Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia by leveraging pleiotropy with cardiovascular-disease risk factors - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2013 Feb 7;92(2):197-209.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 31.
Srdjan Djurovic, Wesley K Thompson, Andrew J Schork, Kenneth S Kendler, Michael C O'Donovan, Dan Rujescu, Thomas Werge, Martijn van de Bunt, Andrew P Morris, Mark I McCarthy; International Consortium for Blood Pressure GWAS; Diabetes Genetics Replication and Meta-analysis Consortium; Psychiatric Genomics Consortium Schizophrenia Working Group; J Cooper Roddey, Linda K McEvoy, Rahul S Desikan, Anders M Dale
Collaborators, Affiliations
- PMID: 23375658
- PMCID: PMC3567279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.01.001
Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia by leveraging pleiotropy with cardiovascular-disease risk factors
Ole A Andreassen et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2013.
Abstract
Several lines of evidence suggest that genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have the potential to explain more of the "missing heritability" of common complex phenotypes. However, reliable methods for identifying a larger proportion of SNPs are currently lacking. Here, we present a genetic-pleiotropy-informed method for improving gene discovery with the use of GWAS summary-statistics data. We applied this methodology to identify additional loci associated with schizophrenia (SCZ), a highly heritable disorder with significant missing heritability. Epidemiological and clinical studies suggest comorbidity between SCZ and cardiovascular-disease (CVD) risk factors, including systolic blood pressure, triglycerides, low- and high-density lipoprotein, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and type 2 diabetes. Using stratified quantile-quantile plots, we show enrichment of SNPs associated with SCZ as a function of the association with several CVD risk factors and a corresponding reduction in false discovery rate (FDR). We validate this "pleiotropic enrichment" by demonstrating increased replication rate across independent SCZ substudies. Applying the stratified FDR method, we identified 25 loci associated with SCZ at a conditional FDR level of 0.01. Of these, ten loci are associated with both SCZ and CVD risk factors, mainly triglycerides and low- and high-density lipoproteins but also waist-to-hip ratio, systolic blood pressure, and body mass index. Together, these findings suggest the feasibility of using genetic-pleiotropy-informed methods for improving gene discovery in SCZ and identifying potential mechanistic relationships with various CVD risk factors.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
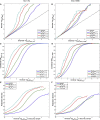
Figure 1
Enrichment and Replication (A and B) Stratified Q-Q plot of nominal versus empirical –log10 p values (corrected for inflation) in SCZ below the standard GWAS threshold of p < 5 × 10−8 as a function of significance of association with (A) TGs and (B) WHR at the levels of –log10(p) > 0, –log10(p) > 1, –log10(p) > 2, and –log10(p) > 3, which correspond to p < 1, p < 0.1, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively. Dashed lines indicate the null hypothesis. (C and D) Stratified TDR plots illustrating the TDR increase associated with increased pleiotropic enrichment in (C) SCZ conditioned on TG (SCZ|TG) and (D) SCZ conditioned on WHR (SCZ|WHR). (E and F) Cumulative replication plot showing the average rate of replication (p < 0.05) within SCZ substudies for a given p value threshold demonstrates that pleiotropic enriched SNP categories replicate at a higher rate in independent SCZ samples for (E) SCZ conditioned on TG (SCZ|TG) and (F) SCZ conditioned on WHR (SCZ|WHR). The vertical intercept is the overall replication rate per category.
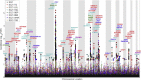
Figure 2
Conditional Manhattan Plot Conditional Manhattan plot of conditional –log10 (FDR) values for SCZ alone (black) and SCZ given the following CVD risk factors: TGs (SCZ|TG, red), LDL (SCZ|LDL, orange), HDL (SCZ|HDL, cyan), SBP (SCZ|SBP, green), BMI (SCZ|BMI, purple), WHR (SCZ|WHR, blue), and T2D (SCZ|T2D, chartreuse). SNPs with conditional –log10 FDR > 1.3 (i.e., FDR < 0.05) are shown with large points. A black line around the large points indicates the most significant SNP in each LD block, and this SNP was annotated with the closest gene, which is listed above the symbols in each locus (except for the HLA region on chromosome 6) and in Table S2. The figure shows the localization of 106 loci on a total of 21 chromosomes (1–19, 21, and 22). Details for the loci with –log10 FDR > 2 (i.e., FDR < 0.01) are shown in Table 1.
Similar articles
- Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder using pleiotropy-informed conditional false discovery rate.
Andreassen OA, Thompson WK, Schork AJ, Ripke S, Mattingsdal M, Kelsoe JR, Kendler KS, O'Donovan MC, Rujescu D, Werge T, Sklar P; Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC); Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia Working Groups; Roddey JC, Chen CH, McEvoy L, Desikan RS, Djurovic S, Dale AM. Andreassen OA, et al. PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003455. Epub 2013 Apr 25. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23637625 Free PMC article. - Shared common variants in prostate cancer and blood lipids.
Andreassen OA, Zuber V, Thompson WK, Schork AJ, Bettella F; PRACTICAL Consortium; CRUK GWAS; Djurovic S, Desikan RS, Mills IG, Dale AM. Andreassen OA, et al. Int J Epidemiol. 2014 Aug;43(4):1205-14. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyu090. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Int J Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24786909 Free PMC article. - Identifying common genetic variants in blood pressure due to polygenic pleiotropy with associated phenotypes.
Andreassen OA, McEvoy LK, Thompson WK, Wang Y, Reppe S, Schork AJ, Zuber V, Barrett-Connor E, Gautvik K, Aukrust P, Karlsen TH, Djurovic S, Desikan RS, Dale AM; International Consortium for Blood Pressure Genome-Wide Association Studies, Genetic Factors for Osteoporosis Consortium. Andreassen OA, et al. Hypertension. 2014 Apr;63(4):819-26. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02077. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24396023 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive identification of pleiotropic loci for body fat distribution using the NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies.
Kaur Y, Wang DX, Liu HY, Meyre D. Kaur Y, et al. Obes Rev. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-406. doi: 10.1111/obr.12806. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Obes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565845 Review. - How can genetics help understand the relationship between cognitive dysfunction and schizophrenia?
Smeland OB, Andreassen OA. Smeland OB, et al. Scand J Psychol. 2018 Feb;59(1):26-31. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12407. Scand J Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29356008 Review.
Cited by
- CLIMB: High-dimensional association detection in large scale genomic data.
Koch H, Keller CA, Xiang G, Giardine B, Zhang F, Wang Y, Hardison RC, Li Q. Koch H, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 12;13(1):6874. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34360-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36371401 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular disease and psychiatric disorders: An-up-to date review.
Parlati ALM, Nardi E, Basile C, Paolillo S, Marzano F, Chirico A, Buonocore D, Colella A, Fontanarosa S, Gallo L, Fierro MF, Carbone F, Gargiulo P, Prastaro M, Delle Grottaglie S, Santoro C, Marchesi A, Marchetti MF, Giovanni Carta M, Perrone Filardi P, Montisci R. Parlati ALM, et al. J Public Health Res. 2024 Oct 8;13(4):22799036241278817. doi: 10.1177/22799036241278817. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Public Health Res. 2024. PMID: 39398345 Free PMC article. Review. - A genome-wide association study of social trust in 33,882 Danish blood donors.
Sequeros CB, Hansen TF, Westergaard D, Louloudis I, Kalamajski S, Röder T, Rohde PD, Schwinn M, Clemmensen LH, Didriksen M, Nyegaard M, Hjalgrim H, Nielsen KR, Bruun MT, Ostrowski SR, Erikstrup C, Mikkelsen S, Sørensen E; DBDS Genomic Consortium; Pedersen OBV, Brunak S, Banasik K, Giordano GN. Sequeros CB, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 16;14(1):1402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51636-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38228779 Free PMC article. - Detection of Genetic Overlap Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Using GWAS Summary Statistics.
Lu H, Zhang J, Jiang Z, Zhang M, Wang T, Zhao H, Zeng P. Lu H, et al. Front Genet. 2021 Mar 18;12:656545. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.656545. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33815486 Free PMC article. - Schizophrenia is associated with excess multiple physical-health comorbidities but low levels of recorded cardiovascular disease in primary care: cross-sectional study.
Smith DJ, Langan J, McLean G, Guthrie B, Mercer SW. Smith DJ, et al. BMJ Open. 2013 Apr 17;3(4):e002808. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002808. Print 2013. BMJ Open. 2013. PMID: 23599376 Free PMC article.
References
- Glazier A.M., Nadeau J.H., Aitman T.J. Finding genes that underlie complex traits. Science. 2002;298:2345–2349. - PubMed
- Hirschhorn J.N., Daly M.J. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:95–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 098017/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG031224/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB005970/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- G0800509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HD061414/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DA029475/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical