Myeloid Krüppel-like factor 4 deficiency augments atherogenesis in ApoE-/- mice--brief report - PubMed (original) (raw)
Myeloid Krüppel-like factor 4 deficiency augments atherogenesis in ApoE-/- mice--brief report
Nikunj Sharma et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Dec.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the role of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), an essential transcriptional regulator of macrophage polarization (M1/M2), in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
Methods and results: Despite the acknowledged importance of macrophages in atherosclerosis, the role of M1 (classically activated or proinflammatory) versus M2 (alternatively activated or anti-inflammatory) macrophages in this process remains incompletely understood. We recently identified KLF4 as a regulator of macrophage subset specification; that is, KLF4 promotes M2 and inhibits M1 phenotype. Here, we provide evidence that KLF4-deficient macrophages exhibit enhanced proinflammatory activation and foam cell formation in response to oxidized lipids. In vivo, myeloid KLF4-deficient mice (ApoE(-/-) background) develop significantly more vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic lesion formation.
Conclusions: Our findings identify myeloid KLF4 as an essential regulator of vascular inflammation and experimental atherogenesis.
Figures
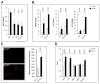
Figure 1. Myeloid KLF4 regulates the response to oxidized lipids
A) After 16hrs treatment of macrophage with IL-1β (20ng/ml), TNF-α (10ng/ml) or POV-PC (10μg/ml), KLF4 expression was analyzed by qPCR. (n=3) B) KLF4+/+ or KLF4Δ/Δ macrophages were treated with POV-PC and expression of pro-inflammatory markers iNOS, IL-6 and IL-1β was analyzed by qPCR. (n=3) C) KLF4+/+ or KLF4Δ/Δ macrophages were incubated with Dil-OxLDL (15μg/ml) for 4 hrs and uptake was analyzed by fluorescence-microscopy and flow cytometry. (n=4) D) Gene expression analysis of lipoprotein receptors in KLF4+/+ and KLF4Δ/Δ macrophages (n=4).
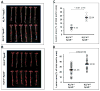
Figure 2. Myeloid KLF4 deficiency augments atherosclerosis
A&B) Representative Sudan IV staining indicating enhanced atherosclerotic lesions in KLF4Δ/ΔApoE−/− vs. KLF4Δ/ΔApoE+/+ mice on normal chow (A) and HFD (B). C&D) Quantitative analysis of lesion area on normal chow (C) and HFD (D) fed mice aortas.
Similar articles
- DNA methyltransferase 1 and Krüppel-like factor 4 axis regulates macrophage inflammation and atherosclerosis.
Tang RZ, Zhu JJ, Yang FF, Zhang YP, Xie SA, Liu YF, Yao WJ, Pang W, Han LL, Kong W, Wang YX, Zhang T, Zhou J. Tang RZ, et al. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 Mar;128:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30659837 - Genetic deficiency of Phactr1 promotes atherosclerosis development via facilitating M1 macrophage polarization and foam cell formation.
Li T, Ding L, Wang Y, Yang O, Wang S, Kong J. Li T, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Sep 18;134(17):2353-2368. doi: 10.1042/CS20191241. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32857129 - Macrophage polarization by angiotensin II-type 1 receptor aggravates renal injury-acceleration of atherosclerosis.
Yamamoto S, Yancey PG, Zuo Y, Ma LJ, Kaseda R, Fogo AB, Ichikawa I, Linton MF, Fazio S, Kon V. Yamamoto S, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Dec;31(12):2856-64. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.237198. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21979434 Free PMC article. - Targeting foam cell formation and macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis: The Therapeutic potential of rhubarb.
Liu X, Wu J, Tian R, Su S, Deng S, Meng X. Liu X, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110433. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110433. Epub 2020 Jun 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32768936 Review. - Role of Kruppel-like factor 4 in atherosclerosis.
Yang C, Xiao X, Huang L, Zhou F, Chen LH, Zhao YY, Qu SL, Zhang C. Yang C, et al. Clin Chim Acta. 2021 Jan;512:135-141. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Clin Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33181148 Review.
Cited by
- Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 deficiency in bone marrow cells prevents plaque progression without decreasing atherogenic inflammation in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice.
Paunel-Görgülü A, Conforti A, Mierau N, Zierden M, Xiong X, Wahlers T. Paunel-Görgülü A, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 16;9:1046273. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1046273. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36465436 Free PMC article. - Regulation of an inflammatory disease: Krüppel-like factors and atherosclerosis.
Jain MK, Sangwung P, Hamik A. Jain MK, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Mar;34(3):499-508. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301925. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24526695 Free PMC article. Review. - Metformin in cardiovascular diabetology: a focused review of its impact on endothelial function.
Ding Y, Zhou Y, Ling P, Feng X, Luo S, Zheng X, Little PJ, Xu S, Weng J. Ding Y, et al. Theranostics. 2021 Sep 9;11(19):9376-9396. doi: 10.7150/thno.64706. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34646376 Free PMC article. Review. - Macrophage deficiency of Akt2 reduces atherosclerosis in Ldlr null mice.
Babaev VR, Hebron KE, Wiese CB, Toth CL, Ding L, Zhang Y, May JM, Fazio S, Vickers KC, Linton MF. Babaev VR, et al. J Lipid Res. 2014 Nov;55(11):2296-308. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M050633. Epub 2014 Sep 19. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 25240046 Free PMC article. - Macrophage Metabolism As Therapeutic Target for Cancer, Atherosclerosis, and Obesity.
Geeraerts X, Bolli E, Fendt SM, Van Ginderachter JA. Geeraerts X, et al. Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 15;8:289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00289. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28360914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Croce K, Libby P. Intertwining of thrombosis and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007;14:55–61. - PubMed
- Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Orchestration of metabolism by macrophages. Cell Metab. 2012;15:432–437. - PubMed
- Bouhlel MA, Derudas B, Rigamonti E, Dievart R, Brozek J, Haulon S, Zawadzki C, Jude B, Torpier G, Marx N, Staels B, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G. Ppargamma activation primes human monocytes into alternative m2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties. Cell metabolism. 2007;6:137–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 HL097023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086548/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110630/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086548/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084154/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL097023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084154/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL097023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097593/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL075427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL097593/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL076754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous