A cell-based approach to the human proteome project - PubMed (original) (raw)
A cell-based approach to the human proteome project
Neil L Kelleher. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2012 Oct.
Abstract
The general scope of a project to determine the protein molecules that comprise the cells within the human body is framed. By focusing on protein primary structure as expressed in specific cell types, this concept for a cell-based version of the Human Proteome Project (CB-HPP) is crafted in a manner analogous to the Human Genome Project while recognizing that cells provide a primary context in which to define a proteome. Several activities flow from this articulation of the HPP, which enables the definition of clear milestones and deliverables. The CB-HPP highlights major gaps in our knowledge regarding cell heterogeneity and protein isoforms, and calls for development of technology that is capable of defining all human cell types and their proteomes. The main activities will involve mapping and sorting cell types combined with the application of beyond the state-of-the art in protein mass spectrometry.
Figures
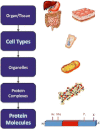
Figure 1
Graphical depiction of the cell-based version of the Human Proteome Project (CB-HPP)
Figure 2
The levels of organization in the human body. The cell-based approach to the Human Proteome Project (CB-HPP) recognizes cell type as a primary context for mass spectrometry-based proteomics to measure the molecular complexity present in the body naturally. The CB-HPP also calls for accelerated development of new and emerging technologies to better define cell types and precisely catalogue whole protein molecules
Similar articles
- Proteome analysis by mass spectrometry.
Ferguson PL, Smith RD. Ferguson PL, et al. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:399-424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141854. Epub 2003 Jan 28. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12574065 Review. - Developments in quantitative mass spectrometry for the analysis of proteome dynamics.
Hughes C, Krijgsveld J. Hughes C, et al. Trends Biotechnol. 2012 Dec;30(12):668-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.09.007. Epub 2012 Oct 27. Trends Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23107010 Review. - Progress on Identifying and Characterizing the Human Proteome: 2018 Metrics from the HUPO Human Proteome Project.
Omenn GS, Lane L, Overall CM, Corrales FJ, Schwenk JM, Paik YK, Van Eyk JE, Liu S, Snyder M, Baker MS, Deutsch EW. Omenn GS, et al. J Proteome Res. 2018 Dec 7;17(12):4031-4041. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00441. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 30099871 Free PMC article. Review. - Progress Identifying and Analyzing the Human Proteome: 2021 Metrics from the HUPO Human Proteome Project.
Omenn GS, Lane L, Overall CM, Paik YK, Cristea IM, Corrales FJ, Lindskog C, Weintraub S, Roehrl MHA, Liu S, Bandeira N, Srivastava S, Chen YJ, Aebersold R, Moritz RL, Deutsch EW. Omenn GS, et al. J Proteome Res. 2021 Dec 3;20(12):5227-5240. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00590. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 34670092 Free PMC article. - The 2022 Report on the Human Proteome from the HUPO Human Proteome Project.
Omenn GS, Lane L, Overall CM, Pineau C, Packer NH, Cristea IM, Lindskog C, Weintraub ST, Orchard S, Roehrl MHA, Nice E, Liu S, Bandeira N, Chen YJ, Guo T, Aebersold R, Moritz RL, Deutsch EW. Omenn GS, et al. J Proteome Res. 2023 Apr 7;22(4):1024-1042. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00498. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Proteome Res. 2023. PMID: 36318223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Identification of a novel proteoform of prostate specific antigen (SNP-L132I) in clinical samples by multiple reaction monitoring.
Végvári A, Sjödin K, Rezeli M, Malm J, Lilja H, Laurell T, Marko-Varga G. Végvári A, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Oct;12(10):2761-73. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.028365. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23842001 Free PMC article. - The Challenge to Search for New Nervous System Disease Biomarker Candidates: the Opportunity to Use the Proteogenomics Approach.
Nery TGM, Silva EM, Tavares R, Passetti F. Nery TGM, et al. J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jan;67(1):150-164. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1220-1. Epub 2018 Dec 15. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30554402 Review. - Characterization and quantification of intact 26S proteasome proteins by real-time measurement of intrinsic fluorescence prior to top-down mass spectrometry.
Russell JD, Scalf M, Book AJ, Ladror DT, Vierstra RD, Smith LM, Coon JJ. Russell JD, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058157. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536786 Free PMC article. - Exposing the subunit diversity and modularity of protein complexes by structural mass spectrometry approaches.
Chorev DS, Ben-Nissan G, Sharon M. Chorev DS, et al. Proteomics. 2015 Aug;15(16):2777-91. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400517. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25727951 Free PMC article. Review. - The Human Proteoform Project: Defining the human proteome.
Smith LM, Agar JN, Chamot-Rooke J, Danis PO, Ge Y, Loo JA, Paša-Tolić L, Tsybin YO, Kelleher NL; Consortium for Top-Down Proteomics. Smith LM, et al. Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 12;7(46):eabk0734. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abk0734. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34767442 Free PMC article.
References
- Cottingham K. HUPO’s Human Proteome Project: the next big thing? J. Proteome Res. 2008;7:2192. doi: 10.1021/pr0837441. - DOI
- Legrain P, Aebersold R, Archakov A, Bairoch A, Bala K, Beretta L, Bergeron J, Borchers CH, Corthals GL, Costello CE, Deutsch EW, Domon B, Hancock W, He F, Hochstrasser D, Marko-Varga G, Salekdeh GH, Sechi S, Snyder M, Srivastava S, Uhlén M, Wu CH, Yamamoto T, Paik YK, Omenn GS. The human proteome project: current state and future direction. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011;10:M111.009993. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.009993. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Paik YK, Jeong SK, Omenn GS, Uhlen M, Hanash S, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Na K, Choi EY, Yan F, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Snyder M, Cheng Y, Chen R, Marko-Varga G, Deutsch EW, Kim H, Kwon JY, Aebersold R, Bairoch A, Taylor AD, Kim KY, Lee EY, Hochstrasser D, Legrain P, Hancock WS. The chromosome-centric Human Proteome Project for cataloging proteins encoded in the genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:221. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2152. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources