The retromer complex - endosomal protein recycling and beyond - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2012 Oct 15;125(Pt 20):4693-702.
doi: 10.1242/jcs.103440. Epub 2012 Nov 12.
Affiliations
- PMID: 23148298
- PMCID: PMC3517092
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.103440
Review
The retromer complex - endosomal protein recycling and beyond
Matthew N J Seaman. J Cell Sci. 2012.
Abstract
The retromer complex is a vital element of the endosomal protein sorting machinery that is conserved across all eukaryotes. Retromer is most closely associated with the endosome-to-Golgi retrieval pathway and is necessary to maintain an active pool of hydrolase receptors in the trans-Golgi network. Recent progress in studies of retromer have identified new retromer-interacting proteins, including the WASH complex and cargo such as the Wntless/MIG-14 protein, which now extends the role of retromer beyond the endosome-to-Golgi pathway and has revealed that retromer is required for aspects of endosome-to-plasma membrane sorting and regulation of signalling events. The interactions between the retromer complex and other macromolecular protein complexes now show how endosomal protein sorting is coordinated with actin assembly and movement along microtubules, and place retromer squarely at the centre of a complex set of protein machinery that governs endosomal protein sorting. Dysregulation of retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting leads to various pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer disease and spastic paraplegia and the mechanisms underlying these pathologies are starting to be understood. In this Commentary, I will highlight recent advances in the understanding of retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting and discuss how retromer contributes to a diverse set of physiological processes.
Figures
Fig. 1.
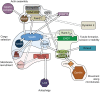
Schematic depiction of the role of the retromer complex in mediating endosomal protein sorting. The cargo-selective retromer complex operates in the endosome-to-Golgi retrieval pathway to sort cargo, such as CIMPR and sortilin (see Table 1). The interaction of retromer with cargo proteins requires its recruitment to the endosomal membrane, a process that is mediated by Rab7a and Snx3. The sorting nexin (Snx) heterodimer dimer, comprising the Snx-BAR proteins Snx1 or Snx2 and Snx5 or Snx6, mediates tubule formation and links to microtubules through the p150-glued–dynein complex. The cargo-selective retromer subcomplex (Vps35–Vps29–Vps26) recruits the WASH complex, which mediates the production of branched actin networks on the surface of endosomes. The cargo-selective retromer complex together with Snx27 and the WASH complex operate in the endosome-to-cell surface recycling of the GPCR β2-adrenergic receptor and of other proteins including α5β1 integrin. Additionally, the cargo-selective retromer complex also regulates the signalling activity of another GPCR, the parathyroid hormone receptor (PTHR).
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram of the interactions between retromer and its associated proteins. Here, the many retromer-interacting proteins that have been identified from studies in higher eukaryotes (e.g. mammalian cells) are depicted. Proteins have been grouped according to function, e.g. Snx3, Rab7a and TBC1D5 regulate the membrane association of the cargo-selective retromer complex. Arrows indicate the relationship between the respective proteins, e.g. Vps35 interacts with Fam21 to mediate recruitment of Fam21 and the WASH complex. In some cases, arrows are double-ended as the respective proteins are mutually dependent. Arrows with a dashed outline indicate an interaction that has not yet been experimentally proven, but is likely based on indirect evidence, e.g. native immunoprecipitations.
Similar articles
- Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: The role of unstructured domains.
Mukadam AS, Seaman MN. Mukadam AS, et al. FEBS Lett. 2015 Sep 14;589(19 Pt A):2620-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.052. Epub 2015 Jun 10. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26072290 Review. - The cargo-selective retromer complex is a recruiting hub for protein complexes that regulate endosomal tubule dynamics.
Harbour ME, Breusegem SY, Antrobus R, Freeman C, Reid E, Seaman MN. Harbour ME, et al. J Cell Sci. 2010 Nov 1;123(Pt 21):3703-17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.071472. Epub 2010 Oct 5. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20923837 Free PMC article. - Regulation of endosomal clathrin and retromer-mediated endosome to Golgi retrograde transport by the J-domain protein RME-8.
Shi A, Sun L, Banerjee R, Tobin M, Zhang Y, Grant BD. Shi A, et al. EMBO J. 2009 Nov 4;28(21):3290-302. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.272. Epub 2009 Sep 17. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19763082 Free PMC article. - Retromer-mediated endosomal protein sorting: all WASHed up!
Seaman MN, Gautreau A, Billadeau DD. Seaman MN, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;23(11):522-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.010. Epub 2013 May 28. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23721880 Free PMC article. Review. - Retromer and sorting nexins in endosomal sorting.
Gallon M, Cullen PJ. Gallon M, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Feb;43(1):33-47. doi: 10.1042/BST20140290. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 25619244 Review.
Cited by
- The WASH complex, an endosomal Arp2/3 activator, interacts with the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome complex BLOC-1 and its cargo phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase type IIα.
Ryder PV, Vistein R, Gokhale A, Seaman MN, Puthenveedu MA, Faundez V. Ryder PV, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jul;24(14):2269-84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-02-0088. Epub 2013 May 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23676666 Free PMC article. - The giardial VPS35 retromer subunit is necessary for multimeric complex assembly and interaction with the vacuolar protein sorting receptor.
Miras SL, Merino MC, Gottig N, Rópolo AS, Touz MC. Miras SL, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):2628-2638. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23810936 Free PMC article. - The Parkinson's disease related mutant VPS35 (D620N) amplifies the LRRK2 response to endolysosomal stress.
McCarron KR, Elcocks H, Mortiboys H, Urbé S, Clague MJ. McCarron KR, et al. Biochem J. 2024 Feb 21;481(4):265-278. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20230492. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 38299383 Free PMC article. - TRPC Channels in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Renal Tubular System: What Do We Know?
Englisch CN, Paulsen F, Tschernig T. Englisch CN, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 22;24(1):181. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010181. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613622 Free PMC article. Review. - Endosomal sorting and trafficking, the retromer complex and neurodegeneration.
Vagnozzi AN, Praticò D. Vagnozzi AN, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2019 Jun;24(6):857-868. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0221-3. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30120416 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Andersen O. M., Reiche J., Schmidt V., Gotthardt M., Spoelgen R., Behlke J., von Arnim C. A., Breiderhoff T., Jansen P., Wu X.et al. (2005). Neuronal sorting protein-related receptor sorLA/LR11 regulates processing of the amyloid precursor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 13461–13466 10.1073/pnas.0503689102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Andersen O. M., Schmidt V., Spoelgen R., Gliemann J., Behlke J., Galatis D., McKinstry W. J., Parker M. W., Masters C. L., Hyman B. T.et al. (2006). Molecular dissection of the interaction between amyloid precursor protein and its neuronal trafficking receptor SorLA/LR11. Biochemistry 45, 2618–2628 10.1021/bi052120v - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials