Measuring factors affecting implementation of health innovations: a systematic review of structural, organizational, provider, patient, and innovation level measures - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Measuring factors affecting implementation of health innovations: a systematic review of structural, organizational, provider, patient, and innovation level measures
Stephenie R Chaudoir et al. Implement Sci. 2013.
Abstract
Background: Two of the current methodological barriers to implementation science efforts are the lack of agreement regarding constructs hypothesized to affect implementation success and identifiable measures of these constructs. In order to address these gaps, the main goals of this paper were to identify a multi-level framework that captures the predominant factors that impact implementation outcomes, conduct a systematic review of available measures assessing constructs subsumed within these primary factors, and determine the criterion validity of these measures in the search articles.
Method: We conducted a systematic literature review to identify articles reporting the use or development of measures designed to assess constructs that predict the implementation of evidence-based health innovations. Articles published through 12 August 2012 were identified through MEDLINE, CINAHL, PsycINFO and the journal Implementation Science. We then utilized a modified five-factor framework in order to code whether each measure contained items that assess constructs representing structural, organizational, provider, patient, and innovation level factors. Further, we coded the criterion validity of each measure within the search articles obtained.
Results: Our review identified 62 measures. Results indicate that organization, provider, and innovation-level constructs have the greatest number of measures available for use, whereas structural and patient-level constructs have the least. Additionally, relatively few measures demonstrated criterion validity, or reliable association with an implementation outcome (e.g., fidelity).
Discussion: In light of these findings, our discussion centers on strategies that researchers can utilize in order to identify, adapt, and improve extant measures for use in their own implementation research. In total, our literature review and resulting measures compendium increases the capacity of researchers to conceptualize and measure implementation-related constructs in their ongoing and future research.
Figures
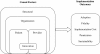
Figure 1
A multi-level framework predicting implementation outcomes.
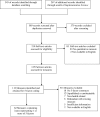
Figure 2
Systematic literature review process.
Similar articles
- Meausures of organizational characteristics associated with adoption and/or implementation of innovations: A systematic review.
Allen JD, Towne SD Jr, Maxwell AE, DiMartino L, Leyva B, Bowen DJ, Linnan L, Weiner BJ. Allen JD, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017 Aug 23;17(1):591. doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2459-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017. PMID: 28835273 Free PMC article. Review. - Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.
Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article. - Psychometric properties of implementation measures for public health and community settings and mapping of constructs against the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research: a systematic review.
Clinton-McHarg T, Yoong SL, Tzelepis F, Regan T, Fielding A, Skelton E, Kingsland M, Ooi JY, Wolfenden L. Clinton-McHarg T, et al. Implement Sci. 2016 Nov 8;11(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13012-016-0512-5. Implement Sci. 2016. PMID: 27821146 Free PMC article. Review. - Evidence Brief: The Quality of Care Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses [Internet].
McCleery E, Christensen V, Peterson K, Humphrey L, Helfand M. McCleery E, et al. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. PMID: 27606392 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.
Osborne SR, Alston LV, Bolton KA, Whelan J, Reeve E, Wong Shee A, Browne J, Walker T, Versace VL, Allender S, Nichols M, Backholer K, Goodwin N, Lewis S, Dalton H, Prael G, Curtin M, Brooks R, Verdon S, Crockett J, Hodgins G, Walsh S, Lyle DM, Thompson SC, Browne LJ, Knight S, Pit SW, Jones M, Gillam MH, Leach MJ, Gonzalez-Chica DA, Muyambi K, Eshetie T, Tran K, May E, Lieschke G, Parker V, Smith A, Hayes C, Dunlop AJ, Rajappa H, White R, Oakley P, Holliday S. Osborne SR, et al. Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
Cited by
- A case study of the development of a valid and pragmatic implementation science measure: the Barriers and Facilitators in Implementation of Task-Sharing Mental Health interventions (BeFITS-MH) measure.
Yang LH, Bass JK, Le PD, Singh R, Gurung D, Velasco PR, Grivel MM, Susser E, Cleland CM, Alvarado R, Kohrt BA, Bhana A. Yang LH, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):1352. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11783-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39501275 Free PMC article. - Mobilizing strategic inflection points for sustainment of an effective intervention in an integrated learning health system: an interpretive description.
Benzies KM, Zanoni P, McNeil DA. Benzies KM, et al. Implement Sci Commun. 2024 Sep 30;5(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s43058-024-00644-2. Implement Sci Commun. 2024. PMID: 39350292 Free PMC article. - Implementing learning into practice from continuous professional development activities: a scoping review of health professionals' views and experiences.
Al-Omary H, Soltani A, Stewart D, Nazar Z. Al-Omary H, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2024 Sep 20;24(1):1031. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06016-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39304841 Free PMC article. Review. - Multilevel barriers to guideline implementation: a nationwide multi-professional cross-sectional study within child and adolescent psychiatry.
Santesson AHE, Holmberg R, Bäckström M, Gustafsson P, Perrin S, Jarbin H. Santesson AHE, et al. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2024 Sep 12;18(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13034-024-00803-2. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39267088 Free PMC article. - Insights gained from a cultural adaptation of preschool promoting alternative thinking strategies©: the importance of teachers' cultures as an implementation driver.
Norman Å, Sedem M, Ferrer-Wreder L, Eninger L, Hau HG. Norman Å, et al. Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1425936. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1425936. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39171241 Free PMC article.
References
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Dissemination and implementation research in health (R01) Bethesda, MD: NIH; 2010. http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-10-038.html.
- Balas EA, Boren SA. In: Yearbook of medical informatics 2000: Patient-centered systems. Bemmel J, McCray AT, editor. Stuttgart, Germany: Schattauer; 2000. Managing clinical knowledge for health care improvement; pp. 65–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources