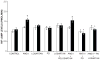The intrarenal renin-angiotensin and dopaminergic systems: control of renal sodium excretion and blood pressure - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The intrarenal renin-angiotensin and dopaminergic systems: control of renal sodium excretion and blood pressure
Robert M Carey. Hypertension. 2013 Mar.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
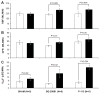
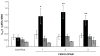
Evidence for a functional intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in uninephrectomized conscious dogs. Panel A: Renal blood flow (RBF); Panel B: glomerular filtration rate (GFR); Panel C: Urinary Na+ excretion (UNaV) in response to intrarenal arterial administration of ACE inhibitor SQ-20881 (2 μg/kg/min) or Ang receptor blocker P-113 (saralasin; 2 μg/kg/min). Control vehicle infusion, white bars; experimental agent infusion, black bars. Sham data include vehicle infusion only. Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. Adapted from Kimbrough HM et al. Circ Res. 1977;40:174–178.
Figure 2
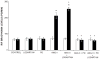
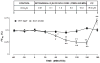
Validation of an independent functional intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in uninephrectomized conscious dogs. Estimated renal plasma flow (ERPF; Panel A), glomerular filtration rate (GFR; Panel B), urine flow rate (UVOL; Panel C) and urinary Na+ excretion (UNaV; Panel D) in response to low-dose intrarenal arterial infusion of Ang receptor blocker saralasin (0.07 μg/kg/min). Numbers on abscissa represent 20 min clearance periods. Adapted from Levens NR et al. Endocrinology. 1983:112:43–49 with permission.
Figure 3
Ang II releases renal bradykinin (BK) by AT2R activation. Renal interstitial fluid BK levels in response to intravenous infusion of Ang II, Losartan, an AT1R antagonist; PD, PD-123319, an AT2R antagonist, and combinations in Sprague-Dawley rats. Control vehicle infusions, white bars; experimental agent infusions, black bars. Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. * P<0.0001 from control; + P<0.05, ++P<0.0001 from Ang II alone. Data from Siragy HM et al. Am J Physiol Reg Int Comp Physiol. 1996;271:R1090–R1095 and Siragy HM and Carey RM, Hypertension 1999;33:1237–1242.
Figure 4
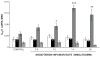
Ang II releases renal cyclic GMP (cGMP) by AT2R activation. Renal interstitial fluid cGMP levels in response to intravenous infusion of Ang II; Losartan, an AT1R antagonist; PD, PD-123319, an AT2R antagonist, and combinations in Sprague-Dawley rats. Control vehicle infusion data, white bars; experimental agent infusion, black bars. Data represent mean ± 1 SE. * P<0.001 from vehicle or time control; + P<0.001 from Ang II alone. Adapted from Siragy *HM and Carey RM. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:1978–1982 and Siragy HM and Carey RM. J Clin Invest. 1997💯264–269 with permission.
Figure 5
Ang III is the preferred endogenous AT2R agonist mediating natriuresis. Urinary Na+ excretion (UNaV) in anesthetized Sprague-Dawley rats in response to direct renal interstitial infusion of vehicle (white bars), Ang II (black bars), Ang III (gray bars) or Ang III +PD (PD-123319, an AT2R antagonist) (striped bars). Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 from time control. Adapted from Padia SH et al. Hypertension. 2006.
Figure 6
Oral fenoldopam lowers BP in hypertensive humans. BP responses to oral fenoldopam (SKF-82526-J) in patients with primary hypertension. Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. Adapted from Carey RM et al. J Clin Invest. 1984;74:2198–2207 with permission.
Figure 7
Evidence that intrarenal dopamine controls renal Na+ excretion by a paracrine mechanism acting at the level of the renal tubule. Urinary Na+ excretion (UNaV) in uninephrectomized conscious dogs infused intrarenally with D1-LIKE receptor antagonist SCH-23390. Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. * P<0.001, ** P<0.0001 from pre-control; † P<0.05, †† P<0.01 from time control. Adapted from Siragy HM et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1988;257:F469–F477 with permission.
Figure 8
Intrarenal interstitial fenoldopam-induced natriruesis is abolished by intrarenal D1-LIKE receptor antagonist SCH-23390 (SCH) or AT2R antagonist PD-123319 (PD) in anesthetized, uninephrectomized Sprague-Dawley rats. Vehicle infusion, white bars; fenoldopam (1 μg/kg/min) infusion, black bars; fenoldopam + PD infusion, gray bars; fenoldopamn + SCH infusion, striped bars. Data are expressed as mean ± 1 SE. Numbers on the abscissa refer to experimental one-hour periods. * P<0.01, ** P<0.001 from vehicle control. Adapted from Salomone LJ et al. Hypertension. 2007;49:155–161 and Padia SH et al. Hypertension. 2012;59:437–445.
Similar articles
- Renal dopamine and angiotensin II receptor signaling in age-related hypertension.
Chugh G, Pokkunuri I, Asghar M. Chugh G, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Jan 1;304(1):F1-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00441.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23097467 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of angiotensin AT(2) receptors in natriuresis: Intrarenal mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
Carey RM, Padia SH. Carey RM, et al. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013 Aug;40(8):527-34. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12059. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23336117 Free PMC article. Review. - Intrarenal dopamine D1-like receptor stimulation induces natriuresis via an angiotensin type-2 receptor mechanism.
Salomone LJ, Howell NL, McGrath HE, Kemp BA, Keller SR, Gildea JJ, Felder RA, Carey RM. Salomone LJ, et al. Hypertension. 2007 Jan;49(1):155-61. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000251881.89610.ee. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Hypertension. 2007. PMID: 17116755 - Angiotensin AT2 receptors: control of renal sodium excretion and blood pressure.
Carey RM, Padia SH. Carey RM, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Apr;19(3):84-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2008.01.003. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18294862 Review. - Interactions between the intrarenal dopaminergic and the renin-angiotensin systems in the control of systemic arterial pressure.
Vaz de Castro PAS, Jose PA, Simões E Silva AC. Vaz de Castro PAS, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Aug 31;136(16):1205-1227. doi: 10.1042/CS20220338. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35979889 Review.
Cited by
- The Angiotensin AT2 Receptor: From a Binding Site to a Novel Therapeutic Target.
Steckelings UM, Widdop RE, Sturrock ED, Lubbe L, Hussain T, Kaschina E, Unger T, Hallberg A, Carey RM, Sumners C. Steckelings UM, et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2022 Oct;74(4):1051-1135. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000281. Pharmacol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36180112 Free PMC article. Review. - A new common functional coding variant at the DDC gene change renal enzyme activity and modify renal dopamine function.
Miramontes-Gonzalez JP, Hightower CM, Zhang K, Kurosaki H, Schork AJ, Biswas N, Vaingankar S, Mahata M, Lipkowitz MS, Nievergelt CM, Baker DG, Ziegler MG, León-Jiménez D, González-Sarmiento R, Ichinose H, O'Connor DT. Miramontes-Gonzalez JP, et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 25;9(1):5055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41504-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30911067 Free PMC article. - Signaling pathways involved in renal oxidative injury: role of the vasoactive peptides and the renal dopaminergic system.
Rukavina Mikusic NL, Kravetz MC, Kouyoumdzian NM, Della Penna SL, Rosón MI, Fernández BE, Choi MR. Rukavina Mikusic NL, et al. J Signal Transduct. 2014;2014:731350. doi: 10.1155/2014/731350. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Signal Transduct. 2014. PMID: 25436148 Free PMC article. Review. - ISN Forefronts Symposium 2015: Maintaining Balance Under Pressure-Hypertension and the Proximal Tubule.
McDonough AA. McDonough AA. Kidney Int Rep. 2016 Sep;1(3):166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Kidney Int Rep. 2016. PMID: 27840855 Free PMC article. - Salt feedback on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Schweda F. Schweda F. Pflugers Arch. 2015 Mar;467(3):565-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1668-y. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25502115 Review.
References
- Carey RM, Siragy HM. Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: potential roles in cardiovascular and renal disease. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:261–267. - PubMed
- deGasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;53:415–472. - PubMed
- Carey RM. Cardiovascular and renal regulation by the angiotensin type 2 receptor: the AT2 receptor comes of age. Hypertension. 2005;45:840–844. - PubMed
- Carey RM. Theodore Cooper Lecture. Renal dopamine system: paracrine regulator of sodium homeostasis and blood pressure. Hypertension. 2001;38:297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL081891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065659/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095796/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources