Structures of Atg7-Atg3 and Atg7-Atg10 reveal noncanonical mechanisms of E2 recruitment by the autophagy E1 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Structures of Atg7-Atg3 and Atg7-Atg10 reveal noncanonical mechanisms of E2 recruitment by the autophagy E1
Stephen E Kaiser et al. Autophagy. 2013 May.
Abstract
Central to most forms of autophagy are two ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs), Atg8 and Atg12, which play important roles in autophagosome biogenesis, substrate recruitment to autophagosomes, and other aspects of autophagy. Typically, UBLs are activated by an E1 enzyme that (1) catalyzes adenylation of the UBL C terminus, (2) transiently covalently captures the UBL through a reactive thioester bond between the E1 active site cysteine and the UBL C terminus, and (3) promotes transfer of the UBL C terminus to the catalytic cysteine of an E2 conjugating enzyme. The E2, and often an E3 ligase enzyme, catalyzes attachment of the UBL C terminus to a primary amine group on a substrate. Here, we summarize our recent work reporting the structural and mechanistic basis for E1-E2 protein interactions in autophagy.
Keywords: Atg10; Atg12; Atg3; Atg7; Atg8; E1 enzyme; E2 enzyme; ubiquitin-like protein.
Figures
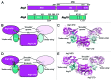
Figure 1. Structural analysis of proteins involved in the autophagy ubiquitin-like protein conjugation systems. (A) Domain diagrams for Atg7, Atg3 and Atg10. NTD, N-terminal domain; CTD, C-terminal domain; AD, adenylation domain; ECTD, extreme C-terminal domain; FR, flexible region; HR, handle region; β, β-hairpin. Catalytic cysteine residues are indicated with yellow lines. (B and C) Schematic and structure of the Atg7-Atg3 complex indicating key structural features involved in binding. Catalytic-cysteine thiols are shown as yellow spheres. (D and E) Schematic and structure of the Atg7-Atg10 complex indicating key structural features involved in binding. Yellow spheres represent the catalytic-cysteine thiols of Atg7 and His131 or Pro132 of Atg10, in which the catalytic cysteine was not visible.
Comment on
- Kaiser SE, Mao K, Taherbhoy AM, Yu S, Olszewski JL, Duda DM, et al. Noncanonical E2 recruitment by the autophagy E1 revealed by Atg7-Atg3 and Atg7-Atg10 structures. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:1242–9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2415.
Similar articles
- Noncanonical E2 recruitment by the autophagy E1 revealed by Atg7-Atg3 and Atg7-Atg10 structures.
Kaiser SE, Mao K, Taherbhoy AM, Yu S, Olszewski JL, Duda DM, Kurinov I, Deng A, Fenn TD, Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA. Kaiser SE, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1242-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2415. Epub 2012 Nov 11. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23142976 Free PMC article. - A switch element in the autophagy E2 Atg3 mediates allosteric regulation across the lipidation cascade.
Zheng Y, Qiu Y, Grace CRR, Liu X, Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA. Zheng Y, et al. Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 9;10(1):3600. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11435-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31399562 Free PMC article. - Binding to E1 and E3 is mutually exclusive for the human autophagy E2 Atg3.
Qiu Y, Hofmann K, Coats JE, Schulman BA, Kaiser SE. Qiu Y, et al. Protein Sci. 2013 Dec;22(12):1691-7. doi: 10.1002/pro.2381. Protein Sci. 2013. PMID: 24186333 Free PMC article. - Allosteric regulation through a switch element in the autophagy E2, Atg3.
Qiu Y, Zheng Y, Grace CRR, Liu X, Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA. Qiu Y, et al. Autophagy. 2020 Jan;16(1):183-184. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1688550. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31690182 Free PMC article. Review. - Two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems that mediate membrane formation during autophagy.
Nakatogawa H. Nakatogawa H. Essays Biochem. 2013;55:39-50. doi: 10.1042/bse0550039. Essays Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24070470 Review.
Cited by
- Role of ATG7-dependent non-autophagic pathway in angiogenesis.
Chen J, Liang Y, Hu S, Jiang J, Zeng M, Luo M. Chen J, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;14:1266311. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1266311. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38269279 Free PMC article. Review. - HSF1 Attenuates the Release of Inflammatory Cytokines Induced by Lipopolysaccharide through Transcriptional Regulation of Atg10.
Tan H, Huang F, Huang M, Wu X, Tong Z. Tan H, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0305922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03059-22. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36598250 Free PMC article. - The c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.
Sun W, Li J, Zhou L, Han J, Liu R, Zhang H, Ning T, Gao Z, Liu B, Chen X, Ba Y. Sun W, et al. Theranostics. 2020 Jan 12;10(5):1981-1996. doi: 10.7150/thno.37621. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32104496 Free PMC article. - Insights on E1-like enzyme ATG7: functional regulation and relationships with aging-related diseases.
Liu J, Xiao Y, Cao L, Lu S, Zhang S, Yang R, Wang Y, Zhang N, Yu Y, Wang X, Guo W, Wang Z, Xu H, Xing C, Song X, Cao L. Liu J, et al. Commun Biol. 2024 Mar 29;7(1):382. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06080-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38553562 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of Ferroptosis Pathway by Ubiquitination.
Wang X, Wang Y, Li Z, Qin J, Wang P. Wang X, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 13;9:699304. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.699304. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34485285 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5P30CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM053396/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077053/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM077053/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM053396/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases