No association of genetic variants in BDNF with major depression: a meta- and gene-based analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
. 2013 Jan;162B(1):61-70.
doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32122. Epub 2012 Nov 26.
Affiliations
- PMID: 23184535
- PMCID: PMC3725128
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32122
Meta-Analysis
No association of genetic variants in BDNF with major depression: a meta- and gene-based analysis
Joseph P Gyekis et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2013 Jan.
Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a complex psychiatric condition with strong genetic predisposition. The association of MDD with genetic polymorphisms, such as Val66Met (rs6265), in the brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), have been reported in many studies and the results were conflicting. In this study, we performed a systematic literature search and conducted random-effects meta-analysis to evaluate genetic variants in BDNF with MDD. A gene-based analysis was also conducted to investigate the cumulative effects of genetic polymorphisms in BDNF. A total of 28 studies from 26 published articles were included in our analysis. Meta-analysis yielded an estimated odds ratio (OR) of 0.96 (95% CI: 0.89-1.05; P = 0.402) for Val66Met (rs6265), 0.83 (95% CI: 0.67-1.04; P = 0.103) for 11757C/G, 1.16 (95% CI: 0.74-1.82; P = 0.527) for 270T/C, 1.03 (95% CI: 0.18-5.75; P = 0.974) for 712A/G and 0.98 (95% CI: 0.85-1.14; P = 0.831) for rs988748. The gene-based analysis indicated that BDNF is not associated with MDD (P > 0.21). Our updated meta- and novel gene-based analyses provide no evidence of the association of BDNF with major depression.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
FIG. 1
Flow diagram of studies included in the systematic review
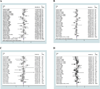
FIG. 2
Odds ratios of Val66Met (rs6265) with major depressive disorder (A: Val/val vs. met;B:Met vs. val; C: Met/met vs. val/val; D:Met/val vs. val/val).
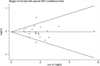
FIG. 3
Funnel plot for meta-analysis of Val66Met.
Similar articles
- The brain-derived neurotrophic-factor (BDNF) val66met polymorphism is associated with geriatric depression: a meta-analysis.
Pei Y, Smith AK, Wang Y, Pan Y, Yang J, Chen Q, Pan W, Bao F, Zhao L, Tie C, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhen W, Zhou J, Ma X. Pei Y, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012 Jul;159B(5):560-6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32062. Epub 2012 May 18. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012. PMID: 22610920 Free PMC article. - Meta-analysis of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in major depressive disorder: effects of gender and ethnicity.
Verhagen M, van der Meij A, van Deurzen PA, Janzing JG, Arias-Vásquez A, Buitelaar JK, Franke B. Verhagen M, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar;15(3):260-71. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.109. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 18852698 - Plasma BDNF Level in Major Depression: Biomarker of the Val66Met BDNF Polymorphism and of the Clinical Course in Met Carrier Patients.
Colle R, Trabado S, David DJ, Brailly-Tabard S, Hardy P, Falissard B, Fève B, Becquemont L, Verstuyft C, Corruble E. Colle R, et al. Neuropsychobiology. 2017;75(1):39-45. doi: 10.1159/000478862. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Neuropsychobiology. 2017. PMID: 28848102 - BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and hippocampal volume in neuropsychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Harrisberger F, Smieskova R, Schmidt A, Lenz C, Walter A, Wittfeld K, Grabe HJ, Lang UE, Fusar-Poli P, Borgwardt S. Harrisberger F, et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Aug;55:107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25956254 Review. - Genetics of bipolar disorder: focus on BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.
Fan J, Sklar P. Fan J, et al. Novartis Found Symp. 2008;289:60-72; discussion 72-3, 87-93. doi: 10.1002/9780470751251.ch5. Novartis Found Symp. 2008. PMID: 18497095 Review.
Cited by
- Epistasis of HTR1A and BDNF risk genes alters cortical 5-HT1A receptor binding: PET results link genotype to molecular phenotype in depression.
Kautzky A, James GM, Philippe C, Baldinger-Melich P, Kraus C, Kranz GS, Vanicek T, Gryglewski G, Hartmann AM, Hahn A, Wadsak W, Mitterhauser M, Rujescu D, Kasper S, Lanzenberger R. Kautzky A, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 16;9(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0308-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30664620 Free PMC article. - Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor rs6265 polymorphism is associated with severe cancer-related fatigue and neuropathic pain in female cancer survivors.
Goto T, Von Ah D, Li X, Xiang L, Kwiat C, Nguyen C, Hsiao CP, Saligan LN. Goto T, et al. J Cancer Surviv. 2024 Dec;18(6):1851-1860. doi: 10.1007/s11764-023-01426-w. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Cancer Surviv. 2024. PMID: 37462904 Free PMC article. - Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mental disorders.
Lin CC, Huang TL. Lin CC, et al. Biomed J. 2020 Apr;43(2):134-142. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 May 5. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32386841 Free PMC article. Review. - The genetics of major depression.
Flint J, Kendler KS. Flint J, et al. Neuron. 2014 Feb 5;81(3):484-503. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.027. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24507187 Free PMC article. Review. - Mice with altered BDNF signaling as models for mood disorders and antidepressant effects.
Lindholm JS, Castrén E. Lindholm JS, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Apr 30;8:143. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00143. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24817844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Press; 2000.
- Anttila S, Huuhka K, Huuhka M, Rontu R, Hurme M, Leinonen E, Lehtimaki T. Interaction between 5-HT1A and BDNF genotypes increases the risk of treatment-resistant depression. J Neural Transm. 2007;114:1065–1068. - PubMed
- Chen L, Lawlor DA, Lewis SJ, Yuan W, Abdollahi MR, Timpson NJ, Day IN, Ebrahim S, Smith GD, Shugart YY. Genetic association study of BDNF in depression: Finding from two cohort studies and a meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet Part B. 2008;147B:814–821. - PubMed
- Chen L, Wang Y, Xiao H, Wang L, Wang C, Guo S, Zhao Y, Hua P, Liu W, Zhang N. The 712A/G polymorphism of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with Parkinson’s disease but not major depressive disorder in a Chinese Han population. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408:318–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0902227/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 DA010075/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50DA010075-16/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K013041/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000733/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources