Hypoxia-regulated microRNAs in human cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Hypoxia-regulated microRNAs in human cancer
Guomin Shen et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Mar.
Abstract
Hypoxia plays an important role in the tumor microenvironment by allowing the development and maintenance of cancer cells, but the regulatory mechanisms by which tumor cells adapt to hypoxic conditions are not yet well understood. MicroRNAs are recognized as a new class of master regulators that control gene expression and are responsible for many normal and pathological cellular processes. Studies have shown that hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF1) regulates a panel of microRNAs, whereas some of microRNAs target HIF1. The interaction between microRNAs and HIF1 can account for many vital events relevant to tumorigenesis, such as angiogenesis, metabolism, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, proliferation, metastasis, and resistance to anticancer therapy. This review will summarize recent findings on the roles of hypoxia and microRNAs in human cancer and illustrate the machinery by which microRNAs interact with hypoxia in tumor cells. It is expected to update our knowledge about the regulatory roles of microRNAs in regulating tumor microenvironments and thus benefit the development of new anticancer drugs.
Figures
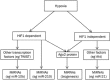
Figure 1
The machinery that hypoxia regulates miRNA expression.
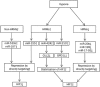
Figure 2
The machinery that miRNA regulates HIF1.
Similar articles
- Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: the role of microRNA.
Madanecki P, Kapoor N, Bebok Z, Ochocka R, Collawn JF, Bartoszewski R. Madanecki P, et al. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2013 Mar;18(1):47-57. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0037-0. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23124858 Free PMC article. Review. - A macrophage-dominant PI3K isoform controls hypoxia-induced HIF1α and HIF2α stability and tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
Joshi S, Singh AR, Zulcic M, Durden DL. Joshi S, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Oct;12(10):1520-31. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0682. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25103499 - The tumour hypoxia induced non-coding transcriptome.
Choudhry H, Harris AL, McIntyre A. Choudhry H, et al. Mol Aspects Med. 2016 Feb-Mar;47-48:35-53. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Mol Aspects Med. 2016. PMID: 26806607 Review. - Interactional role of microRNAs and bHLH-PAS proteins in cancer (Review).
Li Y, Wei Y, Guo J, Cheng Y, He W. Li Y, et al. Int J Oncol. 2015 Jul;47(1):25-34. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3007. Epub 2015 May 15. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25997457 Review. - An HRE-Binding Py-Im Polyamide Impairs Hypoxic Signaling in Tumors.
Szablowski JO, Raskatov JA, Dervan PB. Szablowski JO, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Apr;15(4):608-17. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0719. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26719577 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Cascades between miRNAs, lncRNAs and the NF-κB signaling pathway in gastric cancer (Review).
Chen R, Yang M, Huang W, Wang B. Chen R, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):769. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10201. Epub 2021 May 17. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34055068 Free PMC article. Review. - Placental Origins of Chronic Disease.
Burton GJ, Fowden AL, Thornburg KL. Burton GJ, et al. Physiol Rev. 2016 Oct;96(4):1509-65. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2015. Physiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27604528 Free PMC article. Review. - miRNA Pattern in Hypoxic Microenvironment of Kidney Cancer-Role of PTEN.
Majewska A, Brodaczewska K, Filipiak-Duliban A, Kajdasz A, Kieda C. Majewska A, et al. Biomolecules. 2022 May 11;12(5):686. doi: 10.3390/biom12050686. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625614 Free PMC article. - MicroRNAs in Tumor Cell Metabolism: Roles and Therapeutic Opportunities.
Pedroza-Torres A, Romero-Córdoba SL, Justo-Garrido M, Salido-Guadarrama I, Rodríguez-Bautista R, Montaño S, Muñiz-Mendoza R, Arriaga-Canon C, Fragoso-Ontiveros V, Álvarez-Gómez RM, Hernández G, Herrera LA. Pedroza-Torres A, et al. Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 11;9:1404. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01404. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921661 Free PMC article. Review. - The oncogenic MicroRNA Hsa-miR-155-5p targets the transcription factor ELK3 and links it to the hypoxia response.
Robertson ED, Wasylyk C, Ye T, Jung AC, Wasylyk B. Robertson ED, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e113050. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113050. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25401928 Free PMC article.
References
- Noman MZ, Buart S, Romero P, Ketari S, Janji B, Mari B, et al. Hypoxia-inducible miR-210 regulates the susceptibility of tumor cells to lysis by cytotoxic T cells. Cancer Res. 2012;72:4629–41. - PubMed
- Vaupel P, Mayer A, Hockel M. Tumor hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 2004;381:335–54. - PubMed
- Semenza GL. HIF-1 and tumor progression: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:S62–7. - PubMed
- Pocock R. Invited review: decoding the microRNA response to hypoxia. Pflugers Arch. 2011;461:307–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources