Comparison of symptom management strategies for pain, erectile dysfunction, and depression in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis: a cluster randomized effectiveness trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Comparison of symptom management strategies for pain, erectile dysfunction, and depression in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis: a cluster randomized effectiveness trial
Steven D Weisbord et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Jan.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Pain, erectile dysfunction (ED), and depression are common yet frequently untreated in chronic hemodialysis patients. This study compared two management strategies for these symptoms in this patient population.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Pain, ED, and depression were assessed monthly during an observation usual care phase. Patients were then randomized to 12-month participation in either a feedback arm in which these symptoms were assessed monthly, renal providers were informed of patients' symptoms, and treatment was left treatment at their discretion; or a nurse management arm in which symptoms were assessed monthly and trained nurses were used to evaluate patients and generate and facilitate the implementation of treatment recommendations.
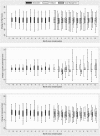
Results: Of 288 patients enrolled into observation between January 1, 2009 and March 30, 2010, 220 (76%) were randomized. Compared with the feedback approach, the results (shown as Δ symptom score [95% confidence interval]) indicated that nurse management was not associated with improved pain (0.49 [-0.56, 1.54]), ED (0.20 [-0.55, 0.95]), or depression (0.32 [-0.94, 1.58]). Relative to their symptoms during observation, feedback patients experienced small, statistically significant improvements in pain (-0.98 [-1.67, -0.28]), ED (-0.98 [-1.54, -0.41]), and depression (-1.36 [-2.19, -0.54]), whereas nurse management patients experienced small, statistically significant improvements in ED (-0.78 [-1.41, -0.15]) and depression (-1.04 [-2.04, -0.04]).
Conclusions: Compared with informing renal providers of their patients' pain, ED, and depression and leaving management at their discretion, a nurse-implemented management strategy does not improve these symptoms. Both approaches modestly reduced symptoms relative to usual care.
Figures
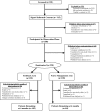
Figure 1.
Recruitment and follow-up of the study population.
Figure 2.
Longitudinal change in symptom scores by study phase and intervention arm for patients with pain, erectile dysfunction, and depression.
Comment in
- Improving symptoms of pain, erectile dysfunction, and depression in patients on dialysis.
Hedayati SS. Hedayati SS. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Jan;8(1):5-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11811112. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23296377 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Improving symptoms of pain, erectile dysfunction, and depression in patients on dialysis.
Hedayati SS. Hedayati SS. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Jan;8(1):5-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11811112. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23296377 No abstract available. - Methodology of a randomized clinical trial of symptom management strategies in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis: the SMILE study.
Weisbord SD, Shields AM, Mor MK, Sevick MA, Homer M, Peternel J, Porter P, Rollman BL, Palevsky PM, Arnold RM, Fine MJ. Weisbord SD, et al. Contemp Clin Trials. 2010 Sep;31(5):491-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2010.06.005. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Contemp Clin Trials. 2010. PMID: 20601163 Clinical Trial. - Acceptance of Antidepressant Treatment by Patients on Hemodialysis and Their Renal Providers.
Pena-Polanco JE, Mor MK, Tohme FA, Fine MJ, Palevsky PM, Weisbord SD. Pena-Polanco JE, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Feb 7;12(2):298-303. doi: 10.2215/CJN.07720716. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28126707 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Pyrgidis N, Mykoniatis I, Nigdelis MP, Kalyvianakis D, Memmos E, Sountoulides P, Hatzichristou D. Pyrgidis N, et al. J Sex Med. 2021 Jan;18(1):113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Sex Med. 2021. PMID: 33221161 - Sexual dysfunction and depression: etiology, prevalence, and treatment.
Shabsigh R, Zakaria L, Anastasiadis AG, Seidman AS. Shabsigh R, et al. Curr Urol Rep. 2001 Dec;2(6):463-7. doi: 10.1007/s11934-001-0040-x. Curr Urol Rep. 2001. PMID: 12084232 Review.
Cited by
- Longitudinal associations of depressive symptoms and pain with quality of life in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis.
Belayev LY, Mor MK, Sevick MA, Shields AM, Rollman BL, Palevsky PM, Arnold RM, Fine MJ, Weisbord SD. Belayev LY, et al. Hemodial Int. 2015 Apr;19(2):216-24. doi: 10.1111/hdi.12247. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Hemodial Int. 2015. PMID: 25403142 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The efficacy of low-dose tadalafil in patients undergoing hemodialysis with end-stage renal disease.
Bolat MS, Özer İ, Cinar O, Akdeniz E, Aşcı R. Bolat MS, et al. Ren Fail. 2017 Nov;39(1):582-587. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1349678. Ren Fail. 2017. PMID: 28742406 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Use of Electronic Patient Reported Outcomes in Clinical Nephrology Practice: A Qualitative Pilot Study.
Schick-Makaroff K, Tate K, Molzahn A. Schick-Makaroff K, et al. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019 Sep 30;6:2054358119879451. doi: 10.1177/2054358119879451. eCollection 2019. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632681 Free PMC article. - Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients.
Natale P, Palmer SC, Ruospo M, Saglimbene VM, Rabindranath KS, Strippoli GF. Natale P, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 2;12(12):CD004542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31789430 Free PMC article. - Rapid decline in kidney function is associated with rapid deterioration of health-related quality of life in chronic kidney disease.
Kim HJ, Kim DW, Rhee H, Song SH, Park SK, Kim SW, Kim YH, Sung S, Oh KH, Seong EY. Kim HJ, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 31;13(1):1786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28150-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36720969 Free PMC article.
References
- Evans RW, Rader B, Manninen DL, Cooperative Multicenter EPO Clinical Trial Group : The quality of life of hemodialysis recipients treated with recombinant human erythropoietin. JAMA 263: 825–830, 1990 - PubMed
- Simmons RG, Abress L: Quality-of-life issues for end-stage renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis 15: 201–208, 1990 - PubMed
- Kimmel PL, Emont SL, Newmann JM, Danko H, Moss AH: ESRD patient quality of life: Symptoms, spiritual beliefs, psychosocial factors, and ethnicity. Am J Kidney Dis 42: 713–721, 2003 - PubMed
- Unruh ML, Weisbord SD, Kimmel PL: Health-related quality of life in nephrology research and clinical practice. Semin Dial 18: 82–90, 2005 - PubMed
- Kimmel PL, Patel SS: Quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: Focus on end-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis. Semin Nephrol 26: 68–79, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical