HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner - PubMed (original) (raw)
HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner
Melissa Malvaez et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013.
Abstract
Nonspecific histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition has been shown to facilitate the extinction of drug-seeking behavior in a manner resistant to reinstatement. A key open question is which specific HDAC is involved in the extinction of drug-seeking behavior. Using the selective HDAC3 inhibitor RGFP966, we investigated the role of HDAC3 in extinction and found that systemic treatment with RGFP966 facilitates extinction in mice in a manner resistant to reinstatement. We also investigated whether the facilitated extinction is related to the enhancement of extinction consolidation during extinction learning or to negative effects on performance or reconsolidation. These are key distinctions with regard to any compound being used to modulate extinction, because a more rapid decrease in a defined behavior is interpreted as facilitated extinction. Using an innovative combination of behavioral paradigms, we found that a single treatment of RGFP966 enhances extinction of a previously established cocaine-conditioned place preference, while simultaneously enhancing long-term object-location memory within subjects. During extinction consolidation, HDAC3 inhibition promotes a distinct pattern of histone acetylation linked to gene expression within the infralimbic cortex, hippocampus, and nucleus accumbens. Thus, the facilitated extinction of drug-seeking cannot be explained by adverse effects on performance. These results demonstrate that HDAC3 inhibition enhances the memory processes involved in extinction of drug-seeking behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: G.A.R. and M.A.W. received research support from a Sponsored Research Agreement from Repligen Corp. V.J., S.C., and J.R.R. are employed by Repligen Corp. M.M. and S.C.M. report no financial disclosures.
Figures
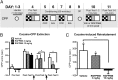
Fig. 1.
HDAC3 inhibition enhances the rate and persistence of extinction of cocaine-CPP. (A) Schematic of cocaine-CPP training and extinction. (B) Treatment with RGFP966 (10 mg/kg) after posttest 1 significantly reduced cocaine-CPP, and the effect was maintained in subsequent CPP tests. Vehicle, n = 12; RGFP966 3 mg/kg, n = 12; RGFP966 10 mg/kg, n = 12. (C) Mice treated with RGFP966 (10 mg/kg) during extinction consolidation did not reinstate cocaine-seeking behavior; Vehicle, n = 8; RGFP966 3 mg/kg, n = 7; RGFP966 10 mg/kg, n = 8. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. †Significantly different from 0. *Significantly different from vehicle; P < 0.05.
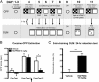
Fig. 2.
HDAC3 inhibition simultaneously reduces drug-seeking behavior and enhances memory. (A) Schematic of cocaine-CPP training and extinction, followed in parallel with OLM training. RGFP966 was administered immediately after extinction training, 1 h before OLM training in the same mice. Vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966 10 mg/kg; n = 6. (B) RGFP966 administered immediately after a nonreinforced exposure resulted in loss of CPP the next day. (C) RGFP966 treatment resulted in significantly enhanced object location memory. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *Significantly different from vehicle; P < 0.05.
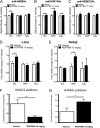
Fig. 3.
HDAC3 inhibition promotes histone acetylation and gene expression during extinction consolidation. (A) RGFP966 treatment promoted acetylation of H4K8 in the IFC (vehicle, n = 5; RGFP966, n = 5), but not in the HIPP (vehicle, n = 3; RGFP966, n = 3) or NAc (vehicle, n = 3; RGFP966, n = 3). (B and C) RGFP966 treatment increased acetylation of H3K14 in the IFC (vehicle, n = 5; RGFP966, n = 5), HIPP (vehicle, n = 5; RGFP966, n = 5), and NAc (vehicle, n = 5; RGFP966, n = 6) during extinction consolidation (B), with no difference in acetylation of H2BK12 (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 5 for each brain region) (C). (D) c-FOS expression was significantly increased in the IFC (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 5), but not in the HIPP (vehicle, n = 7; RGFP966, n = 6) or NAc (vehicle, n = 9; RGFP966, n = 7), of mice treated with RGFP966. (E) NR4A2 expression was significantly increased in the HIPP (vehicle, n = 5; RGFP966, n = 5), but not in the IFC (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 5) or NAc (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 5), after RGFP966 treatment during extinction consolidation. (F and G) RGFP966 treatment led to decreased HDAC3 occupancy at the c-fos promoter (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 7) (F), with a corresponding increase in acetylation of H4K8 (vehicle, n = 6; RGFP966, n = 8) (G). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *Significantly different from vehicle; P < 0.05.
Comment in
- Opening the genome to reduce cocaine-seeking behavior.
LaLumiere RT. LaLumiere RT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 12;110(7):2442-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222128110. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23382247 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Effects of a histone deacetylase 3 inhibitor on extinction and reinstatement of cocaine self-administration in rats.
Hitchcock LN, Raybuck JD, Wood MA, Lattal KM. Hitchcock LN, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):517-529. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5122-2. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30488346 Free PMC article. - Enhancement of BDNF Expression and Memory by HDAC Inhibition Requires BET Bromodomain Reader Proteins.
Sartor GC, Malvezzi AM, Kumar A, Andrade NS, Wiedner HJ, Vilca SJ, Janczura KJ, Bagheri A, Al-Ali H, Powell SK, Brown PT, Volmar CH, Foster TC, Zeier Z, Wahlestedt C. Sartor GC, et al. J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 23;39(4):612-626. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1604-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30504275 Free PMC article. - Modulation of chromatin modification facilitates extinction of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference.
Malvaez M, Sanchis-Segura C, Vo D, Lattal KM, Wood MA. Malvaez M, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Jan 1;67(1):36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.032. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 19765687 Free PMC article. - Distinct roles for the deacetylase domain of HDAC3 in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex in the formation and extinction of memory.
Alaghband Y, Kwapis JL, López AJ, White AO, Aimiuwu OV, Al-Kachak A, Bodinayake KK, Oparaugo NC, Dang R, Astarabadi M, Matheos DP, Wood MA. Alaghband Y, et al. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Nov;145:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28890149 Free PMC article. - The Class I HDAC inhibitor RGFP963 enhances consolidation of cued fear extinction.
Bowers ME, Xia B, Carreiro S, Ressler KJ. Bowers ME, et al. Learn Mem. 2015 Mar 16;22(4):225-31. doi: 10.1101/lm.036699.114. Print 2015 Apr. Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25776040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor RGFP109 Overcomes Temozolomide Resistance by Blocking NF-κB-Dependent Transcription in Glioblastoma Cell Lines.
Li ZY, Li QZ, Chen L, Chen BD, Wang B, Zhang XJ, Li WP. Li ZY, et al. Neurochem Res. 2016 Dec;41(12):3192-3205. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2043-5. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27632183 - Regulation of pDC fate determination by histone deacetylase 3.
Zhang Y, Wu T, He Z, Lai W, Shen X, Lv J, Wang Y, Wu L. Zhang Y, et al. Elife. 2023 Nov 27;12:e80477. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80477. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38011375 Free PMC article. - Kinetic Analysis and Quantification of [¹¹C]Martinostat for in Vivo HDAC Imaging of the Brain.
Wey HY, Wang C, Schroeder FA, Logan J, Price JC, Hooker JM. Wey HY, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 May 20;6(5):708-15. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00066. Epub 2015 Mar 25. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25768025 Free PMC article. - FDG-PET imaging reveals local brain glucose utilization is altered by class I histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Schroeder FA, Chonde DB, Riley MM, Moseley CK, Granda ML, Wilson CM, Wagner FF, Zhang YL, Gale J, Holson EB, Haggarty SJ, Hooker JM. Schroeder FA, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2013 Aug 29;550:119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.016. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23810801 Free PMC article. - HDAC3 Activity is Essential for Human Leukemic Cell Growth and the Expression of β-catenin, MYC, and WT1.
Beyer M, Romanski A, Mustafa AM, Pons M, Büchler I, Vogel A, Pautz A, Sellmer A, Schneider G, Bug G, Krämer OH. Beyer M, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 26;11(10):1436. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101436. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31561534 Free PMC article.
References
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293(5532):1074–1080. - PubMed
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128(4):693–705. - PubMed
- Alarcón JM, et al. Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP+/− mice: A model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron. 2004;42(6):947–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 DA031989/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA025922/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS045540/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31DA29368/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS045540/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA029368/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DA031520/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32DA031520/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases