H, Treede RD. Fischbach T, et al. J Neurophysiol. 2007 Aug;98(2):929-38. doi: 10.1152/jn.01096.2006. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17581853 - Effects of inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase vs. the anandamide membrane transporter on TRPV1-mediated calcium responses in adult DRG neurons; the role of CB receptors.
Millns PJ, Chimenti M, Ali N, Ryland E, de Lago E, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Chapman V, Kendall DA. Millns PJ, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Dec;24(12):3489-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05236.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17229097 - The contribution of the endogenous TRPV1 ligands 9-HODE and 13-HODE to nociceptive processing and their role in peripheral inflammatory pain mechanisms.
Alsalem M, Wong A, Millns P, Arya PH, Chan MS, Bennett A, Barrett DA, Chapman V, Kendall DA. Alsalem M, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(8):1961-74. doi: 10.1111/bph.12092. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23278358 Free PMC article. - Biochemistry and pharmacology of endovanilloids.
Starowicz K, Nigam S, Di Marzo V. Starowicz K, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Apr;114(1):13-33. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.01.005. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17349697 Review. - Anandamide in primary sensory neurons: too much of a good thing?
Sousa-Valente J, Varga A, Ananthan K, Khajuria A, Nagy I. Sousa-Valente J, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Feb;39(3):409-18. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12467. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24494681 Review.
Cited by
- A review of the direct targets of the cannabinoids cannabidiol, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, N-arachidonoylethanolamine and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
Wright NJD. Wright NJD. AIMS Neurosci. 2024 Apr 30;11(2):144-165. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2024009. eCollection 2024. AIMS Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38988890 Free PMC article. Review. - Interactions Between the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System, Nrf2, and the Cannabinoidome as Protective Strategies to Combat Neurodegeneration: Review on Experimental Evidence.
Monsalvo-Maraver LA, Ovalle-Noguez EA, Nava-Osorio J, Maya-López M, Rangel-López E, Túnez I, Tinkov AA, Tizabi Y, Aschner M, Santamaría A; Students from Programa Delfín 2022. Monsalvo-Maraver LA, et al. Neurotox Res. 2024 Feb 23;42(2):18. doi: 10.1007/s12640-024-00694-3. Neurotox Res. 2024. PMID: 38393521 Free PMC article. Review. - 2012 cannabinoid themed section.
Alexander SP. Alexander SP. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;167(8):1573-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02238.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23194253 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Spinal Reflex Control of Arterial Blood Pressure: The Role of TRP Channels and Their Endogenous Eicosanoid Modulators.
Minic Z, O'Leary DS, Reynolds CA. Minic Z, et al. Front Physiol. 2022 Feb 23;13:838175. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.838175. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35283783 Free PMC article. Review. - Pharmacological Evaluation of Signals of Disproportionality Reporting Related to Adverse Reactions to Antiepileptic Cannabidiol in VigiBase.
Calapai F, Mannucci C, McQuain L, Salvo F. Calapai F, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;16(10):1420. doi: 10.3390/ph16101420. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895891 Free PMC article.
References
- Akopian AN. Regulation of nociceptive transmission at the periphery via TRPA1-TRPV1 interactions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12:89–94. - PubMed
- Batetta B, Griinari M, Carta G, Murru E, Ligresti A, Cordeddu L, et al. Endocannabinoids may mediate the ability of (n-3) fatty acids to reduce ectopic fat and inflammatory mediators in obese Zucker rats. J Nutr. 2009;139:1495–1501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous