The glaucoma-associated olfactomedin domain of myocilin is a novel calcium binding protein - PubMed (original) (raw)
The glaucoma-associated olfactomedin domain of myocilin is a novel calcium binding protein
Rebecca K Donegan et al. J Biol Chem. 2012.
Abstract
Myocilin is a protein found in the trabecular meshwork extracellular matrix tissue of the eye that plays a role in regulating intraocular pressure. Both wild-type and certain myocilin variants containing mutations in the olfactomedin (OLF) domain are linked to the optic neuropathy glaucoma. Because calcium ions are important biological cofactors that play numerous roles in extracellular matrix proteins, we examined the calcium binding properties of the myocilin OLF domain (myoc-OLF). Our study reveals an unprecedented high affinity calcium binding site within myoc-OLF. The calcium ion remains bound to wild-type OLF at neutral and acidic pH. A glaucoma-causing OLF variant, myoc-OLF(D380A), is calcium-depleted. Key differences in secondary and tertiary structure between myoc-OLF(D380A) and wild-type myoc-OLF, as well as limited access to chelators, indicate that the calcium binding site is largely buried in the interior of the protein. Analysis of six conserved aspartate or glutamate residues and an additional 18 disease-causing variants revealed two other candidate residues that may be involved in calcium coordination. Our finding expands our knowledge of calcium binding in extracellular matrix proteins; provides new clues into domain structure, function, and pathogenesis for myocilin; and offers insights into highly conserved, biomedically relevant OLF domains.
Figures
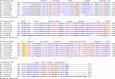
FIGURE 1.
PROMALS (30) sequence alignment of the OLF domain of myocilins from human (gi_3065674), zebrafish (gi_62632725), cow (gi_74356501), pig (gi_47522798), mouse (gi_15077142), and rat (gi_3845607), as well as (non-myocilin) amassin (gi_28453877) from sea urchin. Consensus secondary structure (SS) is depicted above the alignment. e, β-strand; h, helix. Asterisk indicates location of glaucoma-causing mutations examined in this study. Red residues are identical; blue residues are similar. Highlighted residues are conserved aspartate/glutamate positions subjected to site-directed mutagenesis in this study.
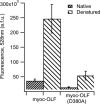
FIGURE 2.
Ca2+ binding assay for myoc-OLF and myoc-OLF(D380A). Fluorescence (in a.f.u., arbitrary fluorescence units) of chelator Quin-2 due to Ca2+ binding is measured under native and denaturing conditions.
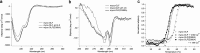
FIGURE 3.
Structural and stability comparison of myoc-OLF and myoc-OLF(D380A). Shown is a comparison of secondary structure from far-UV spectra (a) and tertiary structure from near-UV spectra (b) among wild-type myoc-OLF at pH 7.2, wild-type myoc-OLF at pH 4.6, and myoc-OLF(D380A) at pH 7.2. c, CD thermal melts for myoc-OLF and myoc-OLF(D380A) in MES pH 6.0, monitored at 215 nm in the presence and absence of exogenous Ca2+.
Similar articles
- The effects of myocilin expression on functionally relevant trabecular meshwork genes: a mini-review.
Borrás T. Borrás T. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar-Apr;30(2-3):202-12. doi: 10.1089/jop.2013.0218. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24564495 Free PMC article. Review. - The glaucoma-associated olfactomedin domain of myocilin forms polymorphic fibrils that are constrained by partial unfolding and peptide sequence.
Hill SE, Donegan RK, Lieberman RL. Hill SE, et al. J Mol Biol. 2014 Feb 20;426(4):921-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24333014 Free PMC article. - Structural basis for misfolding in myocilin-associated glaucoma.
Donegan RK, Hill SE, Freeman DM, Nguyen E, Orwig SD, Turnage KC, Lieberman RL. Donegan RK, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Apr 15;24(8):2111-24. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu730. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25524706 Free PMC article. - The stability of myocilin olfactomedin domain variants provides new insight into glaucoma as a protein misfolding disorder.
Burns JN, Turnage KC, Walker CA, Lieberman RL. Burns JN, et al. Biochemistry. 2011 Jul 5;50(26):5824-33. doi: 10.1021/bi200231x. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21612213 Free PMC article. - Molecular Insights into Myocilin and Its Glaucoma-Causing Misfolded Olfactomedin Domain Variants.
Lieberman RL, Ma MT. Lieberman RL, et al. Acc Chem Res. 2021 May 4;54(9):2205-2215. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00060. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33847483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Major review: Molecular genetics of primary open-angle glaucoma.
Liu Y, Allingham RR. Liu Y, et al. Exp Eye Res. 2017 Jul;160:62-84. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 10. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28499933 Free PMC article. Review. - Differential Misfolding Properties of Glaucoma-Associated Olfactomedin Domains from Humans and Mice.
Patterson-Orazem AC, Hill SE, Wang Y, Dominic IM, Hall CK, Lieberman RL. Patterson-Orazem AC, et al. Biochemistry. 2019 Apr 2;58(13):1718-1727. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01309. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30802039 Free PMC article. - The effects of myocilin expression on functionally relevant trabecular meshwork genes: a mini-review.
Borrás T. Borrás T. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar-Apr;30(2-3):202-12. doi: 10.1089/jop.2013.0218. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24564495 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting the ER-autophagy system in the trabecular meshwork to treat glaucoma.
Stothert AR, Fontaine SN, Sabbagh JJ, Dickey CA. Stothert AR, et al. Exp Eye Res. 2016 Mar;144:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.017. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26302411 Free PMC article. Review. - The olfactomedin domain from gliomedin is a β-propeller with unique structural properties.
Han H, Kursula P. Han H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3612-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.627547. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25525261 Free PMC article.
References
- Evenäs J., Malmendal A., Forsén S. (1998) Calcium. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2, 293–302 - PubMed
- Maurer P., Hohenester E. (1997) Structural and functional aspects of calcium binding in extracellular matrix proteins. Matrix Biol. 15, 569–580 - PubMed
- Zhang K., Zhang L., Weinreb R. N. (2012) Ophthalmic drug discovery: novel targets and mechanisms for retinal diseases and glaucoma. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 541–559 - PubMed
- Polansky J. R., Fauss D. J., Chen P., Chen H., Lütjen-Drecoll E., Johnson D., Kurtz R. M., Ma Z. D., Bloom E., Nguyen T. D. (1997) Cellular pharmacology and molecular biology of the trabecular meshwork inducible glucocorticoid response gene product. Ophthalmologica 211, 126–139 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical