IκB kinase 2 regulates TPL-2 activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by direct phosphorylation of TPL-2 serine 400 - PubMed (original) (raw)
IκB kinase 2 regulates TPL-2 activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by direct phosphorylation of TPL-2 serine 400
Karine Roget et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Nov.
Abstract
Tumor progression locus 2 (TPL-2) functions as a MEK-1/2 kinase, which is essential for Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK-1/2) mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and for inducing the production of the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1β. In unstimulated cells, association of TPL-2 with NF-κB1 p105 prevents TPL-2 phosphorylation of MEK-1/2. LPS stimulation of TPL-2 MEK-1/2 kinase activity requires TPL-2 release from p105. This is triggered by IκB kinase 2 (IKK-2) phosphorylation of the p105 PEST region, which promotes p105 ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. LPS activation of ERK-1/2 additionally requires transphosphorylation of TPL-2 on serine 400 in its C terminus, which controls TPL-2 signaling to ERK-1/2 independently of p105. However, the identity of the protein kinase responsible for TPL-2 serine 400 phosphorylation remained unknown. In the present study, we show that TPL-2 serine 400 phosphorylation is mediated by IKK2. The IKK complex therefore regulates two of the key regulatory steps required for TPL-2 activation of ERK-1/2, underlining the close linkage of ERK-1/2 MAP kinase activation to upregulation of NF-κB-dependent transcription.
Figures
Fig 1
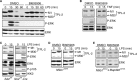
IKK2 regulates LPS-induced phosphorylation of TPL-2. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for the antigens shown. (A, D, and E) BMDM of the indicated genotypes were pretreated with BI605906 or vehicle control (DMSO) and then stimulated with LPS (10 ng/ml) or left unstimulated. WT cells were used in panel A. In panels D and E, no ERK-1/2 phosphorylation was detected after LPS stimulation with or without BI605906 (data not shown). (B) QBI-293A cells were pretreated with BI605906 or vehicle control (DMSO) and then stimulated with TNF for 15 min or left unstimulated. (C) BMDM of the indicated genotypes were stimulated with LPS or left unstimulated.
Fig 2
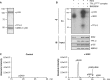
Phosphorylation of TPL-2 by IKK2 in vitro. (A) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel of purified TPL-2D270A/NF-κB1 p105/ABIN-2 complex. (B) TPL-2D270A/NF-κB1 p105/ABIN-2 complex was incubated with recombinant IKK2 plus [32P]ATP for a kinase assay (KA). Labeled proteins were revealed by autoradiography after SDS-PAGE. Cell lysates were immunoblotted (IB) for the indicated antigens. (C) Extracted ion chromatograms of phosphorylated S62, S62/S66, and S400 peptides identified by mass spectrometry of TPL-2D270A complex without (left) and with (right) IKK2 phosphorylation. Absolute intensities and retention times are shown (Table 1).
Fig 3
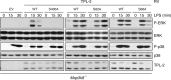
TPL-2 S62 and S66 are not required for TPL-2 activation of ERK. _Map3k8_−/− BMDM were transduced with recombinant retroviruses (RV) encoding TPL-2 (WT), TPL-2S62A, TPL-2S66A, and TPL-2S400A. Cells were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml), and lysates were immunoblotted. P-ERK, phospho-ERK-1/2; P-p38, phospho-p38.
Fig 4
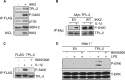
Phosphorylation of TPL-2 S400 by IKK2 in cells. (A) FLAG–TPL-2/HA-p105/ABIN-2-StrepII complex was isolated by anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation (IP) from transiently transfected QBI-293A cells coexpressing HA-IKK2 (+) or empty vector (−). Isolated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (B) C6 cells were transiently transfected with a vector encoding Myc-TPL-2 together with either a vector encoding IKK2 or empty vector (EV). After 48 h, cells were stimulated with IL-1β (20 ng/ml) for 20 min, or left unstimulated. Myc-TPL-2 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with Myc MAb and then immunoblotted. (C) C6 cells were transfected with a vector encoding FLAG–TPL-2 or EV. After 48 h, cells were pretreated with BI605906 (+) or vehicle control (−) and then stimulated with IL-1β for 20 min or left unstimulated. FLAG immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted. (D) _Nfkb1_−/− BMDM, transduced with retrovirus expressing wild-type TPL-2, were pretreated with BI605906 (+) or vehicle control (−) and then stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) or left unstimulated. Cell lysates were immunoblotted. P-ERK, phospho-ERK-1/2; T-ERK, total ERK-1/2.
Fig 5
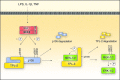
Regulation of TPL-2 activation by IKK. In unstimulated cells, TPL-2 is complexed with NF-κB1 p105. Agonist stimulation induces IKK2, a catalytic subunit of the IKK complex, to phosphorylate p105 on serines 927 and 932 (human p105 numbering) in its PEST region, which triggers p105 K48-linked polyubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. This releases TPL-2 from p105-mediated inhibition, allowing TPL-2 access to its substrates MEK-1/2. TPL-2 activation of MEK-1/2 also requires phosphorylation of the TPL-2 C terminus on S400, which is shown here to be mediated by IKK2. The IKK complex therefore regulates two critical steps in the activation of TPL-2 MEK-1/2 kinase activity.
Similar articles
- IκB kinase-induced interaction of TPL-2 kinase with 14-3-3 is essential for Toll-like receptor activation of ERK-1 and -2 MAP kinases.
Ben-Addi A, Mambole-Dema A, Brender C, Martin SR, Janzen J, Kjaer S, Smerdon SJ, Ley SC. Ben-Addi A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):E2394-403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320440111. Epub 2014 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24912162 Free PMC article. - Phosphorylation of TPL-2 on serine 400 is essential for lipopolysaccharide activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in macrophages.
Robinson MJ, Beinke S, Kouroumalis A, Tsichlis PN, Ley SC. Robinson MJ, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7355-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00301-07. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17709378 Free PMC article. - IκB kinase regulation of the TPL-2/ERK MAPK pathway.
Gantke T, Sriskantharajah S, Sadowski M, Ley SC. Gantke T, et al. Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):168-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01104.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435554 Review. - Regulation and function of TPL-2, an IκB kinase-regulated MAP kinase kinase kinase.
Gantke T, Sriskantharajah S, Ley SC. Gantke T, et al. Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):131-45. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.173. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21135874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Ebola virus VP35 induces high-level production of recombinant TPL-2-ABIN-2-NF-κB1 p105 complex in co-transfected HEK-293 cells.
Gantke T, Boussouf S, Janzen J, Morrice NA, Howell S, Mühlberger E, Ley SC. Gantke T, et al. Biochem J. 2013 Jun 1;452(2):359-65. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121873. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23557442 Free PMC article. - Tumor Progression Locus 2 Protects against Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Influenza A Virus-Infected Mice.
Latha K, Rao S, Sakamoto K, Watford WT. Latha K, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0113622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01136-22. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35980186 Free PMC article. - Regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by TPL-2 kinase.
Sriskantharajah S, Gückel E, Tsakiri N, Kierdorf K, Brender C, Ben-Addi A, Veldhoen M, Tsichlis PN, Stockinger B, O'Garra A, Prinz M, Kollias G, Ley SC. Sriskantharajah S, et al. J Immunol. 2014 Apr 15;192(8):3518-3529. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300172. Epub 2014 Mar 17. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24639351 Free PMC article. - Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity.
Arthur JS, Ley SC. Arthur JS, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Sep;13(9):679-92. doi: 10.1038/nri3495. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23954936 Review. - Tumor progression locus 2-dependent oxidative burst drives phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase during TLR3 and 9 signaling.
Kuriakose T, Rada B, Watford WT. Kuriakose T, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 26;289(52):36089-100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.587121. Epub 2014 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25378393 Free PMC article.
References
- Aoki M, et al. 1993. The human cot proto-oncogene encodes two protein serine/threonine kinases with different transforming activities by alternative initiation of translation. J. Biol. Chem. 268:22723–22732 - PubMed
- Beinke S, Belich MP, Ley SC. 2002. The death domain of NF-κB1 p105 is essential for signal-induced p105 proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 277:24162–24168 - PubMed
- Belich MP, Salmeron A, Johnston LH, Ley SC. 1999. TPL-2 kinase regulates the proteolysis of the NF-κB inhibitory protein NF-κB1 p105. Nature 397:363–368 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DK091222/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U117584209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 AI091637/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086550/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 18864/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- U117584209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 18864/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous