Structure of the Atg12-Atg5 conjugate reveals a platform for stimulating Atg8-PE conjugation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Structure of the Atg12-Atg5 conjugate reveals a platform for stimulating Atg8-PE conjugation
Nobuo N Noda et al. EMBO Rep. 2013 Feb.
Abstract
Atg12 is conjugated to Atg5 through enzymatic reactions similar to ubiquitination. The Atg12-Atg5 conjugate functions as an E3-like enzyme to promote lipidation of Atg8, whereas lipidated Atg8 has essential roles in both autophagosome formation and selective cargo recognition during autophagy. However, the molecular role of Atg12 modification in these processes has remained elusive. Here, we report the crystal structure of the Atg12-Atg5 conjugate. In addition to the isopeptide linkage, Atg12 forms hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions with Atg5, thereby fixing its position on Atg5. Structural comparison with unmodified Atg5 and mutational analyses showed that Atg12 modification neither induces a conformational change in Atg5 nor creates a functionally important architecture. Rather, Atg12 functions as a binding module for Atg3, the E2 enzyme for Atg8, thus endowing Atg5 with the ability to interact with Atg3 to facilitate Atg8 lipidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
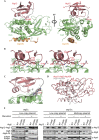
Crystal structure of the Atg12–Atg5 conjugate bound to Atg16N. (A) Ribbon representation of the Atg12–Atg5 conjugate bound to Atg16N. Atg12, Atg5 and Atg6 are coloured salmon pink, green and orange, respectively. Atg12 Phe 185 and Gly 186 and Atg5 Lys 149 are shown with a stick model. The disordered C-terminal region of Atg12 (residues 182–184) is indicated with a broken line. The left figure was obtained by a 90° rotation of the right figure along the vertical axis. The amino- and carboxy-termini are denoted as N and C, respectively. All of the figures representing the molecular structures were generated with PyMOL [26]. (B) Stereo view of the detailed interactions between Atg12 and Atg5. The side chains of the residues involved in the Atg12–Atg5 interaction are shown with a stick model, in which nitrogen and oxygen atoms are coloured red and blue, respectively. (C) Electron density map of the isopeptide linkage between Atg12 Gly 186 and Atg5 Lys 149. The simulated annealing_F_o–_F_c difference Fourier map was calculated by omitting Atg12 Phe 185 and Gly 186 and Atg5 Lys 149, and is shown with black meshes at 5.0σ. (D) Superimposition of the Atg5-Atg16N complex structure (PDB ID 2DYM) on that of the Atg12–Atg5-Atg16N complex. The Atg12–Atg5-Atg16N complex is coloured red, while the Atg5-Atg16N complex is coloured grey. Atg12 Phe 185 and Gly 186 and the side chain of Atg5 Lys 149 are shown with a stick model. (E) In vivo analyses of the Atg12 and Atg5 mutants for studying the functional significance of the non-covalent Atg12-Atg5 interactions. Yeast cells with or without starvation were lysed and subjected to urea SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) followed by western blotting. Ape1, aminopeptidase I; mApe1, mature form of Ape1; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; prApe1, preform of Ape1; WT, wild-type.
Figure 2
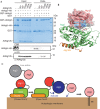
Atg12 functions as a binding module for Atg3. (A) In vitro pull-down assay using recombinant plant Atg homologues. (B) Mapping of the mutated residues on the Atg12–Atg5-Atg16N complex structure. Atg5 and Atg16N are shown with a ribbon model, whereas Atg12 is shown with both surface and ribbon models. The side chains of Tyr 147, Tyr 149 and Phe 154 of Atg12 are shown with a stick model and coloured grey (Tyr 147) or blue (Tyr 149 and Phe 154). Corresponding AtAtg12b residues are indicated in parentheses. Atg12 Phe 185 and Gly 186 and the side chain of Atg5 Lys 149 are shown with a stick model. (C) Proposed model of Atg8–PE conjugate formation mediated by the Atg12–Atg5-Atg16 complex. CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining; GST, glutathione _S_-transferase; HA, haemagglutinin; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; WT, wild-type.
Similar articles
- The Atg12-Atg5 conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in autophagy.
Hanada T, Noda NN, Satomi Y, Ichimura Y, Fujioka Y, Takao T, Inagaki F, Ohsumi Y. Hanada T, et al. J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 28;282(52):37298-302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700195200. Epub 2007 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17986448 - Atg12-Interacting Motif Is Crucial for E2-E3 Interaction in Plant Atg8 System.
Matoba K, Noda NN. Matoba K, et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021 Sep 1;44(9):1337-1343. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00439. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34193767 - Dissecting the role of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation.
Walczak M, Martens S. Walczak M, et al. Autophagy. 2013 Mar;9(3):424-5. doi: 10.4161/auto.22931. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Autophagy. 2013. PMID: 23321721 Free PMC article. - The Atg8 and Atg12 ubiquitin-like conjugation systems in macroautophagy. 'Protein modifications: beyond the usual suspects' review series.
Geng J, Klionsky DJ. Geng J, et al. EMBO Rep. 2008 Sep;9(9):859-64. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.163. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18704115 Free PMC article. Review. - Beyond Atg8 binding: The role of AIM/LIR motifs in autophagy.
Fracchiolla D, Sawa-Makarska J, Martens S. Fracchiolla D, et al. Autophagy. 2017 May 4;13(5):978-979. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1277311. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28121222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Upstream open reading frames mediate autophagy-related protein translation.
Yang Y, Gatica D, Liu X, Wu R, Kang R, Tang D, Klionsky DJ. Yang Y, et al. Autophagy. 2023 Feb;19(2):457-473. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2059744. Epub 2022 Apr 10. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 35363116 Free PMC article. - Evolutionary diversification of the autophagy-related ubiquitin-like conjugation systems.
Zhang S, Yazaki E, Sakamoto H, Yamamoto H, Mizushima N. Zhang S, et al. Autophagy. 2022 Dec;18(12):2969-2984. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2059168. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35427200 Free PMC article. - PACAP-Sirtuin3 alleviates cognitive impairment through autophagy in Alzheimer's disease.
Wang Q, Wang Y, Li S, Shi J. Wang Q, et al. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Oct 27;15(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01334-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37891608 Free PMC article. - Dual PI-3 kinase/mTOR inhibition impairs autophagy flux and induces cell death independent of apoptosis and necroptosis.
Button RW, Vincent JH, Strang CJ, Luo S. Button RW, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5157-75. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6986. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26814436 Free PMC article. - Optineurin promotes autophagosome formation by recruiting the autophagy-related Atg12-5-16L1 complex to phagophores containing the Wipi2 protein.
Bansal M, Moharir SC, Sailasree SP, Sirohi K, Sudhakar C, Sarathi DP, Lakshmi BJ, Buono M, Kumar S, Swarup G. Bansal M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 5;293(1):132-147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801944. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29133525 Free PMC article.
References
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 425–479 - PubMed
- Mizushima N, Noda T, Yoshimori T, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, George MD, Klionsky DJ, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y (1998) A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature 395: 395–398 - PubMed
- Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y (2011) The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 107–132 - PubMed
- Noda NN, Ohsumi Y, Inagaki F (2009) ATG systems from the protein structural point of view. Chem Rev 109: 1587–1598 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases