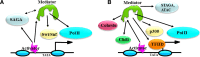Mechanisms of Mediator complex action in transcriptional activation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mechanisms of Mediator complex action in transcriptional activation
Suraiya A Ansari et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Aug.
Abstract
Mediator is a large multisubunit complex that plays a central role in the regulation of RNA Pol II transcribed genes. Conserved in overall structure and function among eukaryotes, Mediator comprises 25-30 protein subunits that reside in four distinct modules, termed head, middle, tail, and CDK8/kinase. Different subunits of Mediator contact other transcriptional regulators including activators, co-activators, general transcription factors, subunits of RNA Pol II, and specifically modified histones, leading to the regulated expression of target genes. This review is focused on the interactions of specific Mediator subunits with diverse transcription regulators and how those interactions contribute to Mediator function in transcriptional activation.
Figures
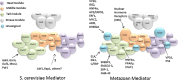
Fig. 1
Interactions of transcriptional activators with Mediator complex. Organization of the yeast and metazoan Mediator complexes is adapted from reference [8]. Abf1 and Rap1 in yeast may interact directly or indirectly with middle or head module subunits, as indicated by the dotted line. Interactions of activators with subunits from metazoan Mediator are mostly derived from studies on mammalian Mediator, but also include some from C. elegans and A. thaliana. See text for more details
Fig. 2
Interactions of Mediator with other co-activator complexes. a In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, activators make direct contacts to recruit both SAGA and Mediator, which may be independent or interdependent in associating with a particular promoter depending on both the activator and the promoter (dotted double arrow). Swi/Snf and Pol II recruitment generally depends on Mediator, with some possible exceptions. b In mammalian cells, Mediator participates in recruitment of a wide range of co-activators; see text for details. For clarity, interactions not involving Mediator are omitted
Similar articles
- Dynamic regulation of pol II transcription by the mammalian Mediator complex.
Malik S, Roeder RG. Malik S, et al. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 May;30(5):256-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.03.009. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15896744 Review. - Tail and Kinase Modules Differently Regulate Core Mediator Recruitment and Function In Vivo.
Jeronimo C, Langelier MF, Bataille AR, Pascal JM, Pugh BF, Robert F. Jeronimo C, et al. Mol Cell. 2016 Nov 3;64(3):455-466. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27773677 Free PMC article. - Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 positively cooperates with Mediator to promote thyroid hormone receptor-dependent transcriptional activation.
Belakavadi M, Fondell JD. Belakavadi M, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2010 May;30(10):2437-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01541-09. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20231357 Free PMC article. - The Mediator Complex: At the Nexus of RNA Polymerase II Transcription.
Jeronimo C, Robert F. Jeronimo C, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;27(10):765-783. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Trends Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28778422 Review. - Facilitated assembly of the preinitiation complex by separated tail and head/middle modules of the mediator.
Galdieri L, Desai P, Vancura A. Galdieri L, et al. J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 20;415(3):464-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.020. Epub 2011 Nov 23. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22137896 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Comparative analysis of retroviral Gag-host cell interactions: focus on the nuclear interactome.
Lambert GS, Rice BL, Maldonado RJK, Chang J, Parent LJ. Lambert GS, et al. Retrovirology. 2024 Jun 19;21(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12977-024-00645-y. Retrovirology. 2024. PMID: 38898526 Free PMC article. - Simple biochemical features underlie transcriptional activation domain diversity and dynamic, fuzzy binding to Mediator.
Sanborn AL, Yeh BT, Feigerle JT, Hao CV, Townshend RJ, Lieberman Aiden E, Dror RO, Kornberg RD. Sanborn AL, et al. Elife. 2021 Apr 27;10:e68068. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68068. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33904398 Free PMC article. - The MAPKKKs Ste11 and Bck1 jointly transduce the high oxidative stress signal through the cell wall integrity MAP kinase pathway.
Jin C, Kim SK, Willis SD, Cooper KF. Jin C, et al. Microb Cell. 2015 Sep 1;2(9):329-342. doi: 10.15698/mic2015.09.226. Microb Cell. 2015. PMID: 27135035 Free PMC article. - Function and dynamics of the Mediator complex: novel insights and new frontiers.
Morse RH. Morse RH. Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):39-52. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2085502. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 35708525 Free PMC article. Review. - The Mediator co-activator complex regulates Ty1 retromobility by controlling the balance between Ty1i and Ty1 promoters.
Salinero AC, Knoll ER, Zhu ZI, Landsman D, Curcio MJ, Morse RH. Salinero AC, et al. PLoS Genet. 2018 Feb 20;14(2):e1007232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007232. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29462141 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources