Comparison between 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and para-aminosalicylic acid (4-PAS) as potential protectors against Mn-induced neurotoxicity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Comparison between 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and para-aminosalicylic acid (4-PAS) as potential protectors against Mn-induced neurotoxicity
Dinamene Santos et al. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013 Apr.
Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is an essential metal for biological systems; however, occupational or clinical exposure to high levels of Mn can produce a neurological disorder called manganism. Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation play major roles in the Mn-induced neurodegeneration leading to dysfunction of the basal ganglia. We investigated the toxic effects of MnCl2 in an immortalized rat brain endothelial cell line (RBE4) and the protective effects of the radical scavenging aminosalicylic acids, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and 4-aminosalicylic acid (4-PAS). Mn cytotoxicity was determined with 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity. A significant decrease in MTT reduction concomitant with increased LDH release was noted in RBE4 cells exposed for 24 h to MnCl2 (600 and 800 μM; p < 0.0001). Our results establish that compared to 4-PAS, 5-ASA has greater efficacy in protecting RBE4 cells from Mn-induced neurotoxicity after preexposure to MnCl2 800 μM (p < 0.0001).
Figures
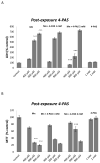
Figure 1
The effect of 4-PAS on MTT reduction (A) and membrane integrity (B) in RBE4 cells cultured in 96-well culture plates treated for 24 h with 400, 600 or 800 μM MnCl2 or medium alone. After 24 h RBE4 cells were treated for 45 minutes with medium or 1 or 2 mM 4-PAS in DMSO. Values of MTT (% control) (A) and LDH (% control) (B) represent mean ± SEM (n=12). ^^^ p<0.0001 significantly different from control group, *** p<0.0001,** p<0.001 significantly different from RBE4 cells exposed to the respective Mn 400, 600 and 800 μM group by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests.
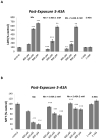
Figure 2
The effect of 5-ASA on MTT reduction (A) and membrane integrity (B) in RBE4 cells cultured in 96-well culture plates treated for 24 h with 400, 600 or 800 μM MnCl2 or medium alone. After 24 h RBE4 cells were treated for 45 minutes with medium, or 1 or 2 mM 5-ASA in HCl. Values of MTT (% control) (A) and LDH (% control) (B) represent mean ± SEM (n=12). ^^^ p<0.0001 significantly different from control group, *** p<0.0001, ** p<0.001 significantly different from RBE4 cells exposed to the respective Mn 400, 600 and 800 μM group by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests.
Similar articles
- "Manganese-induced neurotoxicity: a review of its behavioral consequences and neuroprotective strategies".
Peres TV, Schettinger MR, Chen P, Carvalho F, Avila DS, Bowman AB, Aschner M. Peres TV, et al. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Nov 4;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0099-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27814772 Free PMC article. Review. - Antioxidants prevent the cytotoxicity of manganese in RBE4 cells.
Marreilha dos Santos AP, Santos D, Au C, Milatovic D, Aschner M, Batoréu MC. Marreilha dos Santos AP, et al. Brain Res. 2008 Oct 21;1236:200-5. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.125. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18725210 - Sodium Para-aminosalicylic Acid Protected Primary Cultured Basal Ganglia Neurons of Rat from Manganese-Induced Oxidative Impairment and Changes of Amino Acid Neurotransmitters.
Li SJ, Li Y, Chen JW, Yuan ZX, Mo YH, Lu GD, Jiang YM, Ou CY, Wang F, Huang XW, Luo YN, Ou SY, Huang YN. Li SJ, et al. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 Apr;170(2):357-65. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0472-7. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26286965 - Sodium para-aminosalicylate protected cultured basal ganglia astrocytes from manganese-induced DNA damages and alteration of amino acid neurotransmitter levels.
Li SJ, Luo YN, Li Y, Chen JW, Mo YH, Yuan ZX, Ou SY, Ou CY, Jiang YM, Deng XF. Li SJ, et al. J Toxicol Sci. 2016;41(5):573-81. doi: 10.2131/jts.41.573. J Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27665767 - Treatment of manganese and lead poisoning with sodium para-aminosalicylic acid: A contemporary update.
Xie YH, Song HX, Peng JC, Li SJ, Ou SY, Aschner M, Jiang YM. Xie YH, et al. Toxicol Lett. 2024 Jul;398:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Toxicol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38909920 Review.
Cited by
- "Manganese-induced neurotoxicity: a review of its behavioral consequences and neuroprotective strategies".
Peres TV, Schettinger MR, Chen P, Carvalho F, Avila DS, Bowman AB, Aschner M. Peres TV, et al. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Nov 4;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0099-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27814772 Free PMC article. Review. - Manganese, a Likely Cause of 'Parkinson's in Cirrhosis', a Unique Clinical Entity of Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration.
Mehkari Z, Mohammed L, Javed M, Althwanay A, Ahsan F, Oliveri F, Goud HK, Rutkofsky IH. Mehkari Z, et al. Cureus. 2020 Sep 14;12(9):e10448. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10448. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33072457 Free PMC article. Review. - Levels of major and trace metals in the scalp hair of Crohn's disease patients: correlations among transition metals.
Ogasawara H, Hayasaka M, Maemoto A, Furukawa S, Ito T, Kimura O, Endo T. Ogasawara H, et al. Biometals. 2021 Feb;34(1):197-210. doi: 10.1007/s10534-020-00272-y. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Biometals. 2021. PMID: 33387116 - Roles of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance protein in transporting para-aminosalicylic acid and its N-acetylated metabolite in mice brain.
Hong L, Xu C, O'Neal S, Bi HC, Huang M, Zheng W, Zeng S. Hong L, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Dec;35(12):1577-85. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.103. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 25418377 Free PMC article. - Sodium P-aminosalicylic Acid Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation in BV2 Microglia by Modulating NF-κB Pathway.
Li J, Deng Y, Peng D, Zhao L, Fang Y, Zhu X, Li S, Aschner M, Ou S, Jiang Y. Li J, et al. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Dec;199(12):4688-4699. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02581-w. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 33447908
References
- Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–71. - PubMed
- Blanc P. Poisoning and Drug Overdose. Norwalk, California: Appleton & Lange; 1990.
- Bressler JP, Olivi L, Cheong JH, Kim Y, Bannona D. Divalent metal transporter 1 in lead and cadmium transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1012:142–52. - PubMed
- Cotzias GC, Horiuchi K, Fuenzalida S, Mena I. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clearance of tissue manganese concentrations with persistance of the neurological picture. Neurology. 1968;18:376–82. - PubMed
- Demeuse P, Kerkhofs A, Struys-Ponsar C, Knoops B, Remacle C, van den Bosch de Aguilar P. Compartmentalized coculture of rat brain endothelial cells and astrocytes: a syngenic model to study the blood-brain barrier. J Neurosci Methods. 2002;121:21–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources