Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor Improves Insulin Resistance and Steatosis in a Refractory Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patient: A Case Report - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor Improves Insulin Resistance and Steatosis in a Refractory Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patient: A Case Report
Minoru Itou et al. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2012 May.
Abstract
A 67-year-old Asian woman was referred to Kurume University Hospital due to abnormal liver function tests. She was diagnosed with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD was treated by diet therapy with medication of metformin and pioglitazone; however, NAFLD did not improve. Subsequently, the patient was administered sitagliptin. Although her energy intake and physical activity did not change, her hemoglobin A1c level was decreased from 7.8 to 6.4% 3 months after treatment. Moreover, her serum insulin level and homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance value were also improved, as was the severity of hepatic steatosis. These findings indicate that sitagliptin may improve insulin resistance and steatosis in patients with refractory NAFLD.
Keywords: Diabetes; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV; Glucose intolerance; Incretin; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Figures
Fig. 1
Time course of body mass index and glucose metabolisms during the medical treatment.
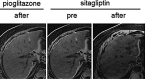
Fig. 2
Changes in MRI imaging during the medical treatment. All images are T1 subtraction images.
Similar articles
- Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors: therapeutic potential in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Yilmaz Y, Atug O, Yonal O, Duman D, Ozdogan O, Imeryuz N, Kalayci C. Yilmaz Y, et al. Med Sci Monit. 2009 Apr;15(4):HY1-5. Med Sci Monit. 2009. PMID: 19333209 - Effects of sitagliptin on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diet-induced obese rats.
Akaslan SB, Degertekin CK, Yilmaz G, Cakir N, Arslan M, Toruner FB. Akaslan SB, et al. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2013 Aug;11(4):243-50. doi: 10.1089/met.2012.0128. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2013. PMID: 23544853 - Intestinal TGR5 agonism improves hepatic steatosis and insulin sensitivity in Western diet-fed mice.
Finn PD, Rodriguez D, Kohler J, Jiang Z, Wan S, Blanco E, King AJ, Chen T, Bell N, Dragoli D, Jacobs JW, Jain R, Leadbetter M, Siegel M, Carreras CW, Koo-McCoy S, Shaw K, Le C, Vanegas S, Hsu IH, Kozuka K, Okamoto K, Caldwell JS, Lewis JG. Finn PD, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Mar 1;316(3):G412-G424. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00300.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30605011 Free PMC article. - Effects of newer antidiabetic drugs on nonalcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis: Think out of the box!
Ranjbar G, Mikhailidis DP, Sahebkar A. Ranjbar G, et al. Metabolism. 2019 Dec;101:154001. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154001. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Metabolism. 2019. PMID: 31672448 Review. - Role of Agents for the Treatment of Diabetes in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
Budd J, Cusi K. Budd J, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Oct 5;20(11):59. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-01349-1. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 33015726 Review.
Cited by
- Review on the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Li CL, Zhao LJ, Zhou XL, Wu HX, Zhao JJ. Li CL, et al. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015 Jun;35(3):333-336. doi: 10.1007/s11596-015-1433-2. Epub 2015 Jun 14. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26072069 Review. - Incretin based therapies: a novel treatment approach for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Blaslov K, Bulum T, Zibar K, Duvnjak L. Blaslov K, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 21;20(23):7356-65. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7356. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24966606 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonalcoholic Fatty liver: a possible new target for type 2 diabetes prevention and treatment.
Fruci B, Giuliano S, Mazza A, Malaguarnera R, Belfiore A. Fruci B, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 20;14(11):22933-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms141122933. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24264040 Free PMC article. Review. - DPP4 in Diabetes.
Röhrborn D, Wronkowitz N, Eckel J. Röhrborn D, et al. Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 27;6:386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00386. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26284071 Free PMC article. Review. - Potential Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors Towards Hepatic Diseases and Associated Glucose Intolerance.
Sharma A, Virmani T, Sharma A, Chhabra V, Kumar G, Pathak K, Alhalmi A. Sharma A, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Jun 16;15:1845-1864. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S369712. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35733643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ratziu V, Bellentani S, Cortez-Pinto H, Day C, Marchesini G. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. J Hepatol. 2010;53:372–384. - PubMed
- Scaglioni F, Ciccia S, Marino M, Bedogni G, Bellentani S. ASH and NASH. Dig Dis. 2011;29:202–210. - PubMed
- Regimbeau JM, Colombat M, Mognol P, Durand F, Abdalla E, Degott C, Degos F, Farges O, Belghiti J. Obesity and diabetes as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2004;10:S69–S73. - PubMed
- Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: A weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010;51:1820–1832. - PubMed
- Lonardo A, Lombardini S, Ricchi M, Scaglioni F, Loria P. Review article: Hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22((suppl 2)):64–70. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources