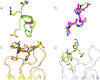Bapineuzumab captures the N-terminus of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta peptide in a helical conformation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Bapineuzumab captures the N-terminus of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta peptide in a helical conformation
Luke A Miles et al. Sci Rep. 2013.
Abstract
Bapineuzumab is a humanized antibody developed by Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson targeting the amyloid (Aβ) plaques that underlie Alzheimer's disease neuropathology. Here we report the crystal structure of a Fab-Aβ peptide complex that reveals Bapineuzumab surprisingly captures Aβ in a monomeric helical conformation at the N-terminus. Microscale thermophoresis suggests that the Fab binds soluble Aβ(1-40) with a K(D) of 89 (±9) nM. The structure explains the antibody's exquisite selectivity for particular Aβ species and why it cannot recognize N-terminally modified or truncated Aβ peptides.
Figures
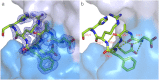
Figure 1. Structure of the humanized 3D6 Fab-Aβ peptide complex.
Both panels show Aβ nestled in the surface of the Fab CDRs. The peptide is shown in green sticks with the light chain in light blue surface and heavy chain in a darker blue surface. (a) A 2_F_o - _F_c electron density map in the vicinity of the peptide contoured at 1.5σ. (b) Intra-Aβ hydrogen bonding, shown as dashed lines, stabilizes the helical conformation of the peptide.
Figure 2. Different conformations of the Aβ peptide.
(a) The helical conformational epitope of Aβ recognized by Bapineuzumab highlighted in green ribbon. (b) Superposition of the main-chain heavy atoms of TFE-stabilized Aβ (residues 1 to 6) NMR structures (9) (in purple) with those of Aβ as recognized by Bapineuzumab (in green). (c), (d) Superposition over light chain of Fab-Aβ complexes with murine antibody Fabs in (c) WO2-Aβ is in orange ribbon, PFA1-Aβ in yellow and (d) Bapineuzumab related Fab in grey with Aβ in green sticks.
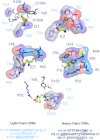
Figure 3. Aβ-Fab interactions.
The Aβ residues are shown as green sticks. Amino acid sequences corresponding to the CDRs of Bapineuzumab are shown in light blue and darker blue for light and heavy chains respectively. Amino acids involved in Fab binding to Aβ are underlined and italicized in the CDR sequences common to 3D6 antibodies including Bapineuzumab. Direct polar contacts between the Fab and Aβ are shown graphically as red dashed lines. Waters involved in the hydrogen bonding network are shown as aquamarine spheres, and their putative hydrogen bonds are shown as aquamarine dashed lines. Fab residue labels and carbon atoms are colored by chain (shades of blue), whereas nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur atoms are shown in dark blue, red and yellow respectively. Surfaces represent non-polar contacts to Fab residues. Intra-chain contacts have been omitted for clarity. Figure produced using LigPlus.
Similar articles
- Structure and Function of Alzheimer's Amyloid βeta Proteins from Monomer to Fibrils: A Mini Review.
Agrawal N, Skelton AA. Agrawal N, et al. Protein J. 2019 Aug;38(4):425-434. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09854-3. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31325011 Review. - Structural basis of C-terminal β-amyloid peptide binding by the antibody ponezumab for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
La Porte SL, Bollini SS, Lanz TA, Abdiche YN, Rusnak AS, Ho WH, Kobayashi D, Harrabi O, Pappas D, Mina EW, Milici AJ, Kawabe TT, Bales K, Lin JC, Pons J. La Porte SL, et al. J Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 24;421(4-5):525-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.047. Epub 2011 Dec 13. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22197375 - N-terminal heterogeneity of parenchymal and vascular amyloid-β deposits in Alzheimer's disease.
Zampar S, Klafki HW, Sritharen K, Bayer TA, Wiltfang J, Rostagno A, Ghiso J, Miles LA, Wirths O. Zampar S, et al. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020 Dec;46(7):673-685. doi: 10.1111/nan.12637. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32497293 Free PMC article. - Abeta targets of the biosimilar antibodies of Bapineuzumab, Crenezumab, Solanezumab in comparison to an antibody against N‑truncated Abeta in sporadic Alzheimer disease cases and mouse models.
Bouter Y, Lopez Noguerola JS, Tucholla P, Crespi GA, Parker MW, Wiltfang J, Miles LA, Bayer TA. Bouter Y, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Nov;130(5):713-29. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1489-x. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 26467270 - Conformations and biological activities of amyloid beta peptide 25-35.
Millucci L, Ghezzi L, Bernardini G, Santucci A. Millucci L, et al. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010 Feb;11(1):54-67. doi: 10.2174/138920310790274626. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010. PMID: 20201807 Review.
Cited by
- Brain pharmacokinetics of two BBB penetrating bispecific antibodies of different size.
Faresjö R, Bonvicini G, Fang XT, Aguilar X, Sehlin D, Syvänen S. Faresjö R, et al. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2021 Jun 2;18(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12987-021-00257-0. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2021. PMID: 34078410 Free PMC article. - A light at the end of the tunnel - from mutation identification to a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
Lannfelt L. Lannfelt L. Ups J Med Sci. 2023 Nov 28;128. doi: 10.48101/ujms.v128.10316. eCollection 2023. Ups J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38084203 Free PMC article. Review. - Structure and Function of Alzheimer's Amyloid βeta Proteins from Monomer to Fibrils: A Mini Review.
Agrawal N, Skelton AA. Agrawal N, et al. Protein J. 2019 Aug;38(4):425-434. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09854-3. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31325011 Review. - Molecular Recognition between Aβ-Specific Single-Domain Antibody and Aβ Misfolded Aggregates.
Zhang M, Zheng J, Nussinov R, Ma B. Zhang M, et al. Antibodies (Basel). 2018 Jul 13;7(3):25. doi: 10.3390/antib7030025. Antibodies (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31544877 Free PMC article. - Comparing the efficacy and neuroinflammatory potential of three anti-abeta antibodies.
Fuller JP, Stavenhagen JB, Christensen S, Kartberg F, Glennie MJ, Teeling JL. Fuller JP, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Nov;130(5):699-711. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1484-2. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 26433971 Free PMC article.
References
- Selkoe D. J. Preventing Alzheimer's disease. Science 337, 1488–1492 (2012). - PubMed
- Mullard A. Sting of Alzheimer's failures offset by upcoming prevention trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 657–660 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases