Effects of perilipin 2 antisense oligonucleotide treatment on hepatic lipid metabolism and gene expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effects of perilipin 2 antisense oligonucleotide treatment on hepatic lipid metabolism and gene expression
Yumi Imai et al. Physiol Genomics. 2012.
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease worldwide. We previously showed that Perilipin 2 (Plin2), a member of lipid droplet protein family, is markedly increased in fatty liver, and its reduction in the liver of diet-induced obese mice by antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) decreased steatosis and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Plin2-ASO treatment markedly suppressed lipogenic gene expression. To gain a better understanding of the biological role of Plin2 in liver, we performed microarray analysis to determine genes differentially regulated by Plin2-ASO compared with a control (scrambled) oligonucleotide (Cont). Male C57BL/6J mice on a high-fat diet were treated with Plin2- or Cont-ASO for 4 wk. Plin2-ASO decreased hepatic triglycerides, and this was associated with changes in expression of 1,363 genes. We analyzed the data for functional clustering and validated the expression of representative genes using real-time PCR. On the high-fat diet, Plin2-ASO decreased the expression of enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism (acsl1, lipe) and steroid metabolism (hmgcr, hsd3b5, hsd17b2), suggesting that Plin2 affects hepatic lipid metabolism at the transcriptional level. Plin2-ASO also increased the expression of genes involved in regulation of hepatocyte proliferation (afp, H19), mitosis (ccna2, incenp, sgol1), and extracellular matrix (col1a1, col3a1, mmp8). Plin2-ASO had similar effects on gene expression in chow-fed mice. Together, these results indicate that Plin2 has diverse metabolic and structural roles in the liver, and its downregulation promotes hepatic fibrosis and proliferation.
Figures
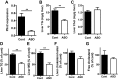
Fig. 1.
Mice on high-fat diet (HF) were treated for 4 wk with Plin2-ASO or control oligo (Cont). A: Plin2 mRNA in the liver was determined by qPCR. Enzymatic colorimetric assay comparing liver triglycerides (TG) (B) and liver cholesterol (Chol) (C) levels. Liver lipids were also separated and quantified by TLC. D: TG, E: monoglycerides (MG), F: cholesterol ester, and G: free cholesterol. Data are means ± SE, n = 5 per group. **P < 0.01 vs. Cont.
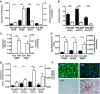
Fig. 2.
Expression of genes in the livers of HF mice treated with Plin2-ASO (ASO) and Cont was measured with qPCR. A: genes associated with fatty acid metabolism, i.e., acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (Acsl4), stearoyl-Coenzyme A desaturase 2 (SCD2), acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (Acsl1), and hormone-sensitive lipase (Lipe). B: genes associated with cholesterol metabolism, i.e., 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (Hmgcr), hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 5 (Hsd3b5), and hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 2 (Hsd17b2). C: α-fetoprotein (Afp) and H19 fetal liver (H19). D: genes associated with mitosis/kinetochore, i.e., cycline A2 (Ccna2), inner centromere protein antigens 135/155kDa (Incenp), and shugoshin-like 1 (Sgol1). E: genes associated with extracellular matrix (ECM), i.e., type 1 α1 collagen (Col1a1), type 1 α2 collagen (Col1a2), type 3 α1 collagen (Col3a1), and matrix metallopeptidase 8 (Mmp8). Data are means ± SE, n = 4–5 per group. *P < 0.05 vs. Cont, **P < 0.01 vs. Cont, ***P < 0.005 vs. Cont. F: histological study of livers from Cont- and Plin2-ASO-treated mice. Top: immunofluorescence showing Plin2 (green) staining in the cytoplasm and DAPI (blue) in the nuclei. Bottom: Sirius red staining of collagen in Cont vs. Plin2-ASO liver. Scale bar, 25 μm.
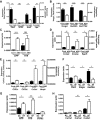
Fig. 3.
A–E: effects of Plin2-ASO on hepatic gene expression in regular chow-fed mice. A: Plin2 and genes associated with fatty acid metabolism, i.e., SCD2, Acsl1, and Lipe. B: genes associated with cholesterol metabolism, i.e., Hmgcr, Hsd3b5, Hsd17b2. C: Afp and H19. D: genes associated with mitosis/kinetochore, i.e., Ccna2, Incenp, and Sgol1. E: genes associated with extracellular matrix, i.e., Col1a1, Col1a2, Col3a1, and Mmp8. F–H: hepatic gene expression in livers from regular chow (NC) and HF livers without Plin2-ASO treatment. F: genes associated with cholesterol metabolism, i.e., Hmgcr, Hsd3b5. G: Afp, H19, and Ccna2. H: ECM genes, i.e., Col1a1, Col1a2, and Col3a1. Data are means ± SE, n = 4 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.001, and n.s. (no significant difference) between the groups.
Similar articles
- Perilipin-2 promotes obesity and progressive fatty liver disease in mice through mechanistically distinct hepatocyte and extra-hepatocyte actions.
Orlicky DJ, Libby AE, Bales ES, McMahan RH, Monks J, La Rosa FG, McManaman JL. Orlicky DJ, et al. J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1565-1584. doi: 10.1113/JP277140. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30536914 Free PMC article. - Reduction of hepatosteatosis and lipid levels by an adipose differentiation-related protein antisense oligonucleotide.
Imai Y, Varela GM, Jackson MB, Graham MJ, Crooke RM, Ahima RS. Imai Y, et al. Gastroenterology. 2007 May;132(5):1947-54. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.02.046. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17484887 - Perilipin-2 Deletion Impairs Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Interfering with Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein (SREBP) Activation and Altering the Hepatic Lipidome.
Libby AE, Bales E, Orlicky DJ, McManaman JL. Libby AE, et al. J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 11;291(46):24231-24246. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.759795. Epub 2016 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27679530 Free PMC article. - Role of lipid droplet proteins in liver steatosis.
Okumura T. Okumura T. J Physiol Biochem. 2011 Dec;67(4):629-36. doi: 10.1007/s13105-011-0110-6. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21847662 Review. - Perilipin 2 and Age-Related Metabolic Diseases: A New Perspective.
Conte M, Franceschi C, Sandri M, Salvioli S. Conte M, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Dec;27(12):893-903. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27659144 Review.
Cited by
- Lipid droplet metabolism.
Khor VK, Shen WJ, Kraemer FB. Khor VK, et al. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2013 Nov;16(6):632-7. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283651106. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2013. PMID: 24100667 Free PMC article. Review. - PLIN5 deletion remodels intracellular lipid composition and causes insulin resistance in muscle.
Mason RR, Mokhtar R, Matzaris M, Selathurai A, Kowalski GM, Mokbel N, Meikle PJ, Bruce CR, Watt MJ. Mason RR, et al. Mol Metab. 2014 Jun 14;3(6):652-63. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.06.002. eCollection 2014 Sep. Mol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25161888 Free PMC article. - Prevention of hepatic fibrosis with liver microsomal triglyceride transfer protein deletion in liver fatty acid binding protein null mice.
Newberry EP, Xie Y, Kennedy SM, Graham MJ, Crooke RM, Jiang H, Chen A, Ory DS, Davidson NO. Newberry EP, et al. Hepatology. 2017 Mar;65(3):836-852. doi: 10.1002/hep.28941. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 27862118 Free PMC article. - Regulation of lipid droplet (LD) formation in hepatocytes via regulation of SREBP1c by non-coding RNAs.
El Sobky SA, Aboud NK, El Assaly NM, Fawzy IO, El-Ekiaby N, Abdelaziz AI. El Sobky SA, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 20;9:903856. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.903856. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36203751 Free PMC article. - Integrated Action of Autophagy and Adipose Tissue Triglyceride Lipase Ameliorates Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Liver-Specific PLIN2 Knockout Mice.
Griffin JD, Bejarano E, Wang XD, Greenberg AS. Griffin JD, et al. Cells. 2021 Apr 25;10(5):1016. doi: 10.3390/cells10051016. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33923083 Free PMC article.
References
- Abbaszade IG, Clarke TR, Park CH, Payne AH. The mouse 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase multigene family includes two functionally distinct groups of proteins. Mol Endocrinol 9: 1214–1222, 1995. - PubMed
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 346: 1221–1231, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK090490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-090490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DK-049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-19525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous