A role for A-to-I RNA editing in temperature adaptation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
A role for A-to-I RNA editing in temperature adaptation
Sandra C Garrett et al. Physiology (Bethesda). 2012 Dec.
Abstract
A-to-I RNA editing can recode mRNAs, giving organisms the option to express diverse, functionally distinct protein isoforms. Here, we propose that RNA editing is inherently geared for temperature adaptation because it tends to recode to smaller, less stabilizing amino acids. Studies on how editing affects protein function support this idea.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
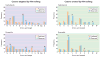
FIGURE 1. Predicted and observed frequencies of codons targeted and created by A-to-I RNA editing
All codons that could be edited to produce a different amino acid were identified. The relative frequencies of these codons in gene coding regions were then determined with the codon usage tables available at
(compiled using sequence data from GenBank, NCBI). Predicted editing percentages were calculated assuming that any adenosine within a codon would be randomly targeted for editing. Observed editing frequencies for Drosophila were based on the 611 sites identified in the developmental transcriptome project (22). For Cephalopods, a list of 79 sites was compiled using published data for Loligo and octopus (11, 18, 35, 49, 52) and also unpublished data from the Rosenthal laboratory. To determine whether the differences between predicted and observed editing frequencies were significant, we calculated the expected standard deviation for sample sizes of 611 and 79. If the observed difference was >2 SD (95% confidence interval) from the expected value, we considered the deviation significant. *Confidence interval of ≥95%. **Confidence interval of ≥99.7%.
Similar articles
- The emerging role of RNA editing in plasticity.
Rosenthal JJ. Rosenthal JJ. J Exp Biol. 2015 Jun;218(Pt 12):1812-21. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119065. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26085659 Free PMC article. Review. - RNA editing generates mRNA isoforms with distinct stabilities that may expand the thermal tolerance of mRNA and proteins in Mytilus species.
Liao ML, Zhu YJ, Zhu XL, Somero GN, Dong YW. Liao ML, et al. Zool Res. 2025 May 18;46(3):527-537. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.383. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 40259733 - Serotonin 2C receptors: suicide, serotonin, and runaway RNA editing.
Schmauss C. Schmauss C. Neuroscientist. 2003 Aug;9(4):237-42. doi: 10.1177/1073858403253669. Neuroscientist. 2003. PMID: 12934707 Review. - Proteome Diversification by RNA Editing.
Eisenberg E. Eisenberg E. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2181:229-251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0787-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32729084 Review. - Quantification of RNA editing of the serotonin 2C receptor (5-HT(₂C)R) ex vivo.
Lanfranco MF, Anastasio NC, Seitz PK, Cunningham KA. Lanfranco MF, et al. Methods Enzymol. 2010;485:311-28. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381296-4.00018-X. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 21050925
Cited by
- Dynamic response of RNA editing to temperature in grape by RNA deep sequencing.
Zhang A, Jiang X, Zhang F, Wang T, Zhang X. Zhang A, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2020 May;20(3):421-432. doi: 10.1007/s10142-019-00727-7. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Funct Integr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31745671 Free PMC article. - Current strategies for Site-Directed RNA Editing using ADARs.
Montiel-Gonzalez MF, Diaz Quiroz JF, Rosenthal JJC. Montiel-Gonzalez MF, et al. Methods. 2019 Mar 1;156:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30502398 Free PMC article. Review. - Dynamic response of RNA editing to temperature in Drosophila.
Rieder LE, Savva YA, Reyna MA, Chang YJ, Dorsky JS, Rezaei A, Reenan RA. Rieder LE, et al. BMC Biol. 2015 Jan 3;13:1. doi: 10.1186/s12915-014-0111-3. BMC Biol. 2015. PMID: 25555396 Free PMC article. - How nontraditional model systems can save us.
Gladfelter AS. Gladfelter AS. Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Nov 1;26(21):3687-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-06-0429. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26515971 Free PMC article. - The cellular and KSHV A-to-I RNA editome in primary effusion lymphoma and its role in the viral lifecycle.
Rajendren S, Ye X, Dunker W, Richardson A, Karijolich J. Rajendren S, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 13;14(1):1367. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37105-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36914661 Free PMC article.
References
- Bhalla T, Rosenthal JJ, Holmgren M, Reenan R. Control of human potassium channel inactivation by editing of a small mRNA hairpin. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:950–956. - PubMed
- Bjelic S, Brandsdal BO, Aqvist J. Cold adaptation of enzyme reaction rates. Biochemistry. 2008;47:10049–10057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS-064259/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS064259/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- FNS-064774A/PHS HHS/United States
- 2 U54 NS-039405-06/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS039405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2G12 RR-003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 8G12 MD-007600/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007600/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources