Genome-wide study of association and interaction with maternal cytomegalovirus infection suggests new schizophrenia loci - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.2. Epub 2013 Jan 29.
D Demontis, J Grove, J Pallesen, M V Hollegaard, C B Pedersen, A Hedemand, M Mattheisen; GROUP investigators10; A Uitterlinden, M Nyegaard, T Ørntoft, C Wiuf, M Didriksen, M Nordentoft, M M Nöthen, M Rietschel, R A Ophoff, S Cichon, R H Yolken, D M Hougaard, P B Mortensen, O Mors
Collaborators
- PMID: 23358160
- PMCID: PMC3932405
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.2
Genome-wide study of association and interaction with maternal cytomegalovirus infection suggests new schizophrenia loci
A D Børglum et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Mar.
Abstract
Genetic and environmental components as well as their interaction contribute to the risk of schizophrenia, making it highly relevant to include environmental factors in genetic studies of schizophrenia. This study comprises genome-wide association (GWA) and follow-up analyses of all individuals born in Denmark since 1981 and diagnosed with schizophrenia as well as controls from the same birth cohort. Furthermore, we present the first genome-wide interaction survey of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and maternal cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. The GWA analysis included 888 cases and 882 controls, and the follow-up investigation of the top GWA results was performed in independent Danish (1396 cases and 1803 controls) and German-Dutch (1169 cases, 3714 controls) samples. The SNPs most strongly associated in the single-marker analysis of the combined Danish samples were rs4757144 in ARNTL (P=3.78 × 10(-6)) and rs8057927 in CDH13 (P=1.39 × 10(-5)). Both genes have previously been linked to schizophrenia or other psychiatric disorders. The strongest associated SNP in the combined analysis, including Danish and German-Dutch samples, was rs12922317 in RUNDC2A (P=9.04 × 10(-7)). A region-based analysis summarizing independent signals in segments of 100 kb identified a new region-based genome-wide significant locus overlapping the gene ZEB1 (P=7.0 × 10(-7)). This signal was replicated in the follow-up analysis (P=2.3 × 10(-2)). Significant interaction with maternal CMV infection was found for rs7902091 (P(SNP × CMV)=7.3 × 10(-7)) in CTNNA3, a gene not previously implicated in schizophrenia, stressing the importance of including environmental factors in genetic studies.
Figures
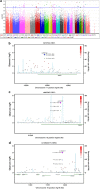
Figure 1
(a) Manhattan plot of genome-wide association (GWA) analysis. The blue line indicates _P_=1 × 10−4. (b) Regional association plot of rs4757144 located in ARNTL. (c) Regional association plot of rs8057927 located in CDH13. (d) Regional association plot of rs12922317 located in RUNDC2A. The _P_-values in green are from the GWA analysis, _P_-values marked in blue are from the combined analysis of Danish individuals, _P_-values marked in purple are from the extended meta-analysis. The linkage disequilibrium (LD; _r_2) between the SNP in focus and its flanking markers genotyped in the GWA study are demonstrated in red (high LD) to white (low LD). The recombination rate is plotted in blue according to HapMap (CEU).
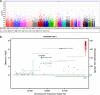
Figure 2
(a) Manhattan plot of region-wise association analysis. The blue line indicates genome-wide significance (_P_=9.0 × 10−7). (b) Regional association plot of rs3123688 located upstream of ZEB1. The _P_-values in green are from the genome-wide association (GWA) analysis and _P_-values marked in blue are from the combined analysis of Danish individuals. The vertical lines represent the region-wise _P_-values. The linkage disequilibrium (LD; _r_2) between the single nucleotide polymorphism in focus and its flanking markers genotyped in the GWA study are demonstrated in red (high LD) to white (low LD). The recombination rate is plotted in blue according to HapMap (CEU).
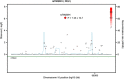
Figure 3
Regional association plot of rs7902091. _P_-values of interaction between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and maternal cytomegalovirus infection. The linkage disequilibrium (LD; _r_2) between the SNP in focus and its flanking markers genotyped in the genome-wide association study are demonstrated in red (high LD) to white (low LD). The recombination rate is plotted in blue according to HapMap (CEU).
Similar articles
- Infection and inflammation in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a genome wide study for interactions with genetic variation.
Avramopoulos D, Pearce BD, McGrath J, Wolyniec P, Wang R, Eckart N, Hatzimanolis A, Goes FS, Nestadt G, Mulle J, Coneely K, Hopkins M, Ruczinski I, Yolken R, Pulver AE. Avramopoulos D, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0116696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116696. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781172 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of risk loci for schizophrenia derived from genome-wide association studies in a German population.
Schanze D, Ekici AB, Gawlik M, Pfuhlmann B, Reis A, Stöber G. Schanze D, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011 Mar;156(2):198-203. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31156. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21302348 - Common variants on 17q25 and gene-gene interactions conferring risk of schizophrenia in Han Chinese population and regulating gene expressions in human brain.
Guan L, Wang Q, Wang L, Wu B, Chen Y, Liu F, Ye F, Zhang T, Li K, Yan B, Lu C, Su L, Jin G, Wang H, Tian H, Wang L, Chen Z, Wang Y, Chen J, Yuan Y, Cong W, Zheng J, Wang J, Xu X, Liu H, Xiao W, Han C, Zhang Y, Jia F, Qiao X; Genetic REsearch on schizophrenia neTwork-China and Netherland (GREAT-CN); Zhang D, Zhang M, Ma H. Guan L, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Sep;21(9):1244-50. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.204. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26728569 - Recent genetic findings in schizophrenia and their therapeutic relevance.
Harrison PJ. Harrison PJ. J Psychopharmacol. 2015 Feb;29(2):85-96. doi: 10.1177/0269881114553647. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25315827 Free PMC article. Review. - Molecular genetic gene-environment studies using candidate genes in schizophrenia: a systematic review.
Modinos G, Iyegbe C, Prata D, Rivera M, Kempton MJ, Valmaggia LR, Sham PC, van Os J, McGuire P. Modinos G, et al. Schizophr Res. 2013 Nov;150(2-3):356-65. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Schizophr Res. 2013. PMID: 24094883 Review.
Cited by
- Maternal Immune Activation and the Development of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission of the Offspring: Relevance for Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses.
Aguilar-Valles A, Rodrigue B, Matta-Camacho E. Aguilar-Valles A, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2020 Aug 21;11:852. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00852. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33061910 Free PMC article. Review. - Toxoplasma gondii-A Gastrointestinal Pathogen Associated with Human Brain Diseases.
Severance EG, Xiao J, Jones-Brando L, Sabunciyan S, Li Y, Pletnikov M, Prandovszky E, Yolken R. Severance EG, et al. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;131:143-163. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27793216 Free PMC article. Review. - High-Quality Exome Sequencing of Whole-Genome Amplified Neonatal Dried Blood Spot DNA.
Poulsen JB, Lescai F, Grove J, Bækvad-Hansen M, Christiansen M, Hagen CM, Maller J, Stevens C, Li S, Li Q, Sun J, Wang J, Nordentoft M, Werge TM, Mortensen PB, Børglum AD, Daly M, Hougaard DM, Bybjerg-Grauholm J, Hollegaard MV. Poulsen JB, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Apr 18;11(4):e0153253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153253. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27089011 Free PMC article. - Increased Striatal Presynaptic Dopamine in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Maternal Immune Activation: A Longitudinal Neurodevelopmental Positron Emission Tomography Study With Implications for Schizophrenia.
Smucny J, Vlasova RM, Lesh TA, Rowland DJ, Wang G, Chaudhari AJ, Chen S, Iosif AM, Hogrefe CE, Bennett JL, Shumann CM, Van de Water JA, Maddock RJ, Styner MA, Geschwind DH, McAllister AK, Bauman MD, Carter CS. Smucny J, et al. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023 May;8(5):505-513. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2022.10.012. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023. PMID: 36805246 Free PMC article. - Association Between Childhood Green Space, Genetic Liability, and the Incidence of Schizophrenia.
Engemann K, Pedersen CB, Agerbo E, Arge L, Børglum AD, Erikstrup C, Hertel O, Hougaard DM, McGrath JJ, Mors O, Mortensen PB, Nordentoft M, Sabel CE, Sigsgaard T, Tsirogiannis C, Vilhjálmsson BJ, Werge T, Svenning JC, Horsdal HT. Engemann K, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2020 Dec 1;46(6):1629-1637. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa058. Schizophr Bull. 2020. PMID: 32415773 Free PMC article.
References
- Cardno AG, Gottesman II. Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bow-and-arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics. Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:12–17. - PubMed
- Rietschel M, Mattheisen M, Degenhardt F, Kahn RS, Linszen DH, Os JV, et al. Association between genetic variation in a region on chromosome 11 and schizophrenia in large samples from Europe. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17:906–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous